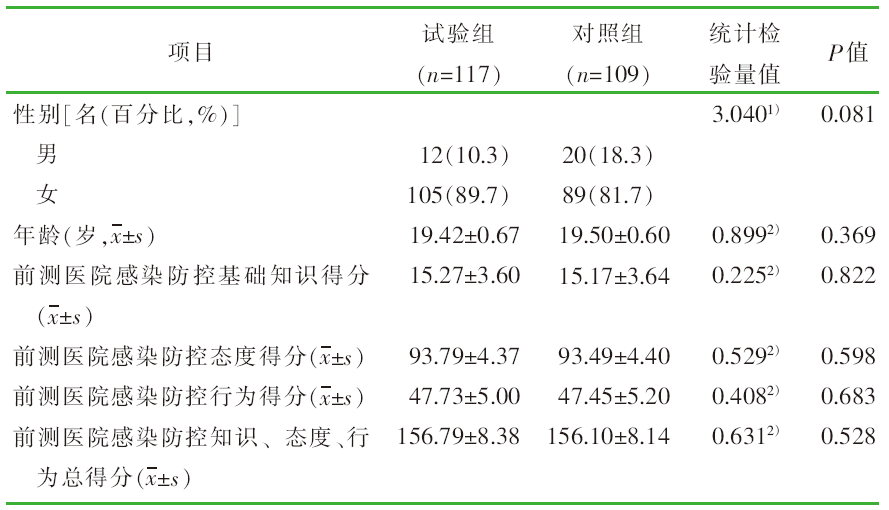
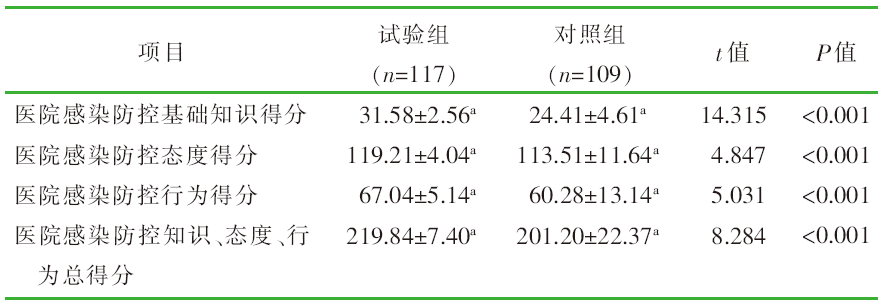
| [1] |
范姜珊. 护理本科生医院感染防控课程内容改革的初步研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2022.
|
|
Fan JS. Preliminary study on curriculum reform of hospital infection prevention and control for nursing undergraduates[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2022.
|
| [2] |
Amavasi B, Zimmerman PA. Infection prevention and control continuous education and training in pre-registration nursing programmes[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2024,133:106051.
|
| [3] |
国家卫生健康委员会. 对十三届全国人大三次会议第6777号建议的答复[EB/OL].(2021-03-02)[2025-08-27]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/jiany/202102/2a7e28bab01c45bf812e172d2347f168.shtml.
|
|
National Health Commission. Reply to proposal No.6777 at the Third Session of the 13th National People’s Congress[EB/OL].(2021-03-02)[2025-08-27]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/jiany/202102/2a7e28bab01c45bf812e172d2347f168.shtml.
|
| [4] |
张艳, 时春红, 赖春风. 实习护生医院感染防控知识掌握程度及课程需求的调查研究[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2023, 41(5):145-148.
|
|
Zhang Y, Shi CH, Lai CF. Investigation on the degree of knowledge acquisition of nosocomial infection’s prevention and control and courses requirements of intern nursing students[J]. Health Vocat Educ, 2023, 41(5):145-148.
|
| [5] |
李亚平, 欧阳洋, 张霓妮, 等. 基于塔巴模式的医院感染预防与控制课程设计研究:来自10所院校师生的数据分析[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2022, 21(9):877-884.
|
|
Li YP, Ouyang Y, Zhang NN, et al. Healthcare-associated infec-tion prevention and control course design based on Taba Model:data from teachers and students in 10 universities[J]. Chin J Infect Contr, 2022, 21(9):877-884.
|
| [6] |
Jeong D, Park C, Eun Y. Effects of infection control education program using flipped learning based on the ARCS model for nursing students:a mixed method[J]. Healthcare, 2023, 11(20):2731.
doi: 10.3390/healthcare11202731
|
| [7] |
Saati AA, Alkalash SH. Promotion of knowledge,attitude,and practice among medical undergraduates regarding infection control measures during COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Front Public Health, 2022,10:932465.
|
| [8] |
刘美荣. 本科护理院校医院感染防控教材质量评价研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2024.
|
|
Liu MR. Study on quality evaluation of teaching materials for hospital infection prevention and control in undergraduate nursing colleges[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2024.
|
| [9] |
刘金帅, 张晓霞, 郭芳芳, 等. 2006—2021年长治医学院医院感染学本科教学实践与探索[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(24):3788-3792.
|
|
Liu JS, Zhang XX, Guo FF, et al. Practice and exploration of undergraduate teaching of nosocomiology in Changzhi Medical College from 2006 to 2021[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2022, 32(24):3788-3792.
|
| [10] |
颜丽霞, 田莉, 李敏, 等. 康复治疗专业实习生医院感染防控知信行调查分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2025, 40(6):930-933.
|
|
Yan LX, Tian L, Li M, et al. Survey and analysis of knowled-ge,attitude,and practice of hospital infection prevention and control among rehabilitation therapy interns[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2025, 40(6):930-933.
|
| [11] |
刘蔚, 李育玲, 韩清华, 等. 基于社会学习理论实习护生同伴支持教育方案的构建[J]. 护理学报, 2023, 30(3):16-19.
doi: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2023.03.016
|
|
Liu W, Li YL, Han QH, et al. Construction of peer support education program for nursing students based on social learning theory[J]. J Nurs (China), 2023, 30(3):16-19.
|
| [12] |
卢珍玲, 傅建国, 张小螺. 医学实习生医院感染学培训考核及正确率影响因素[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2025, 24(4):545-550.
|
|
Lu ZL, Fu JG, Zhang XL. Factors affecting the assessment and correct answering rate of healthcare-associated infection train-ing for medical interns[J]. Chin J Infect Contr, 2025, 24(4):545-550.
|
| [13] |
杨晓华, 张明, 马磊. 我国临床医学生医院感染防控实践教育的现状、问题与对策分析[J]. 医学教育研究与实践, 2021, 29(5):687-690.
|
|
Yang XH, Zhang M, Ma L. Current status,problems and coun-termeasures of practical education of prevention and control of nosocomial infection for students major in clinical medi-cine[J]. Med Educ Res Pract, 2021, 29(5):687-690.
|
| [14] |
Mohammedi SB, Landelle C. Review of literature:knowledge and practice of standard precautions by nursing student and teaching techniques used in training[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2023, 51(5):574-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2022.08.032
|
| [15] |
李安安, 侯云英, 李惠玲, 等. 基于任务驱动的翻转课堂在本科老年护理学教学中的应用[J]. 中华护理教育, 2024, 21(4):397-403.
|
|
Li AA, Hou YY, Li HL, et al. The teaching effect of task-driven diversified flipped classroom in Geriatric Nursing[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2024, 21(4):397-403.
|