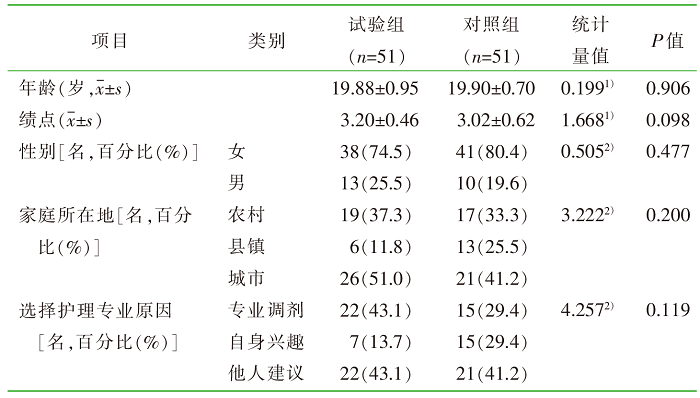
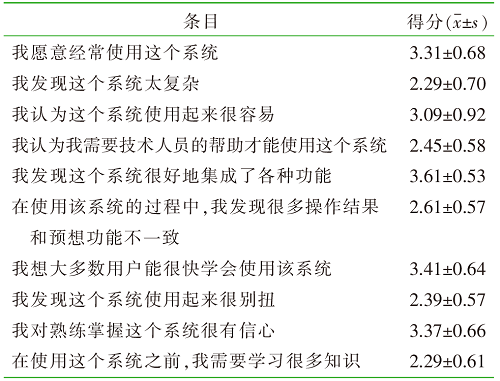
| [1] |
咸亚静, 沙鑫, 贺苗, 等. 不同教学策略对护理专业《健康评估》课程教学效果影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2025, 25(2):155-160.
|
|
Xian YJ, Sha X, He M, et al. Effect of different teaching strategies on the Health Assessment curriculum for the nursing profession:a Network Meta-analysis[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2025, 25(2):155-160.
|
| [2] |
新华社. 中共中央国务院印发《教育强国建设规划纲要(2024—2035年)》[EB/OL]. (2025-01-19). https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/2025/issue_11846/202502/content_7002799.html.
|
|
Xinhua News Agency. The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council Issue the “Outline of the Plan for Building a Strong Education Nation(2024-2035)”[EB/OL]. (2025-01-19). https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/2025/issue_11846/202502/content_7002799.html.
|
| [3] |
Tan CX, Han RJ, Ye RG, et al. Adaptive learning recommendation strategy based on deep Q-learning[J]. Appl Psychol Meas, 2020, 44(4):251-266.
doi: 10.1177/0146621619858674
|
| [4] |
黄昌勤, 钟益华, 王希哲, 等. 从单智能体到多智能体:大模型智能体支持下的激励型学习活动设计与实证研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版), 2025, 43(5):44-56.
|
|
Huang CQ, Zhong YH, Wang XZ, et al. From single-agent to multi-agent:motivational learning activities design and empirical study supported by LLM-based agents[J]. J East China Norm Univ Educ Sci, 2025, 43(5):44-56.
|
| [5] |
余亮, 邓双洁, 张馨月. 人工智能技术赋能教育的演进脉络、内在逻辑和发展趋势[J]. 电化教育研究, 2025, 46(6):13-20,28.
|
|
Yu L, Deng SJ, Zhang XY. The evolutionary trajectory,internal logic and development trends of education empowered by artificial intelligence technology[J]. E Educ Res, 2025, 46(6):13-20,28.
|
| [6] |
葛福鸿, 刘清堂. 人工智能赋能高校教学支持服务:内涵、困境、模型与路径[J]. 中国电化教育, 2025(10):46-54.
|
|
Ge FH, Liu QT. The connotation,dilemmas,models and paths of empowering university teaching support services with artificial intelligence[J]. China Educ Technol, 2025(10):46-54.
|
| [7] |
王彦博, 张洪忠. 从搜索引擎到AI搜索:大模型赋能下的信息获取变迁分析[J]. 编辑之友, 2025(3):74-80.
|
|
Wang YB, Zhang HZ. From search engines to AI search:an analysis of information acquisition evolution empowered by large language models[J]. Editor Friend, 2025(3):74-80.
|
| [8] |
王玉静. 沈阳市三级甲等医院护士临床推理能力现状及与自主学习能力的相关性研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018.
|
|
Wang YJ. Study on the status quo of nurses’ clinical reasoning ability and its correlation with autonomous learning ability in a third-class first-class hospital in Shenyang[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2018.
|
| [9] |
郭娜娜, 安晓, 夏雨, 等. 无法忍受不确定性在本科护生批判性思维与临床推理间的中介效应[J]. 护理学报, 2025, 32(9):1-6.
|
|
Guo NN, An X, Xia Y, et al. Mediating effect of intolerance of uncertainty between critical thinking and clinical reasoning in nursing undergraduates[J]. J Nurs (China), 2025, 32(9):1-6.
|
| [10] |
Brooke J. SUS: a ‘quick and dirty’ usability scale[M]// Usability Evaluation In Industry. Boca Raton: CRC Press,1996:207-212.
|
| [11] |
Wang YH, Lei T, Liu XX. Chinese System Usability Scale:translation,revision,psychological measurement[J]. Int J Hum, 2020, 36(10):953-963.
|
| [12] |
冯梦轩, 乔远静, 李丹丹, 等. 脚本一致性测试的应用现状及对国内护理教育的启示[J]. 护理研究, 2023, 37(13):2370-2374.
|
|
Feng MX, Qiao YJ, Li DD, et al. Application status quo of script concordance test and its enlightenment to nursing education in China[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2023, 37(13):2370-2374.
|
| [13] |
步皓宁, 常起航, 王雪, 等. 人工智能技术在护理教育中应用效果的系统评价[J]. 中华护理教育, 2025, 22(9):1057-1064.
|
|
Bu HN, Chang QH, Wang X, et al. The application of artificial intelligence technology in nursing education:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2025, 22(9):1057-1064.
|