| [1] |
Rampersad C, Brar R, Connelly K, et al. Association of physical activity and poor health outcomes in patients with advanced CKD[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2021, 78(3):391-398.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.12.018
pmid: 33581165
|
| [2] |
Chung YC, Yeh ML, Liu YM. Effects of intradialytic exercise on the physical function,depression and quality of life for haemodialysis patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2017, 26(13/14):1801-1813.
doi: 10.1111/jocn.13514
|
| [3] |
Pomidori L, Lamberti N, Malagoni AM, et al. Respiratory muscle impairment in dialysis patients:can minimal dose of exercise limit the damage? A preliminary study in a sample of patients enrolled in the EXCITE trial[J]. J Nephrol, 2016, 29(6):863-869.
pmid: 27312989
|
| [4] |
Manfredini F, Mallamaci F, D’Arrigo G, et al. Exercise in patients on dialysis:a multicenter,randomized clinical trial[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28(4):1259-1268.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016030378
pmid: 27909047
|
| [5] |
Cooke AB, Ta V, Iqbal S, et al. The impact of intradialytic pedaling exercise on arterial stiffness:a pilot randomized controlled trial in a hemodialysis population[J]. Am J Hypertens, 2018, 31(4):458-466.
doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx191
|
| [6] |
Dicenso A, Bayley L, Haynes RB. Accessing pre-appraised evidence:fine-tuning the 5S model into a 6S model[J]. Evid Based Nurs, 2009, 12(4):99-101.
doi: 10.1136/ebn.12.4.99-b
pmid: 19779069
|
| [7] |
王志稳, 冷敏敏, 孙月. 证据整合研究中文献检索策略的制订[J]. 中华护理教育, 2021, 18(10):883-888.
|
|
Wang ZW, Leng MM, Sun Y. Developing high-quality search strategy in evidence synthesis[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2021, 18(10):883-888.
|
| [8] |
Hoffmann-Eβer W, Siering U, Neugebauer EAM, et al. Guideline appraisal with AGREE II:online survey of the potential influence of AGREE II items on overall assessment of guideline quality and recommendation for use[J]. BMC Heal Serv Res, 2018, 18(1):143.
doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-2954-8
|
| [9] |
顾莺, 张慧文, 周英凤, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具:系统评价的方法学质量评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(8):701-703.
|
| [10] |
The Joanna Briggs Institute(JBI). JBI Critical appraisal[EB/OL].(2017-07-15)[2021-08-05]. https://joannabriggs.org/ebp/critical_ appraisal_toolss.
|
| [11] |
周英凤, 顾莺, 胡雁, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具--干预性研究的质量评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(1):24-26.
|
| [12] |
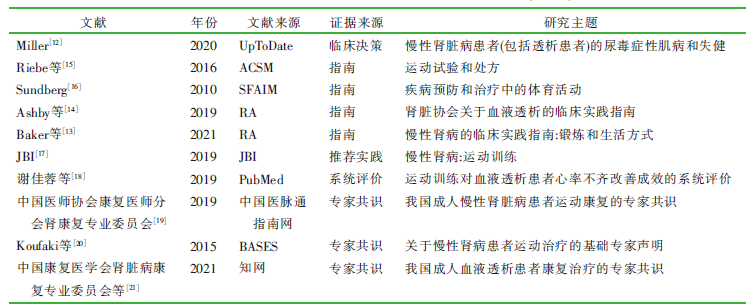
Miller BW. Uremic myopathy and deconditioning in patients with chronic kidney disease[EB/OL].(2020-09-21)[2021-11-16]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/uremic-myopathy-and-deconditioning-in-patients-with-chronic-kidney-disease-including-those-on-dialysis#!.
|
| [13] |
Baker LA, March DS, Wilkinson TJ. Clinical practice guideline exercise and lifestyle in chronic kidney disease[EB/OL]. (2020-04-08)[2021-11-16]. https://renal.org/health-professionals/guidelines/exercise-and-lifestyle-chronic-kidney-disease.
|
| [14] |
Ashby D, Borman N, Burton J, et al. Renal association clinical practice guideline on haemodialysis[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2019, 20 (1):379.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1527-3
|
| [15] |
Riebe D, Ehrman JK, Liguori G, et al. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription[M]. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wol-ters Kluwer, 2016:463-468.
|
| [16] |
Sundberg CJ. Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of disease[M]. 2nd ed. Professional Associations for Physical Activity,Sweden, 2010:427-437.
|
| [17] |
JBI. Recommended Practice. Chronic kidney disease:exercise training[R]. The JBI EBP Database. 2019:JBI24672.
|
| [18] |
谢佳蓉, 陈亭余, 高启雯. 运动训练对于血液透析患者心率变异的改善成效之系统性文献回顾[J]. 护理杂志, 2019, 66(1):70-83.
|
|
Shie JR, Chen TY, Kao CW. The effect of exercise training on heart rate variability in patients with hemodialysis:a systematic review[J]. J Nurs, 2019, 66(1):70-83.
|
| [19] |
中国医师协会康复医师分会肾康复专业委员会. 我国成人慢性肾脏病患者运动康复的专家共识[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2019, 35(7):537-543.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-7097.2019.07.011
|
|
Chinese Medical Doctor Association Rehabilitation Physicians Branch, Professional Committee of Renal Rehabilitation. Expert consensus on exercise rehabilitation for Chinese adults with chronic kidney disease[J]. Chin J Nephrol, 2019, 35(7):537-543.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-7097.2019.07.011
|
| [20] |
Koufaki P, Greenwood S, Painter P, et al. The BASES expert statement on exercise therapy for people with chronic kidney disease[J]. J Sports Sci, 2015, 33(18):1902-1907.
doi: 10.1080/02640414.2015.1017733
|
| [21] |
中国康复医学会肾脏病康复专业委员会, 中关村肾病血液净化联盟肾康复专业委员会, 中国医师协会康复医师分会肾康复治疗专业委员会. 我国成人血液透析患者康复治疗的专家共识[J]. 中国血液净化, 2021, 20(11):721-727.
|
|
Renal Rehabilitation Committee of China Association Rehabilitation Medicine; Renal Rehabilitation Committee of Zhong-guancun Nephrology & Blood Purification Innovation Allia-nce; Renal Rehabilitation Committee of Rehabilitation Physician Branch of China Medical Doctor Association. Expert consensus on rehabilitation treatment of adult hemodialysis patients in China[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2021, 20(11):721-727.
|
| [22] |
Barcellos FC, Santos IS, Umpierre D, et al. Effects of exercise in the whole spectrum of chronic kidney disease:a systematic review[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2015, 8(6):753-765.
doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv099
pmid: 26613036
|
| [23] |
Heiwe S, Jacobson SH. Exercise training in adults with CKD:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2014, 64(3):383-393.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.03.020
|
| [24] |
Sheng K, Zhang P, Chen L, et al. Intradialytic exercise in he-modialysis patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2014, 40(5):478-490.
doi: 10.1159/000368722
|
| [25] |
Gomes Neto M, Lopes AA, et al. Intradialytic exercise training modalities on physical functioning and health-related quality of life in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Rehabilitation, 2018, 32(9):1189-1202.
doi: 10.1177/0269215518760380
|