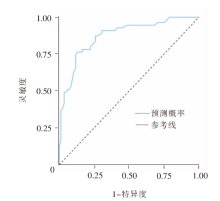
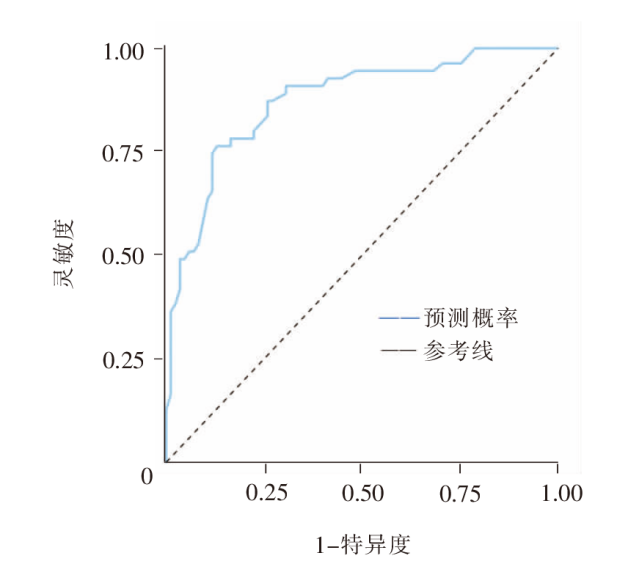
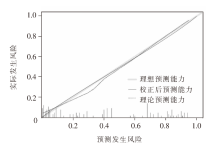
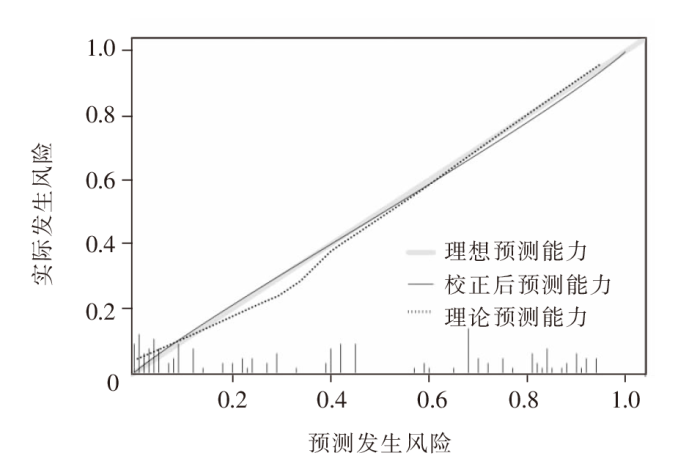
| [1] |
Bhakta N, Force LM, Allemani C, et al. Childhood cancer bur-den:a review of global estimates[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(1):e42-e53.
|
| [2] |
刘娟, 周璇, 张蕾, 等. 白细胞介素-6、C-反应蛋白和降钙素原对儿童血液肿瘤感染的预测价值[J]. 癌症进展, 2020, 18(20):2122-2125,2142.
|
|
Liu J, Zhou X, Zhang L, et al. Interleukin-6,C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in prediction of pediatric hematological tumor infection[J]. Oncol Prog, 2020, 18(20):2122-2125,2142.
|
| [3] |
Zhang YT, Zhou DH, Xia H, et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for detection of pathogens in children with hematological diseases complicated with infection[J]. Mol Cell Probes, 2023, 67:101889.
|
| [4] |
郭秋菊, 徐琛, 乔杨华, 等. 肿瘤患儿化疗后感染情况分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(9):1429-1432.
|
|
Guo QJ, Xu C, Qiao YH, et al. Prevalence of infection in children with cancer after chemotherapy[J]. Chin J Nosocomio-logy, 2019, 29(9):1429-1432.
|
| [5] |
陈森敏, 刘四喜, 麦惠容, 等. 儿童恶性肿瘤化疗后医院感染特征及危险因素分析[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2018, 18(5):454-460.
|
|
Chen SM, Liu SX, Mai HR, et al. Nosocomial infections follow-ing chemotherapy for pediatric malignancies[J]. Chin J Infect Chemother, 2018, 18(5):454-460.
|
| [6] |
孙晓炜. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病VDLP诱导缓解治疗中感染发生的相关分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.
|
|
Sun XW. Correlation analysis of infection in VDLP-induced remission treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2019.
|
| [7] |
Long E, Babl FE, Phillips N, et al. Prevalence and predictors of poor outcome in children with febrile neutropaenia presenting to the emergency department[J]. Emerg Med Australas, 2022, 34(5):786-793.
doi: 10.1111/1742-6723.13978
pmid: 35419955
|
| [8] |
Wang HW, Zhong Y, Ma L. Leukaemia infection diagnosis and intestinal flora disorder[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2022, 22(1):2-7.
|
| [9] |
孙盈盈, 张伟, 万玉. 急性白血病儿童化疗期间医院感染的相关因素及其预测效能[J]. 中外医学研究, 2024, 22(12):155-159.
doi: 10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2024.12.039
|
|
Sun YY, Zhang W, Wan Y. Correlation factors and predictive efficacy of nosocomial infection in children with acute leukemia during chemotherapy[J]. Chin Foreign Med Res, 2024, 22(12):155-159.
doi: 10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2024.12.039
|
| [10] |
黄绍良, 陈纯, 周敦华. 实用小儿血液病学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2014:164.
|
| [11] |
隆云, 陈德昌, 马朋林. 实用重症感染学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2021:138.
|
| [12] |
范列英, 王伟灵, 胡敏, 等. 临床化学检验标准化操作程序[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社,2020:160.
|
|
Fan LY, Wang WL, Hu M, et al. Standardized operating procedures for clinical chemical examination[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers,2020:160.
|
| [13] |
冯升, 成磊, 陆华, 等. 儿科营养不良评估筛查工具用于住院患儿营养风险筛查的诊断效能研究[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2019, 19(4):233-236.
|
|
Feng S, Cheng L, Lu H, et al. The effectiveness research of the Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics for nutrition risk screening among hospitalized children[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2019, 19(4):233-236.
|
| [14] |
付晓莹. 两种营养风险筛查工具对儿童消化系统疾病住院患儿的应用[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2023.
|
|
Fu XY. Application of two nutritional risk screening tools in hospitalized children with digestive system diseases[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2023.
|
| [15] |
Bochennek K, Hogardt M, Lehrnbecher T. Immune signatures,testing,and management of febrile neutropenia in pediatric cancer patients[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2023, 19(3):267-277.
|
| [16] |
Spellberg B. Summary Table[EB/OL].(2020-01). https://www.bradspell-berg.com/shorter-is-better.
|
| [17] |
Stover KR, Morrison A, Collier T, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for bacteremia in pediatric and adolescent patients[J]. J Pharm Pract, 2021, 34(3):360-364.
|
| [18] |
Kollef MH, Torres A, Shorr AF, et al. Nosocomial infection[J]. Crit Care Med, 2021, 49(2):169-187.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004783
pmid: 33438970
|
| [19] |
Nedelcu V, Niculiţă OO, Toporaş E, et al. Hand hygiene among nurses in pediatric blood and marrow transplantation setting:a best practice implementation project[J]. JBI Evid Implement, 2022, 20(3):236-247.
|
| [20] |
Nunn JL, Takashima MD, Wray-Jones EM, et al. Central venous access device adverse events in pediatric patients with cancer:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2024, 32(10):662.
|
| [21] |
Agreiter I, Kozijn AE, Bakunina K, et al. Contribution of nurses to protective environment in haematopoietic cell transplant setting:an international survey by the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2021, 56(6):1433-1440.
|
| [22] |
中华医学会外科学分会, 中华医学会麻醉学分会. 中国加速康复外科临床实践指南(2021)(一)[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2021, 12(5):624-631.
|
| [23] |
国家卫生健康委办公厅医政医管局. 血管导管相关感染预防与控制指南(2021版)[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2021, 20(4):387-388.
|
| [24] |
邱雨, 洪瑞, 王志国, 等. 医用抗菌涂层导管及其在加速康复外科护理中的应用进展[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2024, 40(36):2870-2876.
|
| [25] |
杨书环, 杨贵芳, 田桂荣, 等. 集束化护理降低急性白血病化疗患者肺部感染发病率的效果研究[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2023, 22(4):435-441.
|
|
Yang SH, Yang GF, Tian GR, et al. Effect of bundled care on reducing the incidence of pulmonary infection in patients with acute leukemia receiving chemotherapy[J]. Chin J Infect Contr, 2023, 22(4):435-441.
|
| [26] |
刘珺, 王梦, 钟莉, 等. 基于赋能理论的护理干预对预防急性髓系白血病患者化疗后肛周感染的效果研究[J]. 当代护士(中旬刊), 2023, 30(4):112-115.
|
| [27] |
Hu TY, Zhang ZW, Jiang YF. Albumin corrected anion gap for predicting in-hospital mortality among intensive care patients with sepsis:a retrospective propensity score matching analysis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2021,521:272-277.
|
| [28] |
Yang GB, Wang DD, Phua SZF, et al. Albumin-based thera-peutics capable of glutathione consumption and hydrogen peroxide generation for synergetic chemodynamic and chemo-therapy of cancer[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(2):2319-2329.
|
| [29] |
郭娟, 薛娇, 熊沫, 等. 入院白蛋白、T淋巴细胞亚群、白细胞计数预测中晚期宫颈癌化疗患者医院感染的价值[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2023, 22(20):2185-2189.
|
|
Guo J, Xue J, Xiong M, et al. Values of albumin,T lym-phocyte subsets and leukocyte count on admission in predicting nosocomial infection in patients with advanced cervical cancer undergoing chemotherapy[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2023, 22(20):2185-2189.
|
| [30] |
王超, 栗达, 林巍, 等. 肠内营养制剂在急性淋巴细胞白血病患儿诱导治疗期的营养支持作用及对化疗并发症的影响[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2019, 34(17):1335-1339.
|
|
Wang C, Li D, Lin W, et al. Enteral nutrition support for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the stage of induction chemotherapy and effect on chemotherapy complica-tions[J]. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr, 2019, 34(17):1335-1339.
|