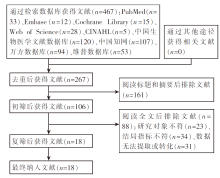
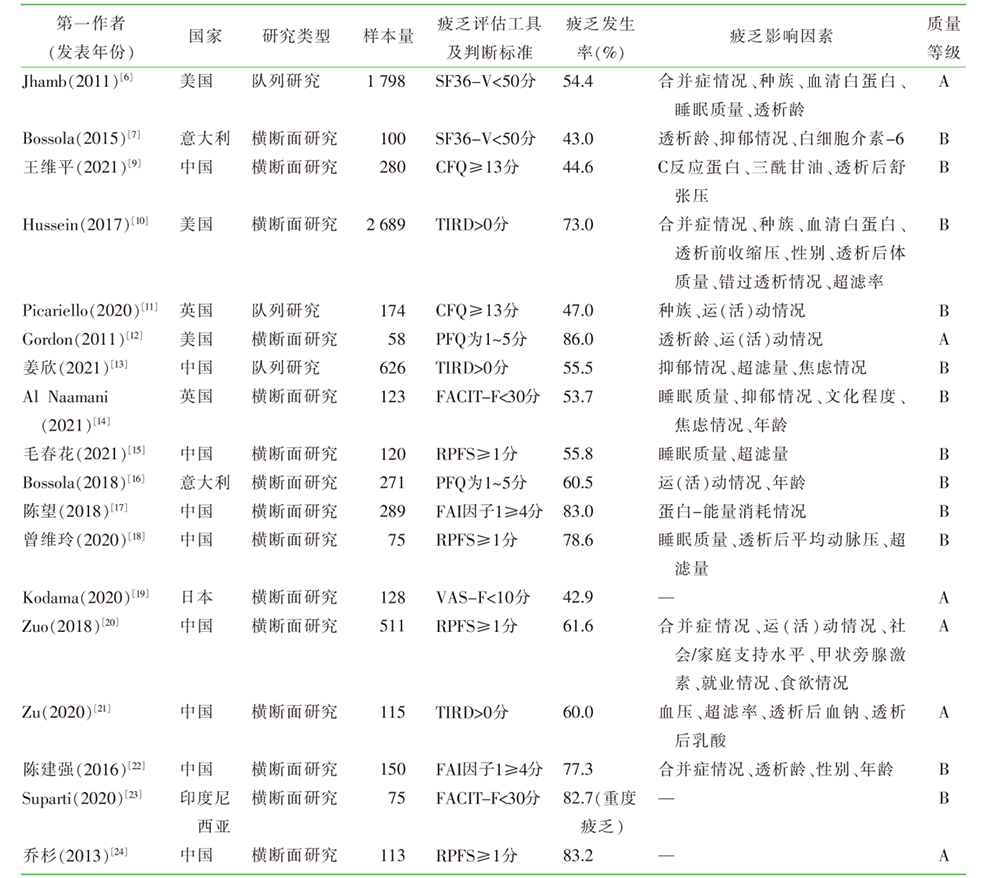
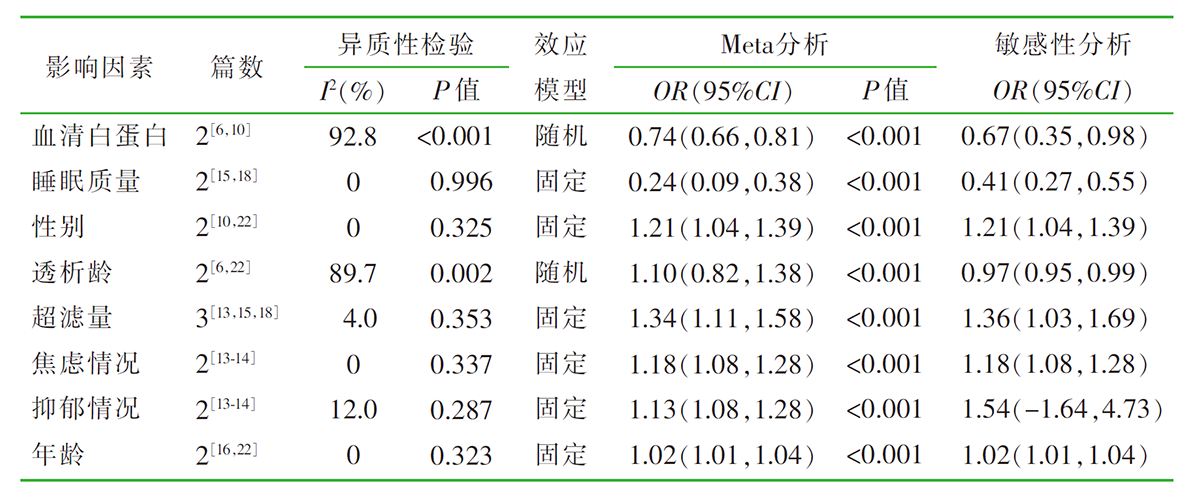
| [1] |
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. and national burden of chronic kidney disease,1990-2017:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225):709-733.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3
|
| [2] |
Bello AK, Okpechi IG, Osman MA, et al. Epidemiology of hae-modialysis outcomes[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2022, 18(6):378-395.
doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00542-7
|
| [3] |
Artom M, Moss-Morris R, Caskey F, et al. Fatigue in advanced kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2014, 86(3):497-505.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.86
pmid: 24694985
|
| [4] |
Picariello F, Moss-Morris R, MacDougall IC, et al. “It’s when you’re not doing too much You feel tired”:a qualitative exploration of fatigue in end-stage kidney disease[J]. Br J Health Psychol, 2018, 23(2):311-333.
doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12289
pmid: 29280249
|
| [5] |
Picariello F, Norton S, Moss-Morris R, et al. Fatigue in preva-lent haemodialysis patients predicts all-cause mortality and kidney transplantation[J]. Ann Behav Med, 2019, 53(6):501-514.
doi: 10.1093/abm/kay061
pmid: 30020399
|
| [6] |
Jhamb M, Pike F, Ramer S, et al. Impact of fatigue on out-comes in the hemodialysis(HEMO) study[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2011, 33(6):515-523.
doi: 10.1159/000328004
|
| [7] |
Bossola M, di Stasio E, Giungi S, et al. Fatigue is associated with serum interleukin-6 levels and symptoms of depression in patients on chronic hemodialysis[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2015, 49(3):578-585.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.07.009
|
| [8] |
周英凤, 顾莺, 胡雁,等. JBI循证卫生保健中心对关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具:患病率及分析性横断面研究的质量评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(3):219-221.
|
|
Zhou YF, Gu Y, Hu Y, et al. The Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools for use in systematic review:prevalence study and analytical cross sectional study[J]. J Nurs Train, 2018, 33(3):219-221.
|
| [9] |
王维平, 何萍, 姜璐,等. 单中心血液透析患者透析后疲劳状态及影响因素[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2021, 22(9):808-811.
|
|
Wang WP, He P, Jiang L, et al. Fatigue status and influencing factors of hemodialysis patients in a single center after dialysis[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol, 2021, 22(9):808-811.
|
| [10] |
Hussein WF, Arramreddy R, Sun SJ, et al. Higher ultrafil-tration rate is associated with longer dialysis recovery time in patients undergoing conventional hemodialysis[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2017, 46(1):3-10.
doi: 10.1159/000476076
pmid: 28554180
|
| [11] |
Picariello F, Norton S, Moss-Morris R, et al. A prospective study of fatigue trajectories among in-centre haemodialysis patients[J]. Br J Health Psychol, 2020, 25(1):61-88.
doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12395
pmid: 31742834
|
| [12] |
Gordon P, Doyle J, Johansen K. Postdialysis fatigue is associa-ted with sedentary behavior[J]. Clin Nephrol, 2011, 75(5):426-433.
pmid: 21543022
|
| [13] |
姜欣. 维持性血液透析患者透析后疲劳恢复时间与预后关系的研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2021.
|
|
Jiang X. Study on the relationship between fatigue recovery time and prognosis of maintenance hemodialysis patients after dialysis[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2021.
|
| [14] |
Al Naamani Z, Gormley K, Noble H, et al. depression and sleep quality in patients undergoing haemodialysis[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2021, 22(1):157.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02349-3
|
| [15] |
毛春花, 黄文娟. 维持性血液透析患者透析后疲劳的危险因素分析[J]. 慢性病学杂志, 2021, 22(11):1778-1780.
|
|
Mao CH, Haung WJ. Analysis of risk factors for fatigue after dialysis in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chron Pathematol J, 2021, 22(11):1778-1780.
|
| [16] |
Bossola M, Marzetti E, di Stasio E, et al. Prevalence and associated variables of post-dialysis fatigue:results of a prospective multicentre study[J]. Nephrology(Carlton), 2018, 23(6):552-558.
|
| [17] |
陈望. 维持性血液透析患者疲乏的多中心现况调查及其相关因素分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2018.
|
| [18] |
曾维玲, 栾中佼, 吴私,等. 维持性血液透析患者透析后疲劳的影响因素分析[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(10):943-948.
|
|
Zeng WL, Luan ZJ, Wu S, et al. Influencing factors of post-dialysis fatigue in patients under maintenance hemodialysis[J]. J Chin Med Univ, 2020, 49(10):943-948.
|
| [19] |
Kodama H, Togari T, Konno Y, et al. A new assessment scale for post-dialysis fatigue in hemodialysis patients[J]. Ren Replace Ther, 2020, 6(1):1-8.
doi: 10.1186/s41100-019-0252-5
|
| [20] |
Zuo MH, Tang J, Xiang MM, et al. Relationship between fati-gue symptoms and subjective and Objective indicators in hemodialysis patients[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2018, 50(7):1329-1339.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-1871-4
|
| [21] |
Zu Y, Lu XX, Yu Q, et al. Higher postdialysis lactic acid is associated with postdialysis fatigue in maintenance of hemodialysis patients[J]. Blood Purif, 2020, 49(5):535-541.
doi: 10.1159/000505612
|
| [22] |
陈建强, 吕志增, 吴唐英. 维持性血液透析患者疲劳状况与生存质量相关性分析[J]. 广东医学院学报, 2016, 34(3):329-331.
|
|
Chen JQ, Lü ZZ, Wu TY, et al. Correlation between fatigue and quality of life in patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Journal of Guangdong Medical University, 2016, 34(3):329-331.
|
| [23] |
Suparti S, Sodikin S, Endiyono E. The relationship between dialysis adequacy and fatigue in patients on maintenance hemodialysis[J]. J Kep Padjadjaran, 2020, 8(1):1-8.
doi: 10.24198/jkp.v8i1
|
| [24] |
乔杉. 血液透析患者疲劳状况与体力活动水平相关性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013.
|
|
Qiao S. Correlation between fatigue status and physical acti-vity level in hemodialysis patients[D]. Changchun: Jilin Uni-versity, 2013.
|
| [25] |
Abdel-Kader K, Jhamb M, Mandich LA, et al. Ecological mo-mentary assessment of fatigue,sleepiness,and exhaustion in ESKD[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2014, 15:29.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-29
pmid: 24502751
|
| [26] |
Brys ADH, Lenaert B, Van Heugten CM, et al. Exploring the diurnal course of fatigue in patients on hemodialysis treatment and its relation with depressive symptoms and classical conditioning[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2019, 57(5):890-898.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.02.010
|
| [27] |
Ju A, Teixeira-Pinto A, Tong A, et al. Validation of a core patient-reported outcome measure for fatigue in patients receiving hemodialysis:the SONG-HD Fatigue Instrument[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 15(11):1614-1621.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.05880420
|
| [28] |
Metzelthin SF, van Rossum E, de Witte LP, et al. Effectiveness of interdisciplinary primary care approach to reduce disability in community dwelling frail older people:cluster randomised controlled trial[J]. BMJ, 2013, 347:f5264.
|
| [29] |
Al Naamani Z, Gormley K, Noble H, et al. depression and sleep quality in patients undergoing haemo-dialysis[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2021, 22(1):157.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02349-3
|
| [30] |
Wu YH, Hsu YJ, Tzeng WC, et al. Correlation between physi-cal activity and psychological distress in patients receiving hemodialysis with comorbidities:a cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(7):3972.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073972
|
| [31] |
de Ridder D, Geenen R, Kuijer R, et al. Psychological adjust-ment to chronic disease[J]. Lancet, 2008, 372(9634):246-255.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61078-8
|
| [32] |
Bossola M, di Stasio E, Antocicco M, et al. 1-year course of fati-gue in patients on chronic hemodialysis[J]. Int Urol Nephrol,2017, 49(4):727-734.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1496-4
|
| [33] |
Tangvoraphonkchai K, Davenport A. Extracellular water excess and increased self-reported fatigue in chronic hemodialysis patients[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2018, 22(2):152-159.
doi: 10.1111/tap.2018.22.issue-2
|