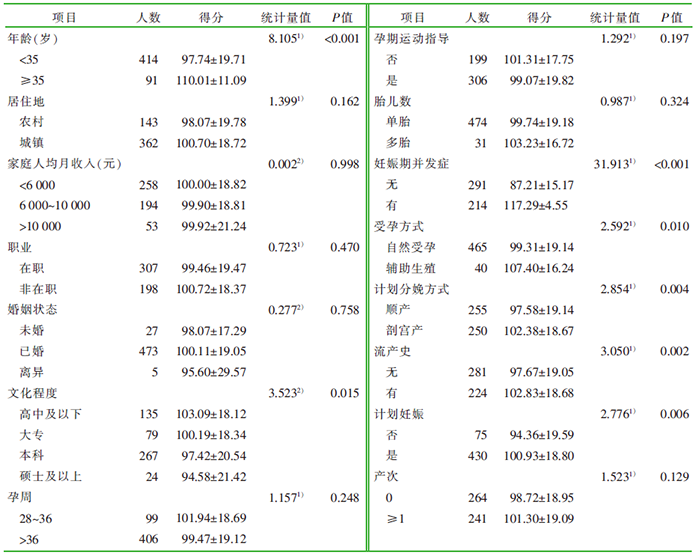
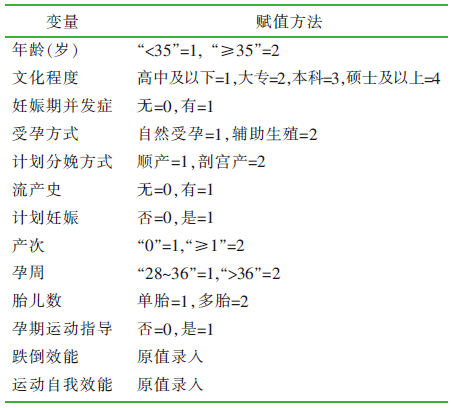
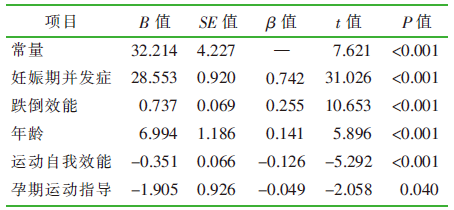
| [1] |
Ribeiro MM, Andrade A, Nunes I. Physical exercise in pregnan-cy:benefits,risks and prescription[J]. J Perinat Med, 2021, 50(1):4-17.
doi: 10.1515/jpm-2021-0315
|
| [2] |
McGee LD, Cignetti CA, Sutton A, et al. Exercise during preg-nancy:obstetricians’ beliefs and recommendations compared to American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ 2015 guidelines[J]. Cureus, 2018, 10(8):e3204.
|
| [3] |
Smith R, Shakespeare J, Williams Z, et al. Physical activity for pregnant women:an infographic for healthcare professionals[J]. Br J Gen Pract, 2017, 67(663):460.
doi: 10.3399/bjgp17X692801
|
| [4] |
新华社. 中共中央国务院印发《“健康中国2030”规划纲要》[EB/OL].(2016-10-25). http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2016-10/25/content_5124174.htm.
|
|
Xinhua News Agency. The CPC Central Committee and the State Council issued the “Healthy China 2030” Blueprint[EB/OL].(2016-10-25). https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2016-10/25/content_5124174.htm.
|
| [5] |
高玲玲, 张舒寒, 向芝萱. 孕妇身体活动影响因素问卷的编制及信度效度检验[J]. 中国护理管理, 2024, 24(3):362-367.
|
|
Gao LL, Zhang SH, Xiang ZX. Development and validation of the questionnaire of factors related to physical activity ques-tionnaire of in pregnant women based on the Socioecological Model[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2024, 24(3):362-367.
|
| [6] |
Zaragoza J, Generelo E, Julián JA, et al. Barriers to adolescent girls’ participation in physical activity defined by physical activity levels[J]. J Sports Med Phys Fitness, 2011, 51(1):128-135.
|
| [7] |
Bauer C, Graf C, Platschek AM, et al. Reasons,motivational fac-tors,and perceived personal barriers to engagement in physical activity during pregnancy vary within the BMI classes:the prenatal prevention project Germany[J]. J Phys Act Health, 2018, 15(3):204-211.
doi: 10.1123/jpah.2016-0563
|
| [8] |
高玲玲, 韩蓉蓉, 张舒寒. 基于社会生态学模型的孕妇身体活动影响因素网络分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2024, 24(6):830-835.
|
|
Gao LL, Han RR, Zhang SH. Network analysis of factors influencing physical activity in pregnant women based on socio-ecological model[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2024, 24(6):830-835.
|
| [9] |
季谋芳, 李若冰, 胡廷进, 等. 非药物干预对孕期抑郁症影响效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2023, 23(11):1713-1719.
|
|
Ji MF, Li RB, Hu TJ, et al. Effects of non-pharmacological interventions on depression during pregnancy:a network Meta-analysis[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2023, 23(11):1713-1719.
|
| [10] |
李晓松. 医学统计学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008:205.
|
|
Li XS. Medical statistics[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Educa-tion Press, 2008:205.
|
| [11] |
Amiri-Farahani L, Ahmadi K, Hasanpoor-Azghady SB, et al. Development and psychometric testing of the ‘barriers to phy-sical activity during pregnancy scale’(BPAPS)[J]. BMC Public Health, 2021, 21(1):1483.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11511-3
pmid: 34325684
|
| [12] |
杨依云, 颜小娜, 王义婷, 等. 孕期身体活动障碍量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2024, 39(8):49-53.
|
|
Yang YY, Yan XN, Wang YT, et al. Translation and validation of the barriers to Physical Activity During Pregnancy Scale[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2024, 39(8):49-53.
|
| [13] |
Kroll T, Kehn M, Ho PS, et al. The SCI Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale(ESES):development and psychometric properties[J]. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act, 2007, 4:34.
doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-4-34
|
| [14] |
Bland HW, Melton BF, Marshall ES, et al. Measuring exercise self-efficacy in pregnant women:psychometric properties of the Pregnancy-Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale(P-ESES)[J]. J Nurs Meas, 2013, 21(3):349-359.
doi: 10.1891/1061-3749.21.3.349
|
| [15] |
杨红梅, 邓永芳, 高玲玲. 中文版孕妇运动自我效能量表的信效度研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2017, 52(5):632-636.
|
|
Yang HM, Deng YF, Gao LL. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Pregnancy Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2017, 52(5):632-636.
|
| [16] |
Yardley L, Beyer N, Hauer K, et al. Development and initial validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International(FES-I)[J]. Age Ageing, 2005, 34(6):614-619.
doi: 10.1093/ageing/afi196
pmid: 16267188
|
| [17] |
郭启云, 郭沐洁, 张林, 等. 国际版跌倒效能量表汉化后信效度评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015, 18(35):4273-4276.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.35.001
|
|
Guo QY, Guo MJ, Zhang L, et al. Evaluation of the reliability and validity of Chinese version of Falls Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2015, 18(35):4273-4276.
|
| [18] |
Dolatabadi Z, Amiri-Farahani L, Ahmadi K, et al. Barriers to physical activity in pregnant women living in Iran and its predictors:a cross sectional study[J]. BMC Pregnancy Child-birth, 2022, 22(1):815.
|
| [19] |
Hay SJ, McLachlan HL, Newton M, et al. Sources of informa-tion during pregnancy and the early parenting period:explor-ing the views of women and their partners[J]. Midwifery, 2022, 105:103236.
doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2021.103236
|
| [20] |
赵欢欢, 李帅, 万慎娴. 妊娠晚期孕妇症状困扰潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2025, 40(2):27-32.
|
|
Zhao HH, Li S, Wan SX. Latent profile analysis and the influencing factors of symptom distress among pregnant women in the third trimester[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2025, 40(2):27-32.
|
| [21] |
王玉鹏, 胡小黎, 吴陆萍, 等. 孕妇跌倒恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理教育, 2022, 19(10):950-955.
|
|
Wang YP, Hu XL, Wu LP, et al. The status and influencing factors of fall fear in pregnant women[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2022, 19(10):950-955.
|
| [22] |
王玉鹏, 徐萍, 冯素文. 影响孕妇孕期体力活动的环境因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(17):2119-2125.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.17.010
|
|
Wang YP, Xu P, Feng SW. Analysis of environmental factors and impact path of physical activity in pregnant women[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(17):2119-2125.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.17.010
|
| [23] |
马嫔, 张广意, 李海霞, 等. 高龄初产妇妊娠晚期症状群识别及其影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理教育, 2024, 21(2):237-244.
|
|
Ma P, Zhang GY, Li HX, et al. Study on symptom group identification and influencing factors of elderly primiparas in the third trimester[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2024, 21(2):237-244.
|
| [24] |
Okafor UB, Goon DT. Uncovering barriers to prenatal physical activity and exercise among South African pregnant women:a cross-sectional,mixed-method analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10:697386.
doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.697386
|
| [25] |
张璐, 郭娜菲, 余燕飞. 孕妇尿失禁知信行量表的汉化及在孕妇中的Rasch模型分析[J]. 现代临床护理, 2024, 23(5):10-18.
|
|
Zhang L, Guo NF, Yu YF. Translation of the knowledge,attitude and practice assessment scale of pregnant women with urinary incontinence into Chinese and test its reliability and validity under Rasch model[J]. Mod Clin Nurs, 2024, 23(5):10-18.
|
| [26] |
肖润希, 周英凤. 妊娠期糖尿病患者孕期参与体力活动促进及障碍因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(14):1683-1689.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.14.003
|
|
Xiao RX, Zhou YF. Facilitators and barriers of physical activity participation among women with gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy:a qualitative study[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(14):1683-1689.
|
| [27] |
Gaston A, Cramp A. Exercise during pregnancy:a review of patterns and determinants[J]. J Sci Med Sport, 2011, 14(4):299-305.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2011.02.006
pmid: 21420359
|