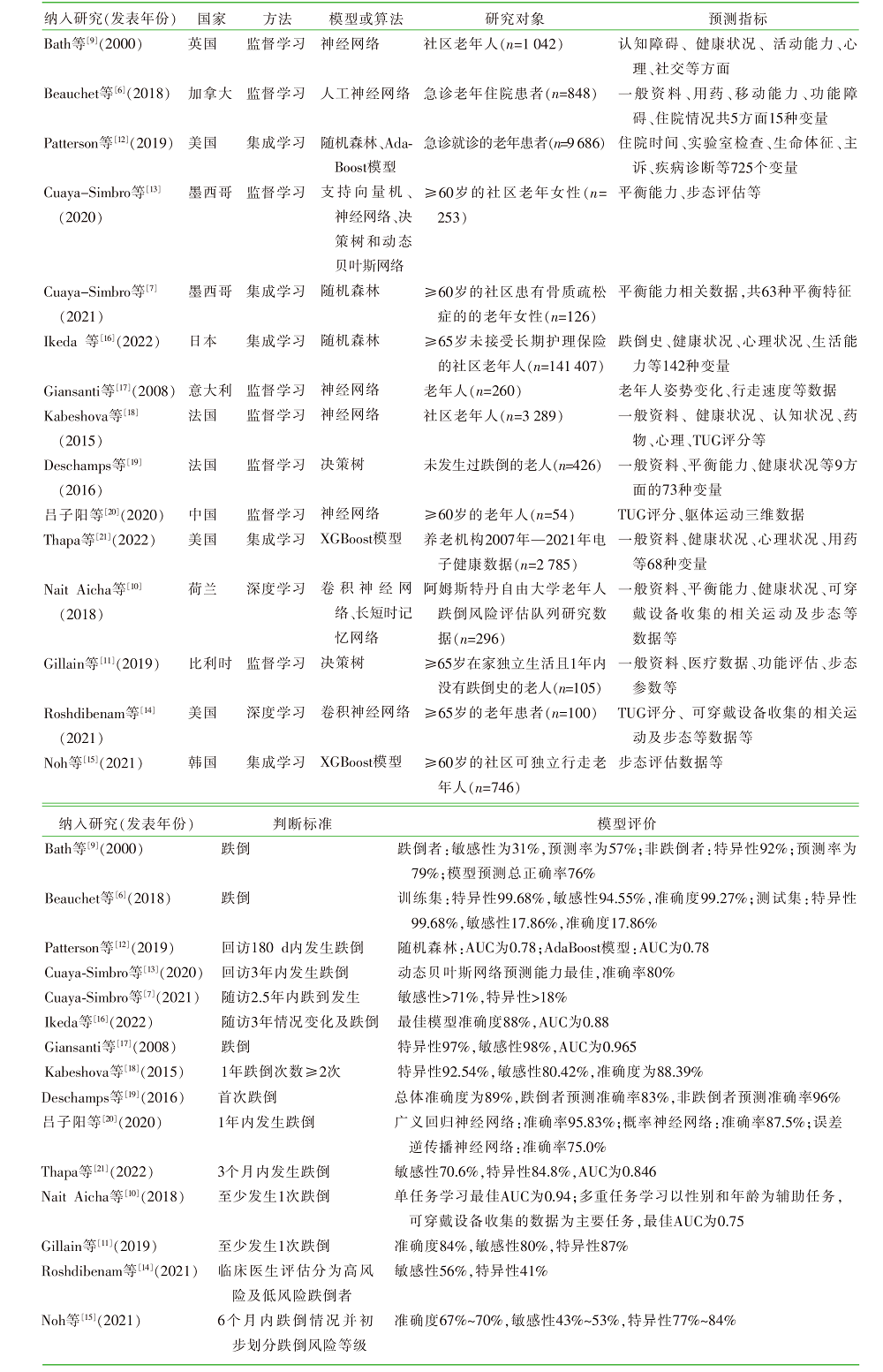
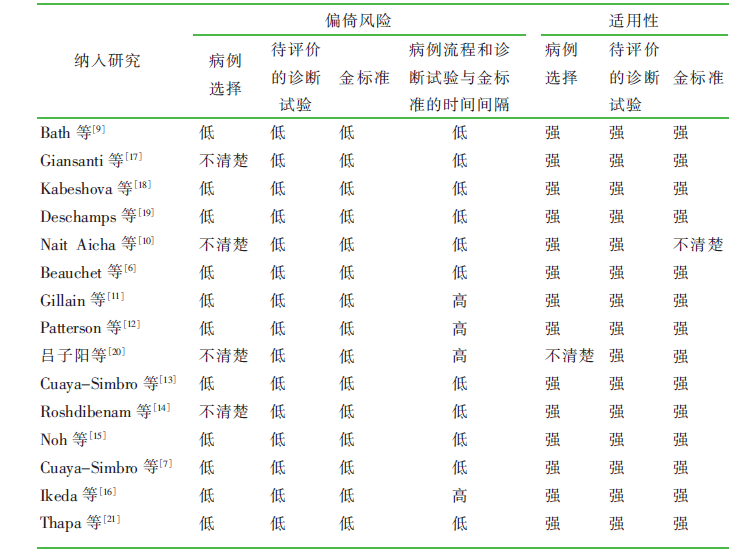
| [1] |
Gazibara T, Kurtagic I, Kisic-Tepavcevic D, et al. Falls,risk factors and fear of falling among persons older than 65 years of age[J]. Psychogeriatrics, 2017, 17(4):215-223.
doi: 10.1111/psyg.12217
pmid: 28130862
|
| [2] |
国家卫生健康委统计信息中心, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心. 中国死因监测数据集2018[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2019.
|
| [3] |
王玉梅, 李凌, 熊莉娟, 等. 老年人跌倒预防临床实践指南的质量评价及内容分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(11):1729-1734.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.11.027
|
|
Wang YM, Li L, Xiong LJ, et al. Quality evaluation and content analysis of clinical practice guidelines for fall prevention in the elderly[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(11):1729-1734.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.11.027
|
| [4] |
Greener JG, Kandathil SM, Moffat L, et al. A guide to machine learning for biologists[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(1):40-55.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00407-0
|
| [5] |
Esteva A, Robicquet A, Ramsundar B, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(1):24-29.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0316-z
pmid: 30617335
|
| [6] |
Beauchet O, Noublanche F, Simon R, et al. Falls risk prediction for older inpatients in acute care medical wards:is there an interest to combine an early nurse assessment and the artificial neural network analysis?[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2018, 22(1):131-137.
doi: 10.1007/s12603-017-0950-z
pmid: 29300432
|
| [7] |
Cuaya-Simbro G, Perez-Sanpablo AI, Morales EF, et al. Compa-ring machine learning methods to improve fall risk detection in elderly with osteoporosis from balance data[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2021, 2021:1-11.
|
| [8] |
曲艳吉, 杨智荣, 孙凤, 等. 偏倚风险评估系列:(六)诊断试验[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(4):524-531.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.04.028
pmid: 29699051
|
|
Qu YJ, Yang ZR, Sun F, et al. Risk on bias assessment:(6) a revised tool for the quality assessment on diagnostic accuracy studies(QUADAS-2)[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(4):524-531.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.04.028
pmid: 29699051
|
| [9] |
Bath PA, Pendleton N, Morgan K, et al. New approach to risk determination:development of risk profile for new falls among community-dwelling older people by use of a Genetic Algorithm Neural Network (GANN)[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2000, 55(1):M17-M21.
doi: 10.1093/gerona/55.1.M17
|
| [10] |
Nait Aicha A, Englebienne G, van Schooten KS, et al. Deep learning to predict falls in older adults based on daily-life trunk accelerometry[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2018, 18(5):1654.
doi: 10.3390/s18051654
|
| [11] |
Gillain S, Boutaayamou M, Schwartz C, et al. Using supervised learning machine algorithm to identify future fallers based on gait patterns:a two-year longitudinal study[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2019, 127:110730.
doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.110730
|
| [12] |
Patterson BW, Engstrom CJ, Sah V, et al. Training and inter-preting machine learning algorithms to evaluate fall risk after emergency department visits[J]. Med Care, 2019, 57(7):560-566.
doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001140
pmid: 31157707
|
| [13] |
Cuaya-Simbro G, Perez-Sanpablo AI, Muñoz-Meléndez A, et al. Comparison of machine learning models to predict risk of falling in osteoporosis elderly[J]. Found Comput Decis Sci, 2020, 45(2):66-77.
|
| [14] |
Roshdibenam V, Jogerst GJ, Butler NR, et al. Machine learning prediction of fall risk in older adults using timed up and go test kinematics[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2021, 21(10):3481.
doi: 10.3390/s21103481
|
| [15] |
Noh B, Youm C, Goh E, et al. XGBoost based machine learn-ing approach to predict the risk of fall in older adults using gait outcomes[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11:12183.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91797-w
|
| [16] |
Ikeda T, Cooray U, Hariyama M, et al. An interpretable mach-ine learning approach to predict fall risk among community-dwelling older adults:a three-year longitudinal study[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2022, 37(11):2727-2735.
doi: 10.1007/s11606-022-07394-8
|
| [17] |
Giansanti D, Macellari V, Maccioni G. New neural network classifier of fall-risk based on the Mahalanobis distance and kinematic parameters assessed by a wearable device[J]. Physiol Meas, 2008, 29(3):N11-N19.
doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/29/3/N01
|
| [18] |
Kabeshova A, Launay CP, Gromov VA, et al. Artificial neural network and falls in community-dwellers:a new approach to identify the risk of recurrent falling?[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2015, 16(4):277-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.09.013
|
| [19] |
Deschamps T, Le Goff CG, Berrut G, et al. A decision model to predict the risk of the first fall onset[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2016, 81:51-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.04.016
pmid: 27114199
|
| [20] |
吕子阳, 高星, 马英楠. 基于神经网络的老年易跌倒人群识别方法[J]. 伤害医学(电子版), 2020, 9(2):9-13.
|
|
Lü ZY, Gao X, Ma YN. Identification method of fall-prone elderly based on neural network[J]. Inj Med Electron Ed, 2020, 9(2):9-13.
|
| [21] |
Thapa R, Garikipati A, Shokouhi S, et al. Predicting falls in long-term care facilities:machine learning study[J]. JMIR Aging, 2022, 5(2):e35373.
doi: 10.2196/35373
|
| [22] |
Lindberg DS, Prosperi M, Bjarnadottir RI, et al. Identification of important factors in an inpatient fall risk prediction model to improve the quality of care using EHR and electronic administrative data:a machine-learning approach[J]. Int J Med Inform, 2020, 143:104272.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104272
|
| [23] |
刘雨安, 杨小文, 李乐之. 机器学习在疾病预测的应用研究进展[J]. 护理学报, 2021, 28(7):30-34.
|
|
Liu Y, Yang XW, Li LZ. Research progress on application of machine learning in disease prediction[J]. J Nurs(China), 2021, 28(7):30-34.
|
| [24] |
曲超然, 王青, 韩琳, 等. 机器学习算法在压力性损伤管理中的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(2):212-217.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.02.009
|
|
Qu CR, Wang Q, Han L, et al. A literature review on the application of machine learning algorithms in pressure injury management[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(2):212-217.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.02.009
|
| [25] |
Haescher M, Chodan W, Höpfner F, et al. Automated fall risk assessment of elderly using wearable devices[J]. J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng, 2020, 7:2055668320946209.
|
| [26] |
刘忠华, 张慧慧, 方勇. 可穿戴设备用于居家养老护理服务管理的可行性研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2020, 35(14):52-57.
|
|
Liu ZH, Zhang HH, Fang Y. Feasibility of wearable devices for home-based nursing service management[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2020, 35(14):52-57.
|
| [27] |
Argañarás JG, Wong YT, Begg R, et al. State-of-the-art weara-ble sensors and possibilities for radar in fall prevention[J]. Sensors(Basel), 2021, 21(20):6836.
|
| [28] |
刘晓燕, 丁霞, 董晨, 等. 社区与住院老年人跌倒的现状及影响因素[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2022, 28(4):389-398.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2022.04.004
|
|
Liu XY, Ding X, Dong C, et al. Status and related factors of fall among the elderly in community and hospital[J]. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract, 2022, 28(4):389-398.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2022.04.004
|
| [29] |
Yokota S, Endo M, Ohe K. Establishing a classification system for high fall-risk among inpatients using support vector machines[J]. Comput Inform Nurs, 2017, 35(8):408-416.
doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000000332
pmid: 28800580
|