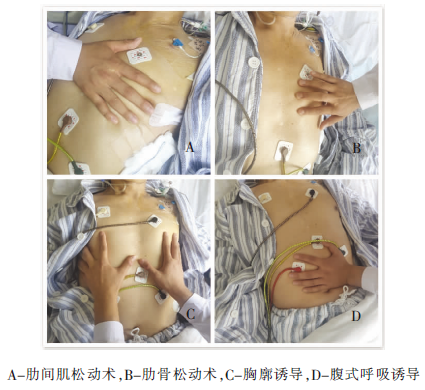
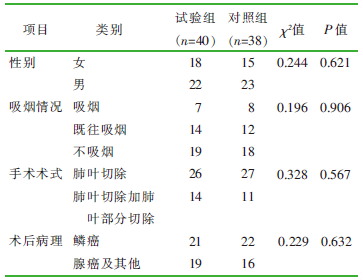
| [1] |
党剑, 张恺, 凌文杰. 负荷深呼吸训练联合吸氧干预对老年人呼吸肌功能的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2018, 40(3):201-202.
|
|
Dang J, Zhang K, Ling WJ. Effects of loading deep breathing training combined with oxygen inhalation on respiratory muscle function of the elderly[J]. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil, 2018, 40(3):201-202.
|
| [2] |
Win T, Groves AM, Ritchie AJ, et al. The effect of lung resection on pulmonary function and exercise capacity in lung cancer patients[J]. Respiratory Care, 2007, 52(6):720-726.
|
| [3] |
Lai Y, Huang J, Yang M, et al. Seven-day intensive preoperative rehabilitation for elderly patients with lung cancer:a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Surg Res, 2017, 209:30-36.
doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.09.033
|
| [4] |
Crandall K, Maguire R, Campbell A, et al. A qualitative study exploring the views,attitudes and beliefs of patients and health professionals towards exercise intervention for people who are surgically treated for lung cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer Care(Engl), 2018, 27(2):e12828.
|
| [5] |
Cavalheri V, Granger C. Preoperative exercise training for patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017, 6(6):CD012020.
|
| [6] |
Cesario A, Ferri L, Galetta D, et al. Post-operative respiratory rehabilitation after lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2007, 57(2):175-180.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.02.017
|
| [7] |
Crandall K, Maguire R, Campbell A, et al. Exercise intervention for patients surgically treated for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer(NSCLC):a systematic review[J]. Surg Oncol, 2014, 23(1):17-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2014.01.001
pmid: 24529937
|
| [8] |
Ries AL, Bauldoff GS, Carlin BW, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation:joint ACCP/AACVPR evidence-based clinical practice gui-delines[J]. Chest, 2007, 131(5 Suppl):4S-42S.
doi: 10.1378/chest.06-2418
|
| [9] |
周坤, 吴砚铭, 苏建华, 等. 肺癌患者术前呼气峰流速可以预测肺叶切除术后肺部并发症吗?[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2017, 20(9):603-609.
|
|
Zhou K, Wu YM, Su JH, et al. Can preoperative peak expiratory flow predict postoperative pulmonary complications in lung cancer patients undergoing lobectomy?[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2017, 20(9):603-609.
|
| [10] |
Ana RL, Ion LA, Carlos A, et al. Perioperative physiotherapy in patients undergoing lung cancer resection[J]. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2014, 19(2):269-281.
doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu126
|
| [11] |
王剑桥, 苏国栋, 孙宜文, 等. 呼吸训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者运动功能、运动耐力、日常生活能力的meta分析[J]. 华西医学, 2019, 34(5):539-547.
|
|
Wang JQ, Su GD, Sun YW, et al. Meta-analysis of respiratory training on motor function,exercise endurance,and activity of daily living in stroke patients[J]. West China Medical Journal, 2019, 34(5):539-547.
|
| [12] |
Gao K, Yu PM, Su JH, et al. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing screening and pre-operative pulmonary rehabilitation reduce postoperative complications and improve fast-track recovery after lung cancer surgery:a study for 342 cases[J]. Thoracic Cancer, 2014, 6(4):443-449.
doi: 10.1111/tca.2015.6.issue-4
|
| [13] |
Vainshelboim B, Oliveira J, Fox BD, et al. Long-term effects of a 12-week exercise training program on clinical outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Lung, 2015, 193(3):345-354.
doi: 10.1007/s00408-015-9703-0
pmid: 25731736
|