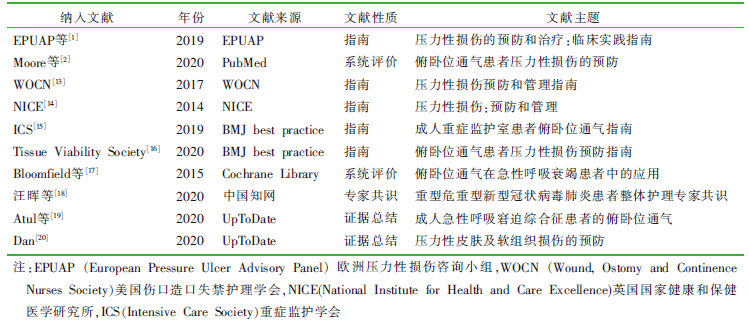
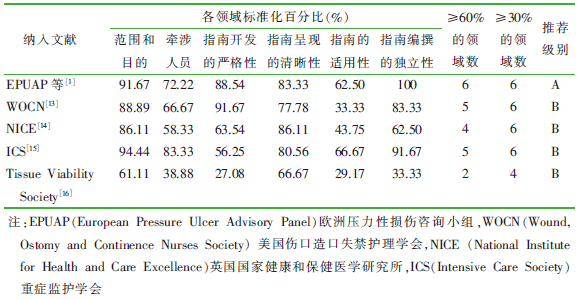
| [1] |
European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel, Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance. Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers /injuries:clinical practice guideline[S]. EPUAP /NPIAP /PPPIA, 2019.
|
| [2] |
Moore Z, Patton D, Avsar P, et al. Prevention of pressure ulcers among individuals cared for in the prone position:lessons for the COVID-19 emergency[J]. J Wound Care, 2020, 29(6):312-320.
doi: 10.12968/jowc.2020.29.6.312
pmid: 32530776
|
| [3] |
Haleem S, Mihai R, Rothenfluh DA, et al. Preventing iatrogenic facial pressure ulcers during spinal surgery:prospective trial using a novel method and review of literature[J]. Int Wound J, 2020, 17(5):1391-1395.
doi: 10.1111/iwj.v17.5
|
| [4] |
Girard R, Baboi L, Ayzac L, et al. The impact of patient positioning on pressure ulcers in patients with severe ARDS:results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial on prone positioning[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2014, 40(3):397-403.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-3188-1
|
| [5] |
Sud S, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, et al. Effect of prone positioning during mechanical ventilation on mortality among patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J De L’association Med Can, 2014, 186(10):E381-E390.
|
| [6] |
Lucchini A, Bambi S, Mattiussi E, et al. Prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients:a retrospective analysis of complications[J]. Dimens Crit Care Nurs, 2020, 39(1):39-46.
doi: 10.1097/DCC.0000000000000393
pmid: 31789984
|
| [7] |
朱政, 胡雁, 邢唯杰, 等. 不同类型循证问题的构成[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2017, 32(21):1991-1994.
|
|
Zhu Z, Hu Y, Xing WJ, et al. The composition of different types of evidence based problems[J]. J Nurses Train, 2017, 32(21):1991-1994.
|
| [8] |
Dicenso A, Bayley L, Haynes RB. Accessing pre-appraised evidence:fine-tuning the 5S model into a 6S model[J]. Evid Based Nurs, 2009, 12(4):99-101.
doi: 10.1136/ebn.12.4.99-b
pmid: 19779069
|
| [9] |
Hoffmann-Eβer W, Siering U, Neugebauer EA, et al. Guideline appraisal with AGREE II:systematic review of the current evi-dence on how users handle the 2 overall assessments[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(3):e0174831. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174831.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174831
|
| [10] |
The Joanna Briggs Institute(JBI). Critical appraisal tools[EB/OL].(2017-07-15)[2020-09-01]. http://joannabriggs.org/research/critical-appraisal-tools.html.
|
| [11] |
余文静, 肖瑶, 胡娟娟, 等. 预防围手术期患者低体温的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(4):589-594.
|
|
Yu WJ, Xiao Y, Hu JJ, et al. Evidence summary for prevention of perioperative hypothermia in patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(4):589-594.
|
| [12] |
王春青, 胡雁. JBI证据预分级及证据推荐级别系统(2014版)[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2015, 30(11):964-967.
|
|
Wang CQ, Hu Y. JBI evidence pre-classification and evidence rank system(2014 Edition)[J]. J Nurses Train, 2015, 30(11):964-967.
|
| [13] |
Wound,Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society-Wound Guide-lines Task Force. WOCN 2016 guideline for prevention and management of pressure injuries(ulcers):an executive summary[J]. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs, 2017, 44(3):241-246.
doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000321
|
| [14] |
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Pressure ulcers:prevention and management[EB/OL]. [2020-09-01]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg179/resources/pressure-ulcers-preven-tion-and-management-pdf-35109760631749.
|
| [15] |
Intensive Care Society. Prone positioning in adult critical care[EB/OL]. [2020-09-01]. https://www.ficm.ac.uk/sites/default/files/prone_position_in_adult_critical_care_2019.pdf.
|
| [16] |
Tissue Viability Society. Pressure ulcer prevention guidance when nursing patients in the prone position[EB/OL]. [2020-09-01]. https://tvs.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Pressure-ulcer-prevention-guidance-when-proning-patients-V5-17th-April-2020-1.pdf.
|
| [17] |
Bloomfield R, Noble DW, Sudlow A. Prone position for acute respiratory failure in adults[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015(11):CD008095.
|
| [18] |
汪晖, 曾铁英, 吴欣娟, 等. 重型危重型新型冠状病毒肺炎患者整体护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(3):337-342.
|
|
Wang H, Zeng TY, Wu XJ, et al. Holistic care for patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019:an expert consensus[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(3):337-342.
|
| [19] |
Atul M, Robert MK. Prone ventilation for adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[EB/OL].(2020-04-21)[2020-08-01]. http://222.247.54.203:1057/contents/prone-ventilation-for-adult-patients-with-acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome?search=pressure%20sores%20and%20prone%20ventilation&source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&selectedTitle=1~150.
|
| [20] |
Dan Berlowitz. Prevention of pressure-induced skin and soft tissue injury[EB/OL].(2020-01-06)[2020-09-01]. http://222.247.54.203:1057/contents/prevention-of-pressure-induced-skin-and-soft-tissue-injury?search=%E5%8E%8B%E7%96%AE&source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&selectedTitle=5~150.
|
| [21] |
Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 368(23):2159-2168.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214103
|
| [22] |
周英凤, 顾莺, 胡雁, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具:干预性研究的质量评价(一)[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(1):24-26.
|
|
Zhou YF, Gu Y, Hu Y, et al. Quality assessment tool of different types of research for JBI evideuce based health care—quality evaluation of intervention study[J]. J Nurses Train, 2018, 33(1):24-26.
|
| [23] |
Chou R, Dana T, Bougatsos C, et al. Pressure ulcer risk assessment and prevention:a systematic comparative effectiveness review[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2013, 159(1):28-38.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-1-201307020-00006
|
| [24] |
Walia GS, Wong AL, Lo AY, et al. Efficacy of monitoring devices in support of prevention of pressure injuries:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Adv Skin Wound Care, 2016, 29(12):567-574.
doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000504579.83707.f6
|
| [25] |
Yap TL, Kennerly SM, Simmons MR, et al. Multidimensional team-based intervention using musical cues to reduce odds of facility-acquired pressure ulcers in long-term care:a paired randomized intervention study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2013, 61(9):1552-1559.
doi: 10.1111/jgs.12422
|
| [26] |
Otero DP, Domínguez DV, Fernández LH, et al. Preventing facial pressure ulcers in patients under non-invasive mechani-cal ventilation:a randomised control trial[J]. J Wound Care, 2017, 26(3):128-136.
doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.3.128
pmid: 28277990
|
| [27] |
Lupiañez-Perez I, Uttumchandani SK, Morilla-Herrera JC, et al. Topical olive oil is not inferior to hyperoxygenated fatty aids to prevent pressure ulcers in high-risk immobilised patients in home care. Results of a multicentre randomised triple-blind controlled non-inferiority trial[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4):e0122238.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122238
|
| [28] |
刘晓黎, 王泠, 王志稳, 等. 无创通气设备相关面部压力性损伤预防的证据总结[J]. 中国护理管理, 2019, 19(10):1532-1537.
|
|
Liu XL, Wang L, Wang ZW, et al. Evidence summary of prevention of noninvasive ventilation related facial pressure injuries[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2019, 19(10):1532-1537.
|