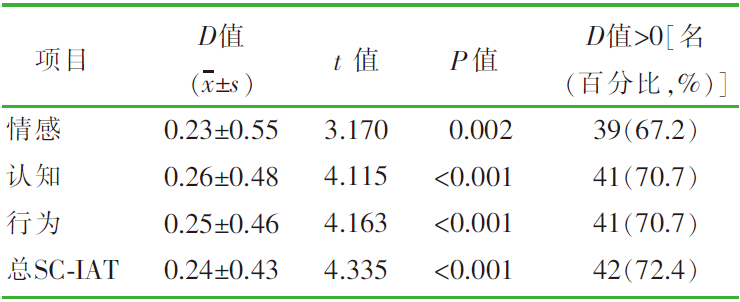
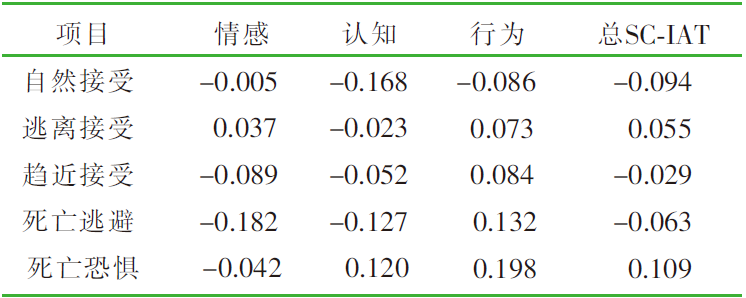
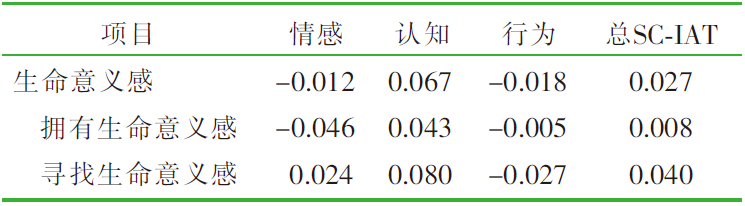
| [1] |
Frankl VE. Man’s search for meaning:an introduction to logotherapy[M]. 4th ed. Boston: Beacon Press. 1992.
|
| [2] |
郭丽婷, 刘薇, 梅永霞, 等. 灵性关怀认知在护理本科生生命意义感与职业认同感间的中介作用[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2021, 38(11):25-28.
|
| [3] |
陈逸雯, 贺惠娟, 张媛, 等. 压力知觉和积极应对在护生生命意义感与职业认同感间的链式中介作用[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(17):85-89.
|
| [4] |
彭子轩, 孙晓莹, 宫淑萍, 等. 护理本科生灵性照护认知与生命意义感、心理资本的关系研究[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2024, 42(15):80-83.
|
| [5] |
Dezutter J, Luyckx K, Hutsebaut D. “Are you afraid to die?” religion and death attitudes in an adolescent sample[J]. J Psychol Theol, 2009, 37(3):163-173.
|
| [6] |
李雪平, 尹礼雯. 大学生死亡态度与心理健康状况关系研究[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2024, 42(18):141-144.
|
|
Li XP, Yin LW. Study on the relationship between collegians’ attitudes toward death and mental health status[J]. Health Vocat Educ, 2024, 42(18):141-144.
|
| [7] |
王申. 死亡态度和生命教育需求调查研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2009.
|
| [8] |
Xie L, Li YJ, Ge WJ, et al. The relationship between death attitude and professional identity in nursing students from mainland China[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2021, 107:105150.
|
| [9] |
胡媛艳, 李成霞, 谭东超, 等. 大学生内隐死亡态度与外显死亡态度的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2017, 31(5):389-394.
|
|
Hu YY, Li CX, Tan DC, et al. Relationships between implicit and explicit attitude toward death in college students[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2017, 31(5):389-394.
|
| [10] |
刘俊升, 桑标. 内隐-外显态度的关系及其行为预测性[J]. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版), 2010, 28(2):59-66.
|
| [11] |
Greenwald AG, Banaji MR. Implicit social cognition:attitudes,self-esteem,and stereotypes[J]. Psychol Rev, 1995, 102(1):4-27.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.102.1.4
pmid: 7878162
|
| [12] |
Greenwald AG, McGhee DE, Schwartz JL. Measuring individual differences in implicit cognition:the implicit association test[J]. J Pers Soc Psychol, 1998, 74(6):1464-1480.
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.74.6.1464
pmid: 9654756
|
| [13] |
Wilson TD, Lindsey S, Schooler TY. A model of dual attitudes[J]. Psychol Rev, 2000, 107(1):101-126.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.107.1.101
pmid: 10687404
|
| [14] |
许晓敏, 朱冰影, 任凯. 高职院校医学生生命意义感与死亡态度的相关性研究[J]. 循证护理, 2021, 7(6):783-786.
|
| [15] |
唐孟言, 李晓玲. 本科护生死亡态度与生命意义感的相关性研究[J]. 中国卫生事业管理, 2018, 35(7):539-541,560.
|
|
Tang MY, Li XL. Studying on the correlation between the attitude towards death and purpose in life among nursing undergraduates[J]. Chin Health Serv Manag, 2018, 35(7):539-541,560.
|
| [16] |
覃郅原, 王向荣, 郑三一, 等. 国内外护生死亡教育研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 护理学报, 2023, 30(4):6-10.
doi: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2023.04.006
|
|
Qin ZY, Wang XR, Zheng SY, et al. Visualization analysis of hotspots of death education for nursing students at home and abroad[J]. J Nurs(China), 2023, 30(4):6-10.
doi: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2023.04.006
|
| [17] |
唐鲁, 张玲, 李玉香, 等. 中文版死亡态度描绘量表用于护士群体的信效度分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2014, 29(14):64-66.
|
|
Tang L, Zhang L, Li YX, et al. Validation and reliability of a Chinese version Death Attitude Profile-Revised(DAP-R) for nurses[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2014, 29(14):64-66.
|
| [18] |
王琼琼, 王海莉, 赵飞燕, 等. 死亡态度描绘量表应用于中国大学生的信效度分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(6):737-740.
|
|
Wang QQ, Wang HL, Zhao FY, et al. Analysis on the reliability and validity of Chinese version Death Attitude Profile-reVised(DAP-R) for Chinese college students[J]. Chin J Dis Contr Prev, 2020, 24(6):737-740.
|
| [19] |
Steger MF, Frazier P, Oishi S, et al. The Meaning in Life Questionnaire:assessing the presence of and search for meaning in life[J]. J Couns Psychol, 2006, 53(1):80-93.
|
| [20] |
刘思斯, 甘怡群. 生命意义感量表中文版在大学生群体中的信效度[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2010, 24(6):478-482.
|
|
Liu SS, Gan YQ. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Meaning in Life Questionnaire[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2010, 24(6):478-482.
|
| [21] |
张慧琳, 何世佳. 基于SC-IAT和AMP的护士内隐死亡态度研究[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2024, 32(1):21-25.
|
|
Zhang HL, He SJ. The researches of nurses’ implicit attitude toward death based on single category implicit association test and affective misattribution procedure[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2024, 32(1):21-25.
|
| [22] |
刘蕊, 罗艳艳, 张猛, 等. 基于单类内隐联想测验探讨护士对医生内隐态度[J]. 中国职业医学, 2020, 47(3):286-290.
|
|
Liu R, Luo YY, Zhang M, et al. Implicit attitude of nurses towards doctors based on single-category implicit association test[J]. China Occup Med, 2020, 47(3):286-290.
|
| [23] |
顾志华. 护生死亡态度现状及影响因素分析[J]. 全科护理, 2021, 19(5):715-718.
|
| [24] |
李静, 郭英. 大学医学生内隐死亡态度的测量[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2018, 34(23):3634-3636.
|
| [25] |
何世佳. 护士对死亡的内隐和外显态度研究:基于双重态度模型[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2023.
|
| [26] |
黄宇昕, 唐四元, 鄢芳, 等. 体验式生死教育课程对大学生死亡态度的影响[J]. 中华护理教育, 2021, 18(5):420-424.
|
|
Huang YX, Tang SY, Yan F, et al. Evaluation of experiential life and death education course on death attitudes of college students[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2021, 18(5):420-424.
|
| [27] |
吕家俊. 新冠疫情下ICU医护人员职业倦怠、生命意义感与死亡焦虑的关系研究及干预[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023.
|
| [28] |
王艳晖, 郑瑞双, 董凤齐. 肿瘤科护士生命意义感、职业幸福感及离职倾向的调查研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(2):184-187.
|
|
Wang YH, Zheng RS, Dong FQ. A survey of life significance,occupational well-being and turnover intention of nurses in oncology department[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(2):184-187.
|
| [29] |
高冉, 蔡英杰, 李艳娇, 等. 护士生命意义感对死亡态度影响的研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2018, 18(4):461-465.
|
|
Gao R, Cai YJ, Li YJ, et al. The relationship between the meaning in life and attitude death of nurses[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2018, 18(4):461-465.
|
| [30] |
Ranganath KA, Nosek BA. Implicit attitude generalization occurs immediately;explicit attitude generalization takes time[J]. Psychol Sci, 2008, 19(3):249-254.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02076.x
pmid: 18315797
|
| [31] |
刘永芳, 马明娜. 内隐和外显态度预测消费者行为的一致性研究[J]. 心理科学, 2009, 32(3):563-566.
|
| [32] |
Nosek BA, Banaji MR, Greenwald AG. Harvesting implicit group attitudes and beliefs from a demonstration web site[J]. Group Dynamics Theory Research and Practice, 2002, 6(1):101-115.
|