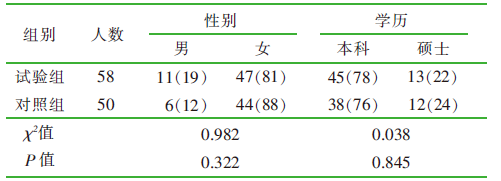
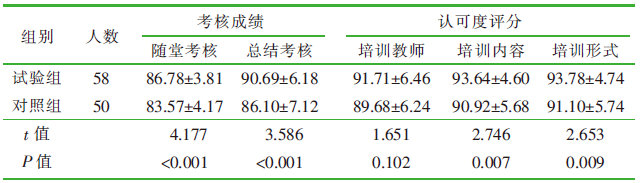
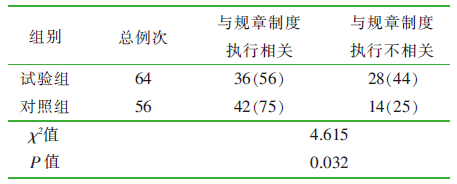
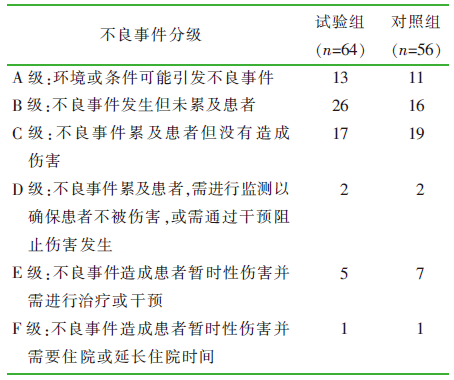
| [1] |
LU Zhiqun.
Reform practice of first-aid teaching in higher vocational nursing specialty from the perspective of the “Five-Education Integration”
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2026, 23(1): 9-15.
|
| [2] |
WANG Lüya, LIU Fan, HUANG Shuqi, LU Zhe.
Practice of standardized training for new nurses in stomatological hospitals
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2025, 22(2): 153-157.
|
| [3] |
XIAO Suqin, REN Jie, JIANG Rong, LIU Hongsuo, XIONG Qin.
A multi-center cross-sectional study on the current status of missed nursing care in intensive care unit
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2025, 22(12): 1475-1481.
|
| [4] |
WEI Shuaifang, LI Zheng.
Application progress of Duffy’s Quality-Caring Model in humanistic nursing care
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(6): 680-685.
|
| [5] |
WU Jie, LI Mengyao, YAN Dexiu, ZHANG Yaqing, ZHANG Yuanyuan.
Development and effect application of MOOC in basic theoretical knowledge training for new graduate nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(2): 140-144.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Yan, QIN Yuanmei, LIU Shu, YANG Yanming, ZHONG Yuan, ZOU Xiaoyan.
Establishment of standardized training evaluation index system for new nurses with bachelor degree in Traditional Chinese Medicine hospitals
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(2): 145-151.
|
| [7] |
LIU Jiahui, LI Jinhua, LI Xuying, CHEN Jiejun, LI Xingfeng, WANG Jing, HU Meihua.
Construction of training objectives list for new nurses in oncology specialized hospitals
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(2): 152-158.
|
| [8] |
YUAN Fang, FENG Qin, QIAN Yuanfang, XU Donge.
Application research of positive and negative case study combined with situational education in the training of humanistic care ability for new nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(10): 1218-1223.
|
| [9] |
WANG Lijuan, ZHANG Miao, XIAO Wenyi, LI Juanjuan, GE Yurong.
Research progress on symptom groups of hemodialysis patients
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(1): 124-128.
|
| [10] |
SUN Shuyi, SUN Guozhen, GAO Min, YU Tianqi, LIU Shenxinyu, WANG Jie.
A concept analysis of ego-depletion in patients of chronic diseases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(8): 963-968.
|
| [11] |
HU Meihua, XIE Aiqing, LI Jinhua, ZHOU Jingfeng, QIU Cuiling, LI Xuying.
Application of open dynamic evaluation model in promoting high quality nursing service
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(8): 969-973.
|
| [12] |
DENG Wei, YAN Jing, WU Linghui, LIU Pengcheng, WANG Ying, LI Xiaozhen.
Evidence summary for the prevention and management of microaspiration around the cuff in adult ICU patients with artificial airway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(7): 870-877.
|
| [13] |
SONG Zhaohui, TAN Meiqi, JIANG Songyun, LUO Ji.
Construction of a training program for new nurses in central sterile supply department
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(6): 702-706.
|
| [14] |
LIANG Yiqing, XU Huiling, CAO Songmei, WANG Jingjing, FAN Yimeng, CAI Peixuan.
Development of evidence-based popular works of oral health management for older adults in the community
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(5): 568-574.
|
| [15] |
DU Lixia, ZHANG Yan, ZANG Shuting, HAN Xu, REN Ying.
The construction of critical nursing training program for new nurses based on case base
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(4): 457-461.
|