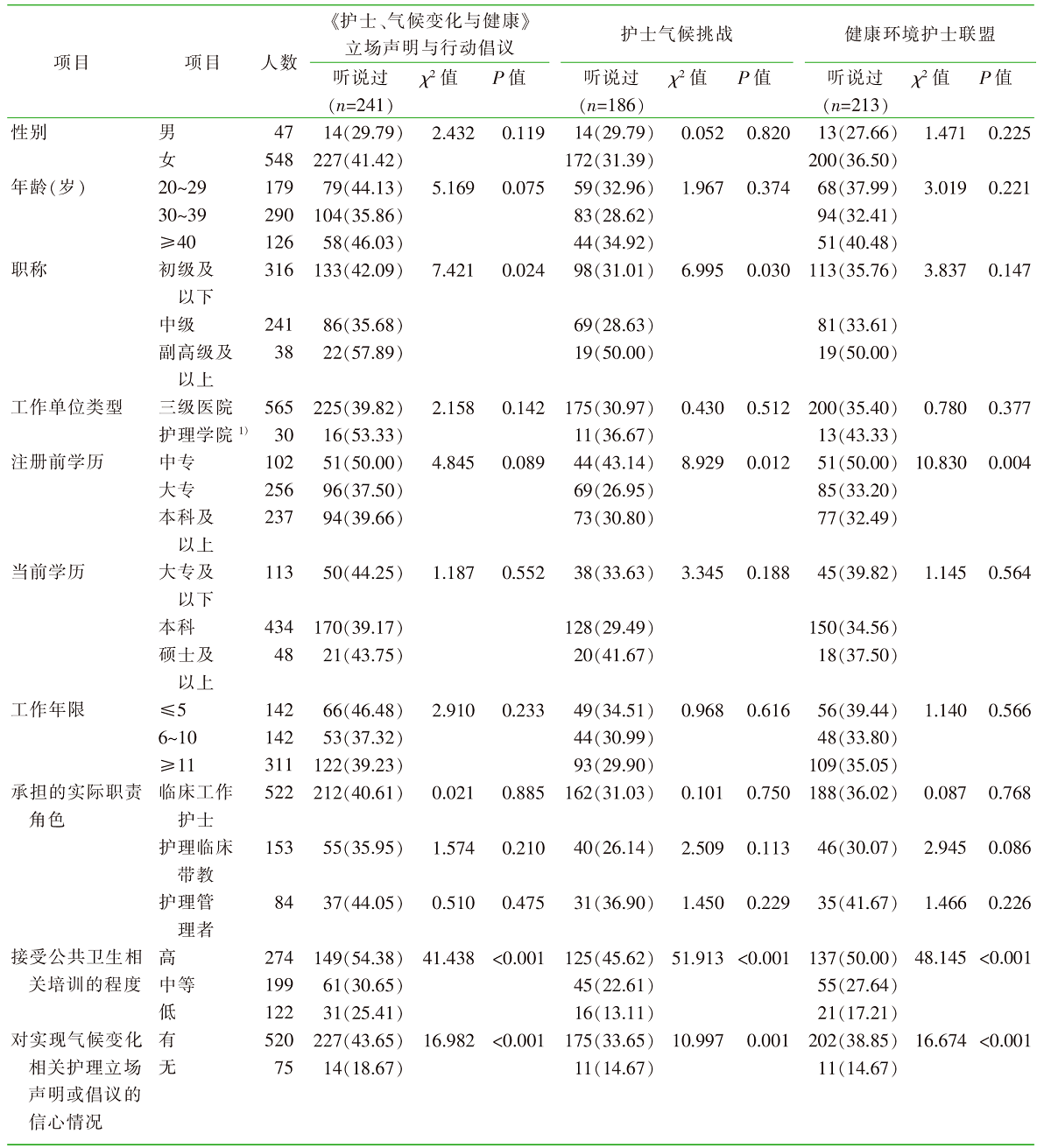
| [1] |
Watts N, Neil Adger W, Agnolucci P, et al. Health and climate change:policy responses to protect public health[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10006):1861-1914.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6
pmid: 26111439
|
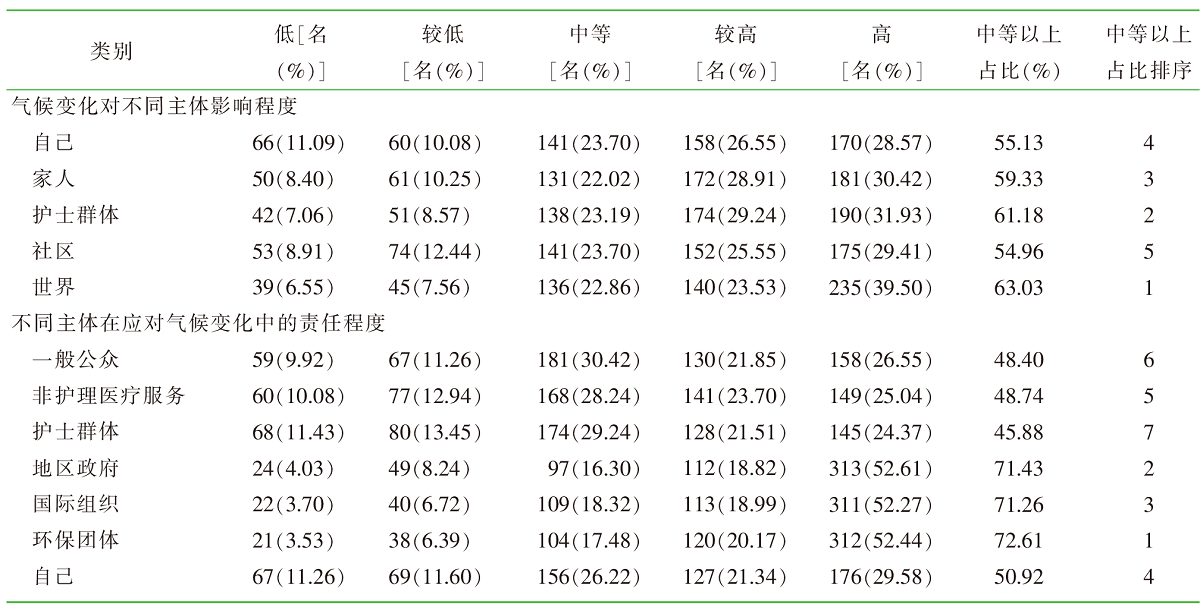
| [2] |
Romanello M, Di Napoli C, Drummond P, et al. The 2022 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change:health at the mercy of fossil fuels[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10363):1619-1654.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01540-9
pmid: 36306815
|
| [3] |
Squires E. Effects of climate change on patients with respira-tory and cardiovascular conditions[J]. Nurs Stand, 2023, 38(7):57-61.
|
| [4] |
刘勇, 张雅宁. 极端高温天气与我国政府卫生支出的相关性研究[J]. 医学与社会, 2023, 36(7):52-56.
|
| [5] |
World Health Organization. State of the world’s nursing 2020:investing in education,jobs and leadership[EB/OL].(2020-04-06)[2024-10-05]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/97892-40003279.
|
| [6] |
Butterfield P, Leffers J, Vásquez MD. Nursing’s pivotal role in global climate action[J]. BMJ, 2021:n1049.
|
| [7] |
Catton H. Nursing our planet[J]. Int Nurs Rev, 2023, 70(1):7-9.
doi: 10.1111/inr.12825
pmid: 36649537
|
| [8] |
New report calls for global action plan to address nursing workforce crisis and prevent an avoidable healthcare disaster[EB/OL].(2022-11-24)[2024-10-05]. https://www.icn.ch/news/new-report-calls-global-action-plan-address-nursing-workforce-cri-sis-and-prevent-avoidable.
|
| [9] |
ICN. International Council of Nurses. International Council of Nurses calls for increased nursing leadership to combat effects of climate change on health[EB/OL].(2018-09-27)[2024-10-05]. https://www.icn.ch/news/international-council-nurses-calls-increa-sed-nursing-leadership-combat-effects-climate-change.
|
| [10] |
İlaslan N, Şahin Orak N. Sustainability attitudes in nursing sur-vey:a cross-cultural adaptation and validation study[J]. J Human Sci, 2023, 20(3):212-222.
|
| [11] |
Fertelli TK. Awareness,worry,and hope regarding climate change among nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. Arch Environ Occup Health, 2023, 78(7/8):413-422.
|
| [12] |
Diallo T, Bérubé A, Roberge M, et al. Nurses’ perceptions of climate change:protocol for a scoping review[J]. JMIR Res Protoc, 2023, 12:e42516.
|
| [13] |
李进. 气候变化未来将如何影响中国?[J]. 生态经济, 2024, 40(9):9-12.
|
| [14] |
生态环境部, 发展改革委, 科技部, 等. 关于印发《国家适应气候变化战略2035》的通知[A].(2022-05-10). https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-06/14/content_5695555.htm.
|
| [15] |
新华社. 中国应对气候变化的政策与行动[EB/OL]. (2021-10-27)[2024-10-04]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-10/27/con-tent_5646697.htm.
|
| [16] |
李本, 蒋倩玉, 周琳琳, 等. 国内外护士、护生对气候变化认知态度及应对策略的研究进展[J]. 全科护理, 2023, 21(35):4927-4930.
|
| [17] |
Cochran W. Sampling techniques[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley,1963.
|
| [18] |
Chau PH, Yu TLT, Hu Y, et al. Preparedness of nurses for climate change:questionnaire development and preliminary validation[J]. Int J Nurs Stud Adv, 2025, 8:100337.
|
| [19] |
赵丽. 社会统计中多选排序题的统计处理方法探讨[J]. 统计与决策, 2014, 30(21):71-73.
|
| [20] |
Iira T, Ruth ML, Hannele T, et al. Finnish nurses’ perceptions of the health impacts of climate change and their preparation to address those impacts[J]. Nurs Forum, 2021, 56(2):365-371.
|
| [21] |
Tiitta I, Cubelo F, McDermott-Levy R, et al. Climate change integration in nursing education:a scoping review[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2024, 139:106210.
|
| [22] |
World Health Organization. Experts warn of serious health impacts from climate change for pregnant women,children,and older people[EB/OL].[2024-08-24]. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-06-2024-experts-warn-of-serious-health-impacts-from-cli-mate-change-for-pregnant-women--children--and-older-people.
|
| [23] |
Nicholas PK, Breakey S. Climate change,climate justice,and environmental health:implications for the nursing profession[J]. J Nurs Scholarsh, 2017, 49(6):606-616.
|
| [24] |
Evans-Agnew R, LeClair J, Sheppard DA. Just-relations and responsibility for planetary health:the global nurse agenda for climate justice[J]. Nurs Inq, 2024, 31(1):e12563.
|
| [25] |
Leap SR, Soled DR, Sampath V, et al. Effects of extreme weather on health in underserved communities[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2024, 133(1):20-27.
|
| [26] |
Anåker A, Nilsson M, Holmner Å, et al. Nurses’ perceptions of climate and environmental issues:a qualitative study[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2015, 71(8):1883-1891.
doi: 10.1111/jan.12655
pmid: 25810044
|
| [27] |
Kalogirou MR, Dahlke S, Davidson S, et al. Nurses’ perspec-tives on climate change,health and nursing practice[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2020, 29(23/24):4759-4768.
|