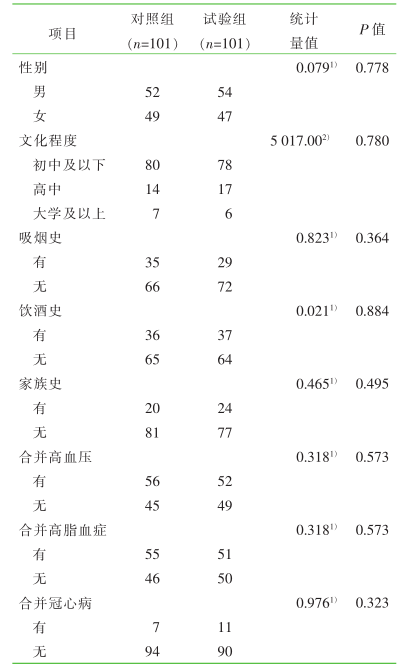
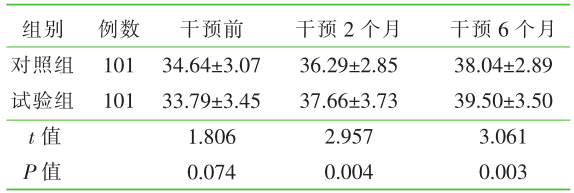
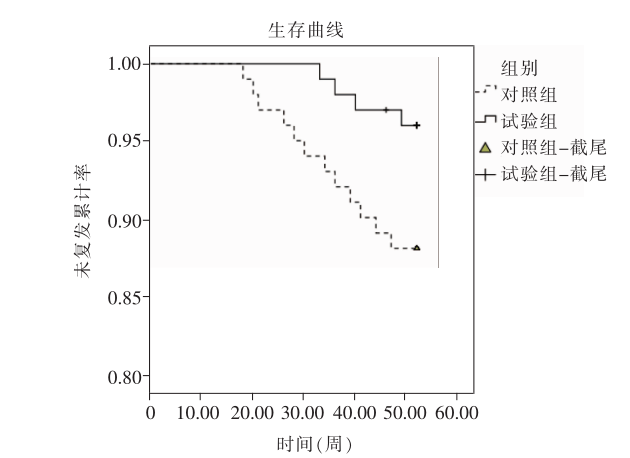
| [1] |
GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke Collaborators, Feigin VL, Nguyen G, et al. Global,regional,and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke,1990 and 2016[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(25):2429-2437.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804492
|
| [2] |
刘福兰, 欧阳松生. 康复护理对脑卒中偏瘫患者运动功能恢复的影响[J]. 养生保健指南, 2017(10):127.
|
|
Liu FL, Ouyang SS. The effect of rehabilitation nursing on the recovery of motor function in stroke patients with hemiplegia[J]. Health Guide, 2017(10):127.
|
| [3] |
王春昕, 赵颖, 李容杭, 等. 健康赋权理论在老年股骨骨折患者术后康复管理中的应用[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2018, 24(10):1199-1203.
|
|
Wang CX, Zhao Y, Li RH, et al. Application of health empowerment theory in postoperative rehabilitation management of elderly patients with femoral fracture[J]. Chin Mod Nurs, 2018, 24(10):1199-1203.
|
| [4] |
杜雅芳. 健康赋权在老年缺血性脑卒中患者中的应用研究[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2018.
|
|
Du YF. Study on the application of health empowerment in elderly patients with ischemic stroke[D]. Kaifeng:Henan Univer-sity, 2018.
|
| [5] |
吴春薇, 王得新. 疲劳严重度量表中译本应用于脑梗死患者的临床与评价[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2007, 29(9):608-611.
|
|
Wu CW, Wang DX. Clinical application and assessment of the Chinese version of Fatigue Severity Scale in stroke patients[J]. Chin J Phys Med Rehabilitation, 2007, 29(9):608-611.
|
| [6] |
杨阳, 曾铁英. 健康赋权理论在老年护理中的启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2016, 51(6):737-741.
|
|
Yang Y, Zeng TY. Enlightenment of health empowerment nursing intervention in elderly nursing[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2016, 51(6):737-741.
|
| [7] |
张秀波. 脑卒中患者赋能护理评价量表的编制及应用[D]. 太原:山西医科大学, 2014.
|
|
Zhang XB. Developing and application on Empowerment Care Evaluation Scale of stroke patients[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi Medical University, 2014.
|
| [8] |
崔慧敏, 夏征, 邢凤梅, 等. 急性缺血性脑卒中患者急性期疲劳现状及其影响因素[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2020, 37(11):9-12,25.
|
|
Cui HM, Xia Z, Xing FM, et al. Fatigue status and its influencing factors among patients in the acute stage of acute ischemic stroke[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2020, 37(11):9-12,25.
|
| [9] |
杨阳, 曾铁英. 老年慢性病病人健康赋权水平及其影响因素[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(2):214-218.
|
|
Yang Y, Zeng TY. Health empowerment level of elderly patients with chronic diseases and its influencing factors[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2019, 33(2):214-218.
|
| [10] |
李力, 王惠娟, 苗江永, 等. 卒中后疲劳:新出现的证据与管理方法[J]. 国际脑血管病杂志, 2017, 25(10):865-876.
|
|
Li Li, Wang HJ, Miao JY, et al. Poststroke fatigue:emerging evidence and approaches to management[J]. International Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2017, 25(10):865-876.
|
| [11] |
刘晓玲, 窦娜, 李丹, 等. 脑卒中患者精神疲劳的影响因素分析[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2018, 27(11):1006-1010.
|
|
Liu X, Dou N, Li D, et al. Influencing factors of mental fatigue in patients with stroke[J]. Chin J Behav Med & Brain Sci, 2018, 27(11):1006-1010.
|
| [12] |
岳萌, 雷梦杰, 刘文艳. 卒中后抑郁与卒中后疲劳相关性的Meta分析[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(2):227-231.
|
|
Yue M, Lei MJ, Liu WY. Correlation between post-stroke depression and post-stroke fatigue:a Meta-analysis[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34(2):227-231.
|
| [13] |
王小丽, 许小明, 刘宁, 等. 卒中后疲劳危险因素的系统评价[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2020, 15(7):759-765.
|
|
Wang XL, Xu XM, Liu N, et al. Risk factors of post-stroke fatigue:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Stroke, 2020, 15(7):759-765.
|