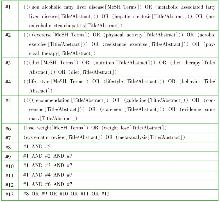
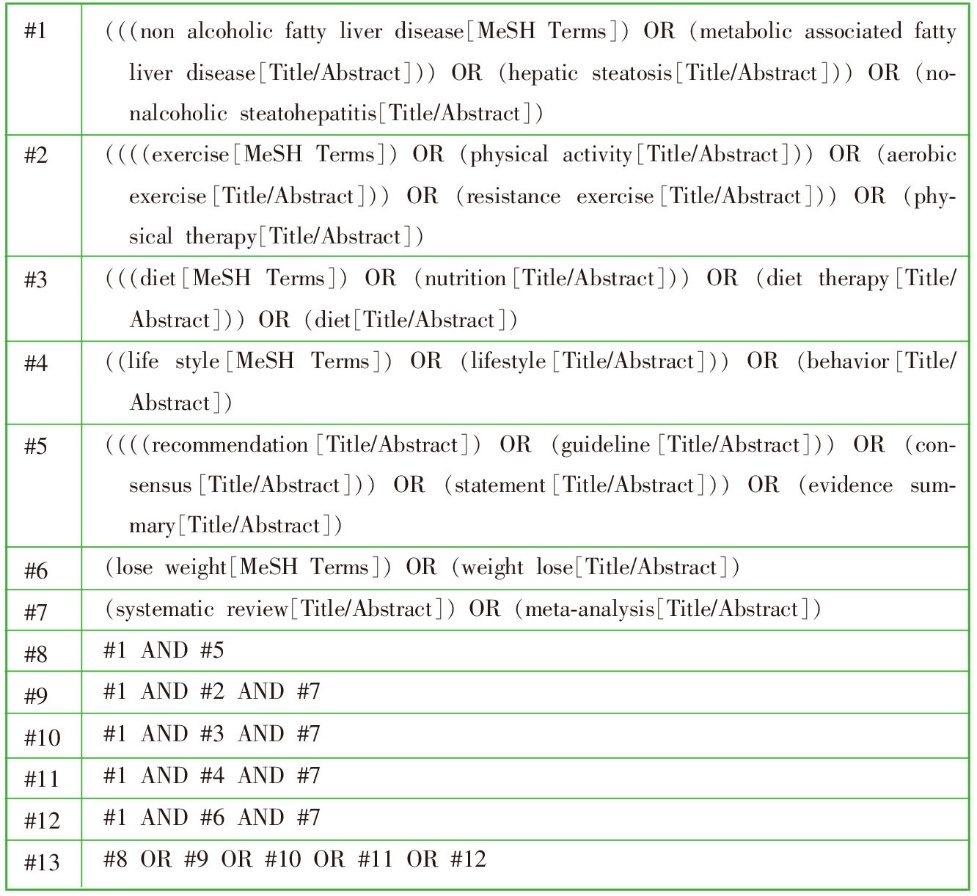
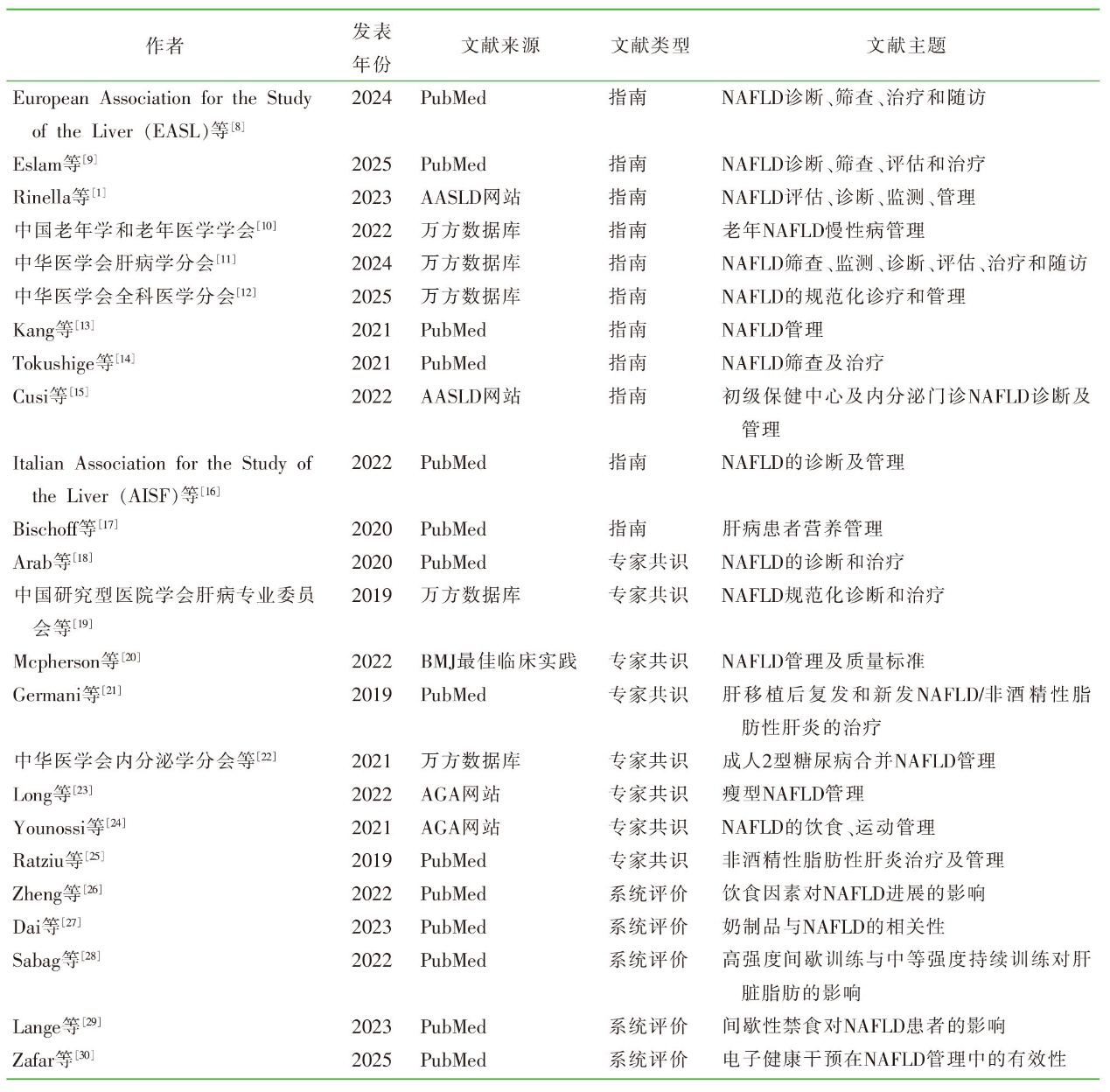
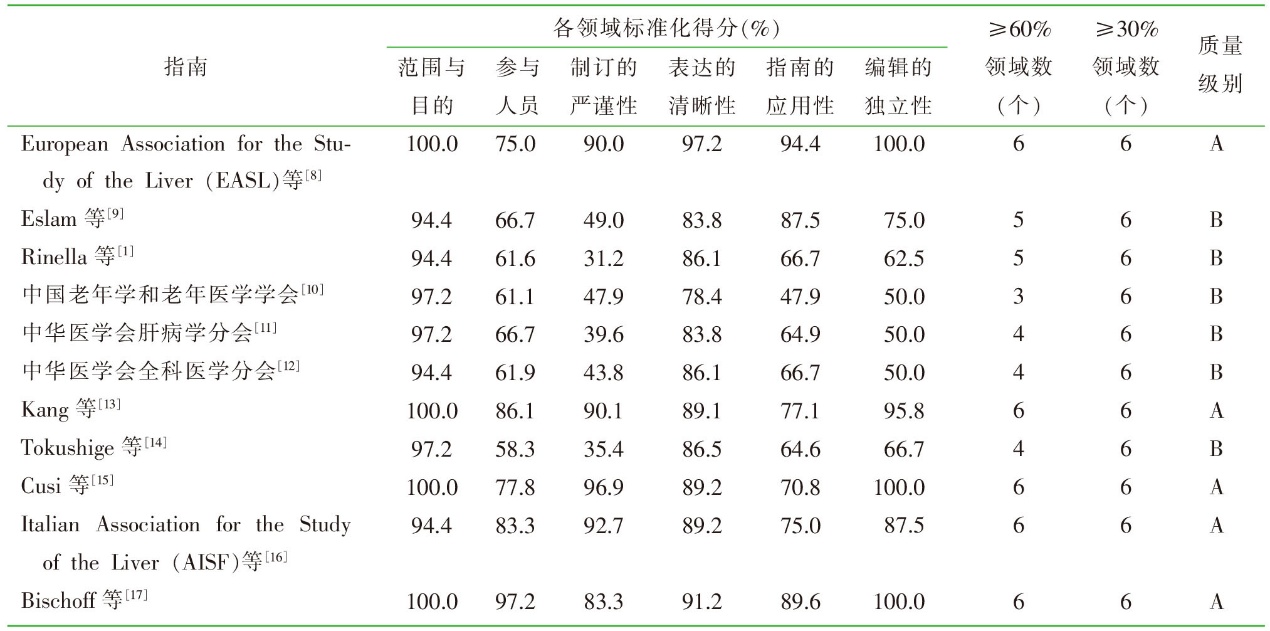
| [1] |
Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, et al. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(5):1797-1835.
doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000323
pmid: 36727674
|
| [2] |
Lee HW, Wong VW. Changing NAFLD epidemiology in China[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4):1095-1098.
doi: 10.1002/hep.30848
pmid: 31298746
|
| [3] |
Wong VW, Ekstedt M, Wong GL, et al. Changing epidemiology,global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(3):842-852.
|
| [4] |
Avery L, Exley C, McPherson S, et al. Lifestyle behavior change in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:a qualitative study of clinical practice[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15(12):1968-1971.
|
| [5] |
周芬, 郝玉芳, 丛雪, 等. 指南研究与评价工具AGREE Ⅱ及各领域分值的补充解释及思考[J]. 护理学报, 2018, 25(18):56-58.
|
| [6] |
周英凤, 顾莺, 胡雁, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具——干预性研究的质量评价(一)[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(1):24-26.
|
| [7] |
顾莺, 张慧文, 周英凤, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具:系统评价的方法学质量评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018, 33(8):701-703.
|
| [8] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver(EASL),European Association for the Study of Diabetes(EASD), Eu-ropean Association for the Study of Obesity(EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease(MASLD)[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 81(3):492-542.
|
| [9] |
Eslam M, Fan JG, Yu ML, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2025, 19(2):261-301.
|
| [10] |
中国老年学和老年医学学会. 老年非酒精性脂肪性肝病慢病管理指南[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2022, 32(8):769-772.
|
| [11] |
中华医学会肝病学分会. 代谢相关(非酒精性)脂肪性肝病防治指南(2024年版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2024, 32(5):418-434.
|
| [12] |
中国医药生物技术协会慢病管理分会, 中国研究型医院学会肝病(中西医结合)专业委员会, 中华医学会全科医学分会, 等. 代谢相关脂肪性肝病基层诊疗与管理指南(2025年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2025, 24(5):513-525.
|
| [13] |
Kang SH, Lee HW, Yoo JJ, et al. KASL clinical practice gui-delines:management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2021, 27(3):363-401.
|
| [14] |
Tokushige K, Ikejima K, Ono M, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nona-lcoholic steatohepatitis 2020[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56(11):951-963.
|
| [15] |
Cusi K, Isaacs S, Barb D, et al. American Association of Clini-cal Endocrinology clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical settings:co-sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases(AASLD)[J]. Endocr Pract, 2022, 28(5):528-562.
|
| [16] |
Italian Association for the Study of the Liver(AISF),the Italian Society of Diabetology(SID),the Italian Society of Obe-sity(SIO). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults 2021:a clinical practice guideline of the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver(AISF),the Italian Society of Diabetology(SID) and the Italian Society of Obesity(SIO)[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2022, 54(2):170-182.
|
| [17] |
Bischoff SC, Bernal W, Dasarathy S, et al. ESPEN practical guideline:clinical nutrition in liver disease[J]. Clin Nutr, 2020, 39(12):3533-3562.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.09.001
pmid: 33213977
|
| [18] |
Arab JP, Dirchwolf M, álvares-da-Silva MR, et al. Latin American Association for the Study of the Liver(ALEH) practice guida-nce for the diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2020, 19(6):674-690.
|
| [19] |
中国研究型医院学会肝病专业委员会, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝与酒精性肝病学组, 等. 中国脂肪性肝病诊疗规范化的专家建议(2019年修订版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(10):748-753.
|
| [20] |
McPherson S, Armstrong MJ, Cobbold JF, et al. Quality stan-dards for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD):consensus recommendations from the British Asso-ciation for the Study of the Liver and British Society of Gastroenterology NAFLD Special Interest Group[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7(8):755-769.
|
| [21] |
Germani G, Laryea M, Rubbia-Brandt L, et al. Management of recurrent and de novo NAFLD/NASH after liver transplanta-tion[J]. Transplantation, 2019, 103(1):57-67.
|
| [22] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会, 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国成人2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病管理专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 37(7):589-598.
|
| [23] |
Long MT, Noureddin M, Lim JK. AGA clinical practice upda-te:diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals:expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 163(3):764-774.e1.
|
| [24] |
Younossi ZM, Corey KE, Lim JK. AGA clinical practice update on lifestyle modification using diet and exercise to achieve weight loss in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3):912-918.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.051
pmid: 33307021
|
| [25] |
Ratziu V, Ghabril M, Romero-Gomez M, et al. Recommenda-tions for management and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohe-patitis[J]. Transplantation, 2019, 103(1):28-38.
doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002483
pmid: 30300289
|
| [26] |
Zheng JL, Zhao LG, Dong JW, et al. The role of dietary factors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma progression:a systematic review[J]. Clin Nutr, 2022, 41(10):2295-2307.
|
| [27] |
Dai W, Liu HY, Zhang TJ, et al. Dairy product consumption was associated with a lower likelihood of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Nutr, 2023,10:1119118.
|
| [28] |
Sabag A, Barr L, Armour M, et al. The effect of high-intensity interval training vs moderate-intensity continuous training on liver fat:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2022, 107(3):862-881.
|
| [29] |
Lange M, Nadkarni D, Martin L, et al. Intermittent fasting im-proves hepatic end points in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2023, 7(8):e0212.
|
| [30] |
Zafar Y, Sohail MU, Saad M, et al. eHealth interventions and patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMJ Open Gastroenterol, 2025, 12(1):e001670.
|
| [31] |
Younossi Z, Aggarwal P, Shrestha I, et al. The burden of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis:a systematic review of health-related quality of life and patient-reported outcomes[J]. JHEP Rep, 2022, 4(9):100525.
|
| [32] |
Stewart KE, Haller DL, Sargeant C, et al. Readiness for beha-viour change in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:implications for multidisciplinary care models[J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35(3):936-943.
doi: 10.1111/liv.12483
pmid: 24521540
|
| [33] |
Kotronoulas G, Papadopoulou C, Simpson MF, et al. Using pa-tient-reported outcome measures to deliver enhanced suppor-tive care to people with lung cancer:feasibility and accepta-bility of a nurse-led consultation model[J]. Support Care Can-cer, 2018, 26(11):3729-3737.
|
| [34] |
Andersen T, Gluud C, Franzmann MB, et al. Hepatic effects of dietary weight loss in morbidly obese subjects[J]. J Hepatol, 1991, 12(2):224-229.
pmid: 2051001
|
| [35] |
Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, et al. Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces fea-tures of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 149(2):367-378.e5;quize14-5.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005
pmid: 25865049
|
| [36] |
邵洁. 基于自我效能理论的护理干预对超重/肥胖不孕患者体质量管理的效果研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021.
|
| [37] |
Young S, Tariq R, Provenza J, et al. Prevalence and profile of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean adults:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2020, 4(7):953-972.
|
| [38] |
Fernández-Mincone T, Contreras-Briceño F, Espinosa-Ramírez M, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia:patho-physiological connections and therapeutic implications[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 14(12):1141-1157.
|
| [39] |
Matsuoka L, Chotai PN, Slaughter J, et al. A single-center study of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohe-patitis recurrence in recipients of liver transplant for treat-ment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis[J]. Exp Clin Transplant, 2022, 20(2):150-156.
doi: 10.6002/ect.2021.0343
pmid: 35037605
|
| [40] |
Losurdo G, Castellaneta A, Rendina M, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis:de novo non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in liver-transplanted patients[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 47(6):704-714.
|
| [41] |
Richards J, Gunson B, Johnson J, et al. Weight gain and obe-sity after liver transplantation[J]. Transpl Int, 2005, 18(4):461-466.
doi: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2004.00067.x
pmid: 15773968
|
| [42] |
Yaskolka Meir A, Rinott E, Tsaban G, et al. Effect of green-Mediterranean diet on intrahepatic fat:the DIRECT PLUS randomised controlled trial[J]. Gut, 2021, 70(11):2085-2095.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323106
pmid: 33461965
|
| [43] |
Ivancovsky-Wajcman D, Zelber-Sagi S, Fliss Isakov N, et al. Serum soluble receptor for AGE(sRAGE) levels are associa-ted with unhealthy lifestyle and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2019, 10(5):1-10.
|
| [44] |
Ryu S, Chang Y, Jung HS, et al. Relationship of sitting time and physical activity with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(5):1229-1237.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.010
pmid: 26385766
|
| [45] |
Hashida R, Kawaguchi T, Bekki M, et al. Aerobic vs. resista-nce exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:a systematic review[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(1):142-152.
doi: S0168-8278(16)30488-3
pmid: 27639843
|
| [46] |
Younossi ZM, Zelber-Sagi S, Henry L, et al. Lifestyle interven-tions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(11):708-722.
doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00800-4
pmid: 37402873
|