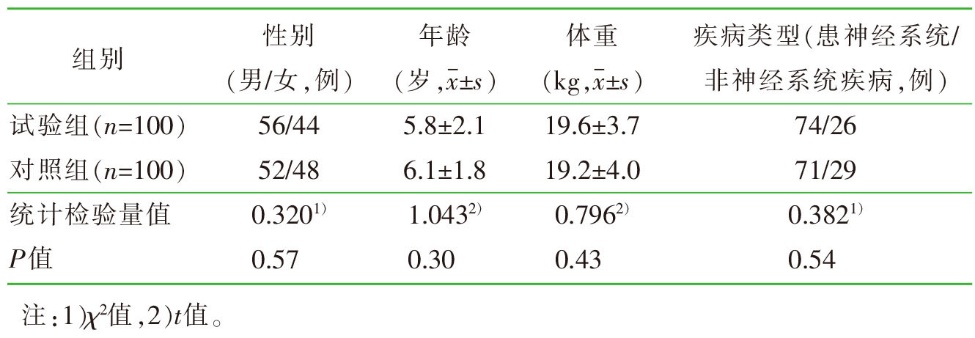
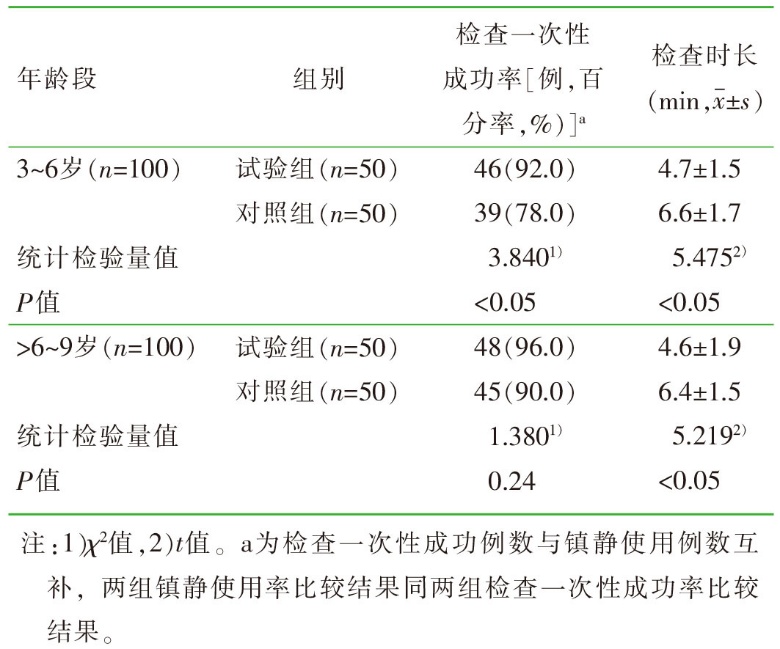
| [1] |
Tyc VL, Fairclough D, Fletcher B, et al. Children’s distress dur-ing magnetic resonance imaging procedures[J]. Child Health Care, 1995, 24(1):5-19.
pmid: 10142086
|
| [2] |
卞勇, 姚莹, 王丹, 等. 水合氯醛口服复合右美托咪定滴鼻用于小儿核磁共振检查镇静的疗效及安全性评估[J]. 国际麻醉学与复苏杂志, 2015, 36(12):1080-1085.
|
|
Bian Y, Yao Y, Wang D, et al. The evaluation of the efficacy and safety of sedation of oral chloral hydrate combination with intranasal dexmedetomidine for magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric patients[J]. Int J Anesthesiol Resusc, 2015, 36(12):1080-1085.
|
| [3] |
Malviya S, Voepel-Lewis T, Prochaska G, et al. Prolonged recove-ry and delayed side effects of sedation for diagnostic imaging studies in children[J]. Pediatrics, 2000, 105(3):E42.
|
| [4] |
Vanderby SA, Babyn PS, Carter MW, et al. Effect of anesthesia and sedation on pediatric MR imaging patient flow[J]. Radiolo-gy, 2010, 256(1):229-237.
|
| [5] |
Jaimes C, Gee MS. Strategies to minimize sedation in pediatric body magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Pediatr Radiol, 2016, 46(6):916-927.
doi: 10.1007/s00247-016-3613-z
pmid: 27229508
|
| [6] |
Stunden C, Stratton K, Zakani S, et al. Comparing a virtual rea-lity-based simulation App(VR-MRI) with a standard preparato-ry manual and child life program for improving success and reducing anxiety during pediatric medical imaging:randomized clinical trial[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2021, 23(9):e22942.
|
| [7] |
Bharti B, Malhi P, Khandelwal N. MRI customized play therapy in children reduces the need for sedation-a randomized con-trolled trial[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2016, 83(3):209-213.
|
| [8] |
Törnqvist E, Månsson Å, Hallström I. Children having magnetic resonance imaging:a preparatory storybook and audio/visual media are preferable to anesthesia or deep sedation[J]. J Child Health Care, 2015, 19(3):359-369.
doi: 10.1177/1367493513518374
pmid: 24486815
|
| [9] |
吴小花, 周莲娟, 俞君, 等. 学龄前儿童磁共振成像检查前心理准备游戏的设计与实践[J]. 中华护理教育, 2023, 20(3):338-342.
|
|
Wu XH, Zhou LJ, Yu J, et al. Design and application of psy-chological preparation play for pre-magnetic resonance imaging examination in preschool children[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2023, 20(3):338-342.
|
| [10] |
吴肖玲, 陈添峰, 吴伟立. 童趣扮演互动式护理对核磁共振患儿检查结果的影响[J]. 中外医学研究, 2023, 21(32):84-88.
|
|
Wu XL, Chen TF, Wu WL. Effect of childlike play interactive nursing on examination results in children with magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Chin Foreign Med Res, 2023, 21(32):84-88.
doi: 10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2023.32.022
|
| [11] |
陶冠澎. 3-6岁幼儿抑制控制与心理理论的发展特点及其相关研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2023.
|
|
Tao GP. Developmental characteristics of inhibitory control and theory of mind in 3- to 6-year-old children and their correlates[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2023.
|
| [12] |
Runge SB, Christensen NL, Jensen K, et al. Children centered care:minimizing the need for anesthesia with a multi-faceted concept for MRI in children aged 4-6[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2018, 107:183-187.
|
| [13] |
Copeland A, Silver E, Korja R, et al. Infant and child MRI:a review of scanning procedures[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021,15:666020.
|
| [14] |
李华玲, 张佳璇, 覃蕾, 等. AI辅助压缩感知技术联合动画音频播放在学龄前儿童头部核磁共振检查中的应用[J]. 神经损伤与功能重建, 2023, 18(12):735-737,820.
|
|
Li HL, Zhang JX, Qin L, et al. AI-assisted compressed sensing technology combined with animation audio playback in head magnetic resonance examination of preschool children[J]. Neural Inj Funct Reconstr, 2023, 18(12):735-737,820.
|
| [15] |
Geuens S, Lemiere J, Nijs J, et al. Testing a home solution for preparing young children for an awake MRI:a promising smartphone application[J]. Children, 2023, 10(12):1866.
|
| [16] |
Dean DC, Dirks H, O’Muircheartaigh J, et al. Pediatric neuroi-maging using magnetic resonance imaging during non-sedated sleep[J]. Pediatr Radiol, 2014, 44(1):64-72.
|