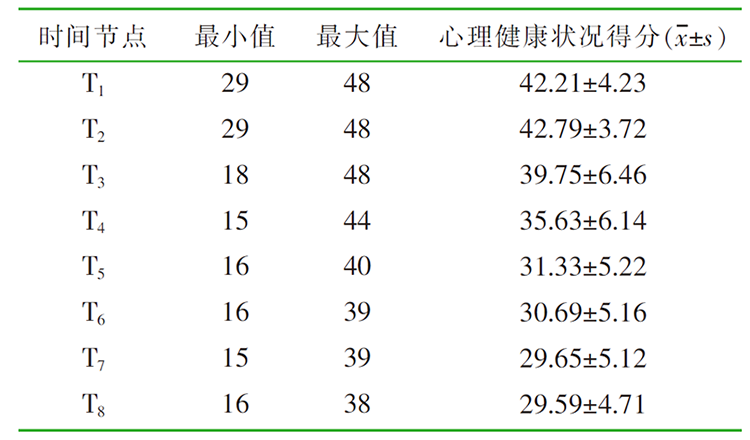
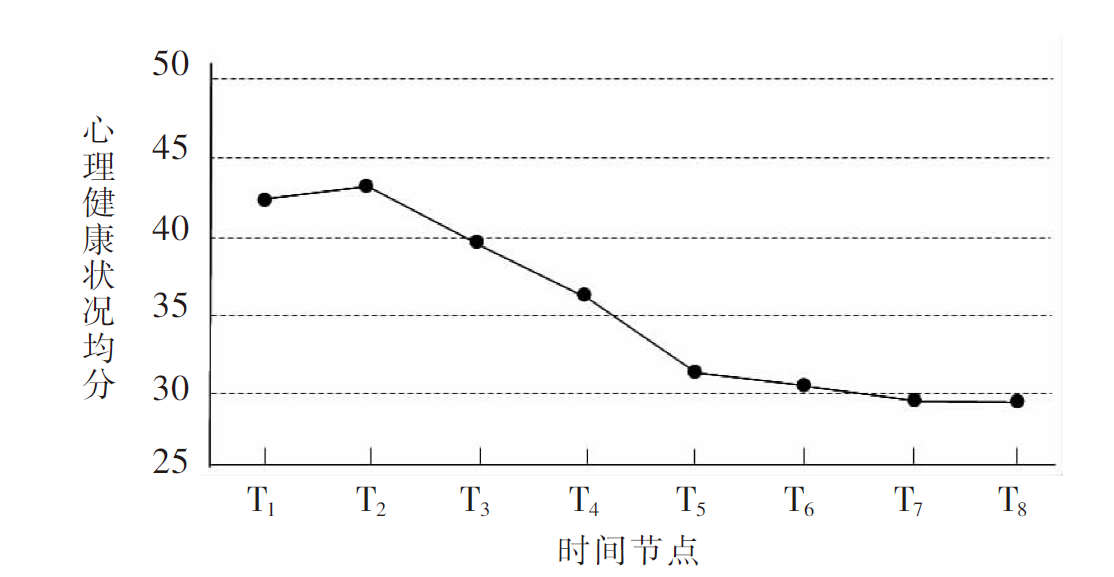
| [1] |
Wang LM, Xu X, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China:results from the sixth China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2023, 183(4):298-310.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6817
|
| [2] |
中国工程院医药卫生学部肾脏病前沿论坛[R]. 大连: 中国医师协会肾脏内科医师分会, 2022.
|
| [3] |
2018亚太地区肾脏病学术会议暨中华医学会肾脏病学分会2018年学术年会[R]. 北京: 中华医学会、中华医学会肾脏病学分会, 2018.
|
| [4] |
何丽芳, 李倩倩, 甘香. 病耻感对中青年维持性血液透析患者心理痛苦的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(21):2585-2591.
|
|
He LF, Li QQ, Gan X. Influence of stigma on psychological distress among young and middle-aged maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(21):2585-2591.
|
| [5] |
许晓娜, 江莎, 谢雪英,等. 血液透析患者心理痛苦与自我管理行为及希望水平的相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2021, 36(10):931-935.
|
| [6] |
文雯. 维持性血液透析患者生活质量及影响因素分析[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2015.
|
|
Wen W. Analysis of quality of life and its influencing factors in maintenance hemodialysis patients[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2015.
|
| [7] |
Stanković Z, Jasović-Gasić M, Lecić-Tosevski D. Psychological problems in patients with type 2 diabetes:clinical considerations[J]. Vojnosanit Pregl, 2013, 70(12):1138-1144.
pmid: 24450259
|
| [8] |
上海慢性肾脏病早发现及规范化诊治与示范项目专家组,高翔,梅长林. 慢性肾脏病筛查诊断及防治指南[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2017, 37(1):28-34.
doi: 10.19538/j.nk2017010108
|
| [9] |
Kessler RC, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, et al. The global burden of mental disorders:an update from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) surveys[J]. Epidemiol Psichiatr Soc, 2009, 18(1):23-33.
doi: 10.1017/s1121189x00001421
pmid: 19378696
|
| [10] |
徐凌忠, 王建新, 孙辉,等. Kessler 10在我国的首次应用研究及其重要意义[J]. 卫生软科学, 2005, 19(6):410-412,421.
|
| [11] |
周成超, 楚洁, 王婷,等. 简易心理状况评定量表Kessler 10中文版的信度和效度评价[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2008, 16(6):627-629.
|
| [12] |
Santini ZI, Jose PE, York CE, et al. Social disconnectedness,perceived isolation,and symptoms of depression and anxiety among older Americans(NSHAP):a longitudinal mediation analysis[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2020, 5(1):e62-e70.
|
| [13] |
Levy J. 牛津临床透析手册[M]. 2版. 王梅译. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006.
|
| [14] |
Hiramatsu T, Okumura S, Asano Y, et al. Quality of life and emotional distress in peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis patients[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2020, 24(4):366-372.
doi: 10.1111/tap.v24.4
|
| [15] |
Riba MB, Donovan KA, Andersen B, et al. Distress management,version 3. 2019,NCCN clinical practice guidelines in on-cology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2019, 17(10):1229-1249.
doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0048
|
| [16] |
李雪, 孙晓晶. 自我管理行为对维持性血液透析患者自我感受负担的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2016, 51(5):562-566.
|
|
Li X, Sun XJ. A study on the relationship between self-perceived burden and self-management behavior among maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2016, 51(5):562-566.
|
| [17] |
陈可人, 李洁, 周敏,等. 家庭亲密度、适应性与产前抑郁的关系:基本心理需要满足的中介作用[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2022, 28(2):186-190.
|
|
Chen KR, Li J, Zhou M, et al. Relationship between family cohesion,adaptability and prenatal depression:the mediating role of basic psychology needs satisfaction[J]. J Tianjin Med Univ, 2022, 28(2):186-190.
|
| [18] |
陈啟念, 尤黎明, 张栢菱. 中国澳门地区维持性血液透析患者液体摄入依从性现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(10):1472-1477.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.10.005
|
|
Chen QN, You LM, Zhang BL. Research on the fluid intake compliance and influencing factors of patients on maintenance hemodialysis in Macao China[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(10):1472-1477.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.10.005
|