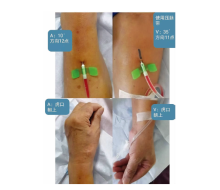
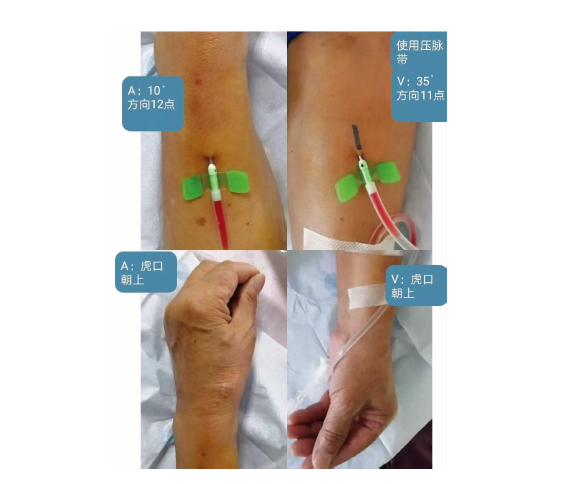
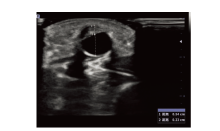
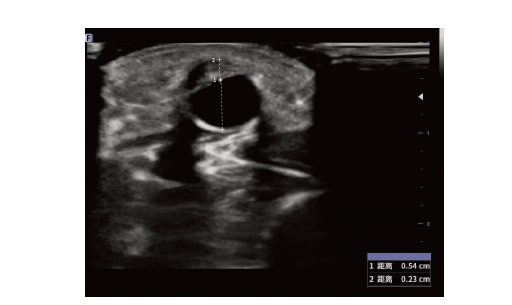
| [1] |
陈香美. 血液净化标准操作规程:2010版[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2010.
|
| [2] |
洪成波, 江瑞, 凌扣荣, 等. 疑难内瘘患者穿刺方法的改良及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(5):727-730.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2020.05.0019
|
|
Hong CB, Jiang R, Ling KR, et al. Application of zero-pressure modified puncture technique in hemodialysis patients with difficult arteriovenous fistula[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(5):727-730.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2020.05.0019
|
| [3] |
Lok CE, Huber TS, Lee T, et al. KDOQI clinical practice guide-line for vascular access:2019 update[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2020, 75(4Suppl 2): S1-S164.
|
| [4] |
吴春燕, 蒋欣欣, 王文娟, 等. 扣眼穿刺法在自体动静脉内瘘中的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2013, 48(11):1033-1035.
|
|
Wu CY, Jiang XX, Wang WJ, et al. Progress of application of buttonhole puncture in autologous arteriovenous fistula[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2013, 48(11):1033-1035.
|
| [5] |
张尧, 王霄, 杜楠楠, 等. 动静脉内瘘扣眼穿刺处内膜增生特点及停止穿刺的效果观察[J]. 中国血液净化, 2023, 22(5):396-400.
|
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Du NN, et al. Characteristics of intimal hyperplasia at the buttonhole puncture segments of arteriove-nous fistula and the effect of discontinuing the puncture[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2023, 22(5):396-400.
|
| [6] |
赵秀明, 牛洪艳, 刘金凤, 等. 血液透析行扣眼穿刺患者动静脉内瘘发生内膜增生的影响因素分析[J]. 中国血液净化, 2023, 22(9):710-714.
|
|
Zhao XM, Niu HY, Liu JF, et al. The influencing factors for the intimal hyperplasia in arteriovenous fistula in patients with buttonhole puncture for hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2023, 22(9):710-714.
|
| [7] |
董永泽, 许秀君, 沈华娟, 等. 维持性血液透析患者动静脉血管通路穿刺管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9):1135-1141.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.09.016
|
|
Dong YZ, Xu XJ, Shen HJ, et al. Summary of the best evidence for the management of arteriovenous access cannula-tion in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(9):1135-1141.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.09.016
|
| [8] |
傅丽丽, 黄龙. 智能掌上超声诊断仪在疑难动静脉内瘘穿刺中的应用[J]. 中国血液净化, 2018, 17(8):539-541.
|
|
Fu LL, Huang L. The application of intelligent handheld ultra-sound diagnostic instrument for difficult puncture of arteriove-nous arteriovenous fistula[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2018, 17(8):539-541.
|
| [9] |
吴爱纯, 张璜, 吴磊. 彩色多普勒超声引导较深动静脉新内瘘穿刺的临床应用[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2020, 36(1):36-41.
|
| [10] |
王冠群, 刘苗, 肖燕. 透析用留置针在自体动静脉内瘘扣眼穿刺建立隧道中应用[J]. 中国血液净化, 2020, 19(7):500-502.
|
|
Wang GQ, Liu M, Xiao Y. Application of indwelling needle for AVF buttonhole puncture to establish tunnel for dialysis[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2020, 19(7):500-502.
|
| [11] |
中国医院协会血液净化中心分会血管通路工作组. 中国血液透析用血管通路专家共识(第2版)[J]. 中国血液净化, 2019, 18(6):365-381.
|
|
Blood Access Working Group, Branch of Blood Purification Center Management, Chinese Hospital Association. Consensus among experts on blood access used for hemodialyis in China(The 2nd edition)[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2019, 18(6):365-381.
|
| [12] |
Vrtovsnik F, Brunet P, Chauveau P, et al. Clinical practice guideline on peri- and postoperative care of arteriovenous fistulas and grafts for haemodialysis in adults[J]. Nephrol Ther, 2020, 16(6):376-386.
doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2020.05.002
pmid: 33139227
|
| [13] |
Kukita K, Ohira S, Amano I, et al. 2011 update Japanese society for dialysis therapy guidelines of vascular access con-struction and repair for chronic hemodialysis[J]. Ther Apher Dial,2015, 19(Suppl 1):1-39.
|
| [14] |
UK Kidney Association. UK Kidney Association Clinical Practice Guideline Vascular Access for Haemodialysis[EB/OL].(2023-04-12). https://ukkidney.org/sites/renal.org/files/FINAL%20FOR-MATTED%20Vascular%20access%20for%20haemodialysis%20April%202023.pdf.
|
| [15] |
Schmidli J, Widmer MK, Basile C, et al. Editor’s choice-vascular access:2018 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery(ESVS)[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg,2018, 55(6):757-818.
|
| [16] |
Cheng YL, Tang HL, Tong MKL. Clinical practice guidelines for the provision of renal service in Hong Kong:Haemo-dialysis[J]. Nephrology(Carlton), 2019, 24(Suppl 1):41-59.
|
| [17] |
Wasse H, Alvarez AC, Brouwer-Maier D, et al. Patient selection,education,and cannulation of percutaneous arteriovenous fistulae:an ASDIN white paper[J]. J Vasc Access, 2020, 21(6):810-817.
|
| [18] |
Allon M, Berns JS. Overview of hemodialysis arteriovenous graft maintenance and thrombosis prevention[EB/OL].(2021-02-02). https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-hemodia-lysis-arteriovenous-graft-maintenance-and-thrombosis-prevention.
|
| [19] |
王慧, 孙秀丽, 吴红梅, 等. 新建立自体动静脉内瘘首次穿刺时间对内瘘预后影响的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 中国血液净化, 2018, 17(2):107-113.
|
| [20] |
Vascular Access Special Interest Group. Clinical Practice Recommendations for Needling of Arteriovenous Fistulae and Grafts for Haemodialysis[EB/OL]. (2018-09-03). https://www.vasbi.org.uk/media/resources/needling_guidelines2018.pdf.
|
| [21] |
Marticorena RM, Dacouris N, Donnelly SM. Randomized pilot study to compare metal needles versus plastic cannulae in the development of complications in hemodialysis access[J]. J Vasc Access, 2018, 19(3):272-282.
doi: 10.1177/1129729817747535
pmid: 29772982
|
| [22] |
Yin JM, Tian ZW, Li PQ, et al. A time-saving method of creating AVF buttonholes:indwelling trocar technique[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2022, 31(21/22):3102-3109.
|
| [23] |
陈荣荣, 俞燕, 范亚平. 动静脉内瘘血管内膜增生的细胞和分子病理机制[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2016, 25(5):475-478,455.
|
| [24] |
Rønning MI, Benschop WP, Øvrehus MA, et al. Direction- and angle-assisted buttonhole cannulation of arteriovenous fistula in hemodialysis patients:a multicenter randomized controlled trial[J]. Kidney Med, 2022, 4(2):100393.
|
| [25] |
Shigeki T. Relationship between years elapsed after initial buttonhole cannulation and frequency of vascular access-related infections[J]. Contrib Nephroly, 2015,186:57-63.
|