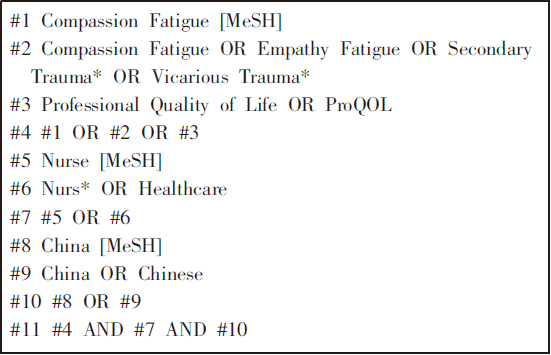
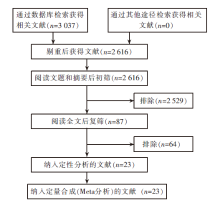
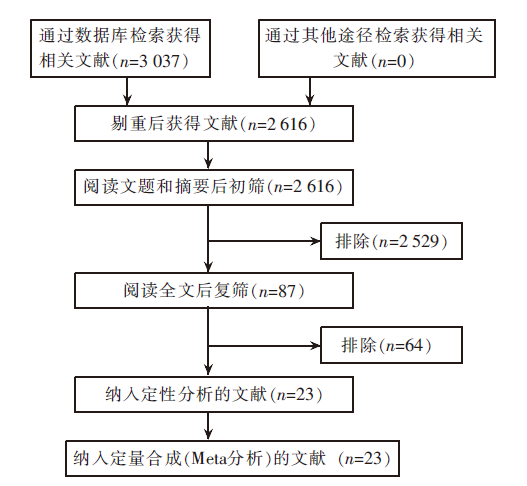
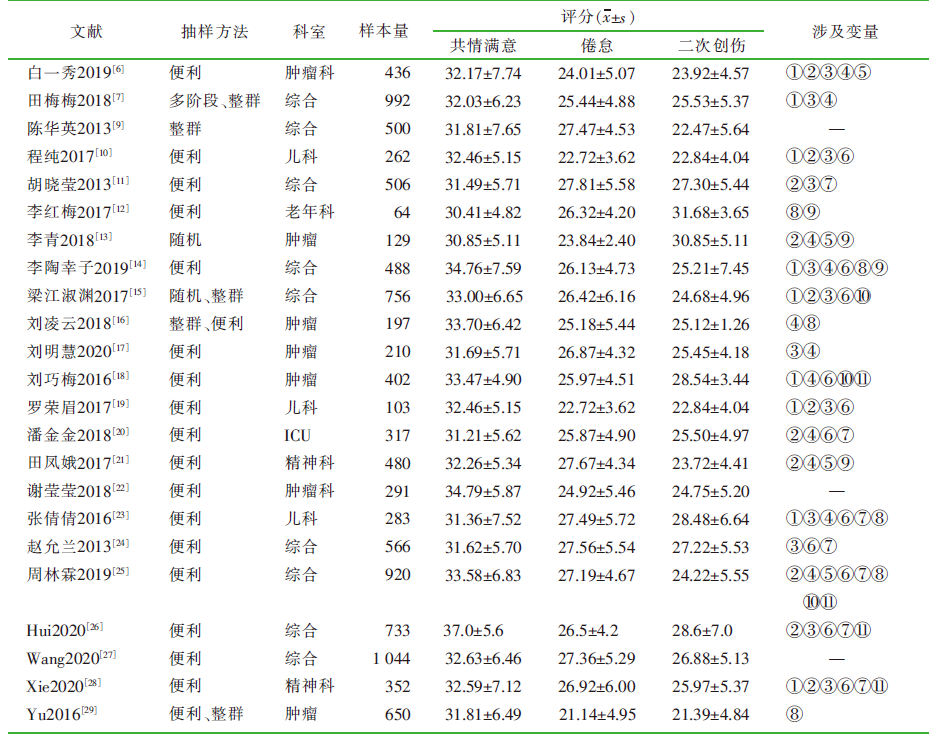
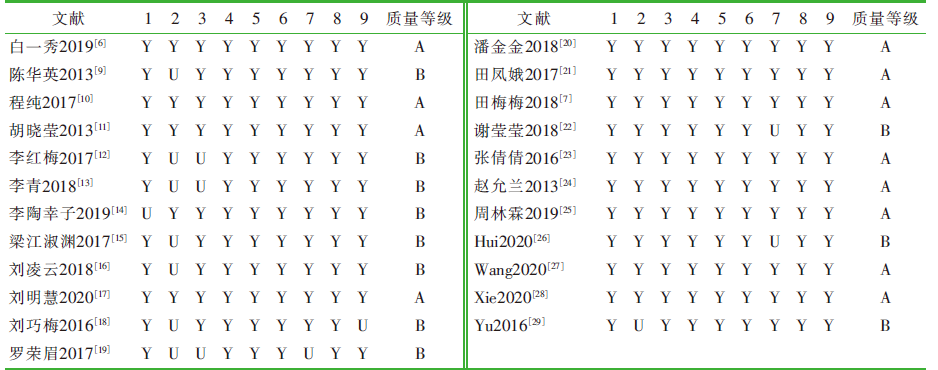
| [1] |
Stamm BH. The concise manual for the Professional Quality of Life Scale[EB/OL]. [2021-07-18]. https://proqol.org/uploads/ProQOL_Concise_2ndEd_12-2010.pdf. 2019.
|
| [2] |
Joinson C. Coping with compassion fatigue[J]. Nursing, 1992,22(4):116-118.
|
| [3] |
Figley CR. Compassion fatigue:psychotherapists’ chronic lack of self care[J]. J Clin Psychol, 2002,58(11):1433-1441.
|
| [4] |
仲卫薇, 李春玉. 护士同情心疲乏的研究进展[J]. 中华护理教育, 2015,12(12):939-943.
|
|
Zhong WW, Li CY. Research progress of nurses’ compassion fatigue[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2015,12(12):939-943.
|
| [5] |
Kelly L, Runge J, Spencer C. Predictors of compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction in acute care nurses[J]. J Nurs Scholarsh, 2015,47(6):522-528.
|
| [6] |
白一秀. 肿瘤科护士临终关怀态度与专业生活品质的相关性研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2019.
|
|
Bai YX. Study on the correlation between hospice attitude and professional quality of life of oncology nurses[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [7] |
田梅梅, 范霖, 施雁, 等. 临床护士共情疲劳的现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018,53(1):76-82.
|
|
Tian MM, Fan L, Shi Y, et al. The Current status and influencing factors of compassion fatigue in clinical nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018,53(1):76-82.
|
| [8] |
周英凤, 顾莺, 胡雁, 等. JBI循证卫生保健中心对关于不同类型研究的质量评价工具:患病率及分析性横断面研究的质量评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2018,33(3):219-221.
|
|
Zhou YF, Gu Y, Hu Y, et al. The joanna briggs institute critical appraisal tools for use in systematic review:prevalence study and analytical cross sectional study[J]. J Nurses Train, 2018,33(3):219-221.
|
| [9] |
陈华英, 王卫红. 临床护士同情疲劳现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2013,22(5):457-459.
|
| [10] |
程纯, 郭惠芳, 邱园新. 儿科护士同情心疲乏现状及其对儿科护理质量的影响[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2017,34(17):35-38.
|
|
Cheng C, Guo HF, Qiu YX. Current status of compassion fatigue of pediatric nurses and its influence on the quality of neonatal care[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2017,34(17):35-38.
|
| [11] |
胡晓莹, 赵允兰, 闵瑰. 临床护士同情心疲乏的相关因素调查[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2013,33(6):857-862.
|
|
Hu XY, Zhao YL, Min G. Survey on related factors of compassion fatigue in clinical nurses[J]. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ(Med Sci), 2013,33(6):857-862.
|
| [12] |
李红梅, 冯晓玲, 李育玲. 临终关怀病房护士共情疲劳及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017,32(18):88-90.
|
|
Li HM, Feng XL, Li YL. Compassion fatigue and associated factors in nurses working in hospice care units[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2017,32(18):88-90.
|
| [13] |
李青. 烟台市三级综合医院肿瘤科护士专业生活品质与职业认同现状研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2018.
|
|
Li Q. Study on the relationship between professional quality of life and professional identity in oncology nurses of third-grade general hospitals in Yantai city[D]. Jinan:Shandong University, 2018.
|
| [14] |
李陶幸子. 临床护士共情疲劳现状及影响因素研究[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2019.
|
|
Li TXZ. Study on the status and influencing factors of clinical nurses’ compassion fatigue[D]. Kaifeng:Henan University, 2019.
|
| [15] |
梁江淑渊. 临床护士同情心疲乏现状及与心理资本、人格特质的相关性研究[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学, 2017.
|
|
Liang JSY. The study on the status of compassion fatigue and its correlation with psychological capital and personality trait among clinical nurses[D]. Shenyang:China Medical University, 2017.
|
| [16] |
刘凌云. 肿瘤科护士替代性创伤及其影响因素研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2018.
|
|
Liu LY. Prevalence and predictors of vicarious trauma among oncology nurses:a cross-sectional survey[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2018.
|
| [17] |
刘明慧, 覃惠英. 210名肿瘤科护士专业生活品质现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学报, 2020,27(5):28-34.
|
|
Liu MH, Qin HY. Curent status of professional quality of life among oncology nurses and its influence factors:a 210-case study[J]. J Nurs (China), 2020,27(5):28-34.
|
| [18] |
刘巧梅, 王媛媛, 谭开宇, 等. 肿瘤科护士共情疲劳现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2016,16(5):614-619,620.
|
|
Liu QM, Wang YY, Tan KY, et al. Research on compassion fatigue status and influencing factors among nurses in oncology[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2016,16(5):614-619,620.
|
| [19] |
罗荣眉, 项旦丹, 阮淑琴, 等. 护士同情心负荷与新生儿护理质量相关性分析[J]. 医院管理论坛, 2017,34(8):42-46.
|
|
Luo RM, Xiang DD, Ruan SQ, et al. Analysis of relationship between the compassion fatigue and the quality of neonatal care in pediatric nurses[J]. Hosp Manag Forum, 2017,34(8):42-46.
|
| [20] |
潘金金, 魏丽丽, 孙黎惠, 等. ICU护士专业生活品质与组织支持感的相关性研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2018,18(9):1208-1212.
|
|
Pan JJ, Wei LL, Sun LH, et al. The relationship between professional quality of life and perceived organizational support among critical care nurses[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2018,18(9):1208-1212.
|
| [21] |
田凤娥, 陈霞, 米长爱, 等. 精神病专科医院护士共情疲劳现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2017,52(6):654-658.
|
|
Tian FG, Chen X, Mi CG, et al. The status of compassion fatigue and its influencing factors among nurses in psychiatric hospitals[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2017,52(6):654-658.
|
| [22] |
谢莹莹, 曹姗姗, 王艾红, 等. 肿瘤内科护士共情疲劳与人格特征的相关性研究[J]. 护理学报, 2018,25(21):1-4.
|
|
Xie YY, Cao SS, Wang) (A/YH, et al. Relationship between compassion fatigue and personality traits in oncology nurses[J]. J Nurs(China), 2018,25(21):1-4.
|
| [23] |
张倩倩. 儿科护士同情心负荷现状调查及其影响因素的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2016.
|
|
Zhang QQ. The study on current status of pediatric nurses’ compassion fatigue and its influencing factors[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2016.
|
| [24] |
赵允兰, 胡晓莹. 护士同情心疲乏的现状及相关因素调查[J]. 医学与哲学, 2013,34(4):75-78.
|
|
Zhao YL, Hu XY. Survey of compassion fatigue for hospital nurse[J]. Med Philos, 2013,34(4):75-78.
|
| [25] |
周林霖, 王卫红, 张照莉, 等. 重庆市护士共情疲劳现状及其影响因素探析[J]. 保健医学研究与实践, 2019,16(4):25-31,35.
|
|
Zhou LL, Wang WH, Zhang ZL, et al. Compassion fatigue among nurses in Chongqing:an investigation of the status quo and influencing factors[J]. Health Med Res & Prac, 2019,16(4):25-31,35.
|
| [26] |
Hui Z, Dai X, Wang X. Mediating effects of empathy on the association between nursing professional values and professional quality of life in Chinese female nurses:a cross-sectional survey[J]. Nurs Open, 2020,7(1):411-418.
|
| [27] |
Wang J, Okoli CTC, He H, et al. Factors associated with compassion satisfaction,burnout,and secondary traumatic stress among Chinese nurses in tertiary hospitals:a cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2020,102:103472.
|
| [28] |
Xie W, Wang J, Okoli CTC, et al. Prevalence and factors of compassion fatigue among Chinese psychiatric nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2020,99(29):e21083.
|
| [29] |
Yu HR, Jiang AL, Shen J. Prevalence and predictors of compas-sion fatigue,burnout and compassion satisfaction among oncology nurses:a cross-sectional survey[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2016,57:28-38.
|
| [30] |
Kelly LA, Lefton C. Effect of meaningful recognition on critical care nurses’ compassion fatigue[J]. Am J Crit Care, 2017,26(6):438-444.
|
| [31] |
张萍, 孙晓明, 陈红琢, 等. 甘肃省各级医院临床护士职业认同感及相关因素研究[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2016,34(12):85-87.
|
|
Zhang P, Sun XM, Chen HZ, et al. Study on professional identity and related factors of clinical nurses in hospitals at all levels in Gansu province[J]. Heal Vocat Educ, 2016,34(12):85-87.
|
| [32] |
曹晓翼, 陆丽清, 刘晓虹. 专业自我概念在护士职业认同与职业倦怠间的中介效应[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010,45(11):965-968.
|
|
Cao XY, Lu LQ, Liu XH. The mediating effect of professional self-concept between nurses’ professional identification and job burnout[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010,45(11):965-968.
|
| [33] |
Wijdenes KL, Badger TA, Sheppard KG. Assessing compassion fatigue risk among nurses in a large urban trauma center[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2019,49(1):19-23.
|
| [34] |
唐昕辉, 李君春, 耿文秀. 国外工作倦怠观的理论探索[J]. 心理科学, 2005,28(5):1185-1187.
|
|
Tang XH, Li JC, Geng WX. A research of foreign theories about job burnout[J]. Psychol Sci, 2005,28(5):1185-1187.
|
| [35] |
Alharbi J, Jackson D, Usher K. Compassion fatigue in critical care nurses. An integrative review of the literature[J]. Saudi Med J, 2019,40(11):1087-1097.
|