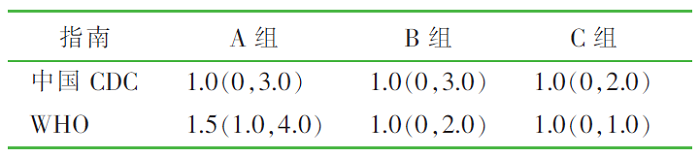
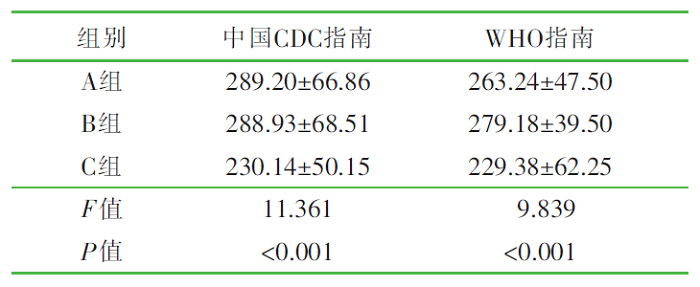
| [1] |
TAO Lin, YI Yinping, JIANG Qiuhuan, ZHANG Hongmei, LI Liming, JING Chan, DU Xiaoning.
The exploration of the construction of clinical teaching base for nutrition support specialty nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(7): 801-806.
|
| [2] |
BAI Yashuang, ZHANG Zengmei, LI Shengyun, JIN Zi, ZHANG Shuli.
Construction and application of a training program for nurses in robotic-assisted surgery
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(5): 517-524.
|
| [3] |
ZOU Ying, XU Mengqi, RUAN Tiantian, DING Yuan, ZHU Lingyan.
Application progress on in situ simulation in nurse airway management training
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(4): 506-512.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Jian, JING Jie, GAI Yubiao, XUE Xue, LIU Qingwei, WEI Lili, ZHANG Yuchen, LI Zunzhu, SUN Jianhua, LIU Yanyan, LUO Hongbo.
Study on the current situation about ICU nurses’ knowledge,attitude and practice of acute skin failure and its influencing factors
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(3): 336-341.
|
| [5] |
WU Jie, LI Mengyao, YAN Dexiu, ZHANG Yaqing, ZHANG Yuanyuan.
Development and effect application of MOOC in basic theoretical knowledge training for new graduate nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2024, 21(2): 140-144.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Xueling, XIAO Ye, ZHANG Shaoying, YANG Jingping, LIN Jingjing, HUANG Minfang, LIN Rongjin.
Construction of training program of nursing ability for the whole process care of midwives in high-risk pregnancy
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(9): 1084-1089.
|
| [7] |
LIU Jing, FENG Xiuqin, CHEN Yilan.
Development and application of emergency echelon nurse training program
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(9): 1090-1094.
|
| [8] |
LIU Xiangyu, GUO Junchen, ZHU Lihui, CHEN Yongyi, XIAO Yazhou, DING Yanming.
The practice and effect of online teaching in the course of palliative care nurse specialty training
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(9): 1034-1037.
|
| [9] |
HE Jingjing, HUANG Ping, LI Chunyan, ZHOU Tiantian.
Construction of stratified training program for disaster nurses in tertiary hospitals
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(7): 829-834.
|
| [10] |
HUANG Jiayi, WU Zhishan, JIANG Liping.
Investigation of status and demands of continuous renal replacement therapy training for ICU nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(7): 835-839.
|
| [11] |
CAI Qiuni, OU Juanjuan, LI Yuanchan, CHEN Yajuan.
The current situation and demand of continuing education and training among wound specialty nurses
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(6): 645-649.
|
| [12] |
WEI Shenyi,LI Jin,LÜ Juan,XU Yu,WANG Lei,GONG Shu.
Development and application of nurse hierarchical training and management system
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(6): 691-696.
|
| [13] |
WANG Qiong,ZHANG Jinhua,WANG Keman,ZHANG Yuanyuan,CHAI Cuiping,HAN Shuhuan.
Construction of a standardized training program for nurses in primary hospitals in the medical consortium
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(6): 697-701.
|
| [14] |
SONG Zhaohui, TAN Meiqi, JIANG Songyun, LUO Ji.
Construction of a training program for new nurses in central sterile supply department
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(6): 702-706.
|
| [15] |
LI Yike, LU Hao, LI Siyu, MA Hongli, SHI Yanhua, JIAO Haixing.
Educational practices for nurses of trauma-informed care:a scoping review
[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023, 20(5): 620-624.
|