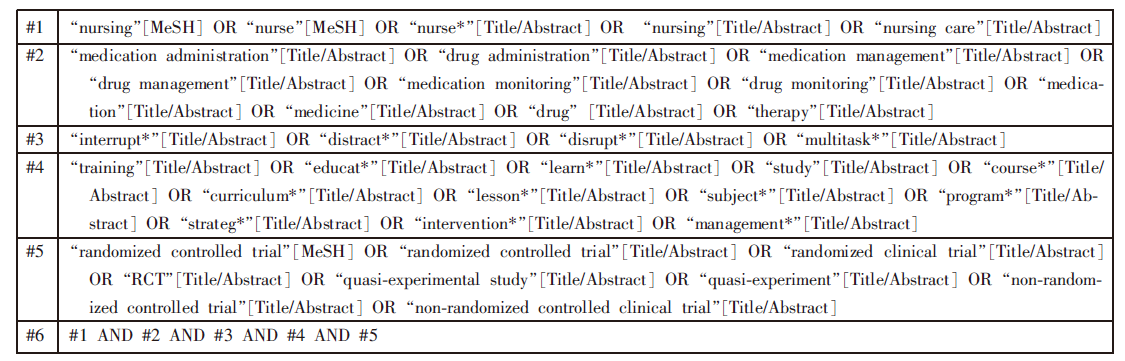
| [1] |
World Health Organization. Medication without harm:policy brief[EB/OL].(2024-03-07)[2024-11-12]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062764.
|
| [2] |
World Health Organization. Global patient safety report 2024[EB/OL].(2024-05-30)[2025-04-07]. https://www.who.int/publi-cations/i/item/9789240095458.
|
| [3] |
Raja, Badil, Ali S, et al. Association of medication administra-tion errors with interruption among nurses in public sector tertiary care hospitals[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2019, 35(5):1318-1321.
doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.5.287
pmid: 31488999
|
| [4] |
Westbrook JI, Woods A, Rob MI, et al. Association of inter-ruptions with an increased risk and severity of medication administration errors[J]. Arch Intern Med, 2010, 170(8):683-690.
doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.65
pmid: 20421552
|
| [5] |
Li SYW, Magrabi F, Coiera E. A systematic review of the psy-chological literature on interruption and its patient safety implications[J]. J Am Med Inform Assoc, 2012, 19(1):6-12.
doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2010-000024
|
| [6] |
谢建飞, 丁四清, 曾赛男, 等. 护理中断事件的概念分析和启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2013, 48(2):175-178.
|
|
Xie JF, Ding SQ, Zeng SN, et al. Nursing interruptions:a con-cept analysis and implications[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2013, 48(2):175-178.
|
| [7] |
马珂珂, 丁四清, 周建大, 等. 给药中断事件现状及管理对策的研究进展[J]. 护理学杂志, 2018, 33(18):21-24.
|
|
Ma KK, Ding SQ, Zhou JD, et al. Research progress on inter-ruptions during medication administration and management strategies[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2018, 33(18):21-24.
|
| [8] |
郭佳. ICU护理用药过程中断现状观察及干预指标的制定[D]. 太原: 山西中医药大学, 2020.
|
|
Guo J. Observation on interruption of ICU nursing medication process and formulation on intervention indicators[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
|
| [9] |
吴钰琦. 用药过程中护理中断事件预防策略的构建[D]. 湖州: 湖州师范学院, 2022.
|
|
Wu YQ. Construction of nursing interruption prevention strategy during medication[D]. Huzhou: Huzhou University, 2022.
|
| [10] |
朱政, 胡雁, 周英凤, 等. 推动证据向临床转化(三)研究的选题和问题构建[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(9):796-799.
|
|
Zhu Z, Hu Y, Zhou YF, et al. Promoting the transformation of evidence to clinical practice:research topic selection and problem construction[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(9):796-799.
|
| [11] |
Alper BS, Brian Haynes R. EBHC pyramid 5.0 for accessing preappraised evidence and guidance[J]. Evid Based Med, 2016, 21(4):123-125.
doi: 10.1136/ebmed-2016-110447
pmid: 27325531
|
| [12] |
王志稳, 冷敏敏, 孙月. 证据整合研究中文献检索策略的制订[J]. 中华护理教育, 2021, 18(10):883-888.
|
|
Wang ZW, Leng MM, Sun Y. Developing high-quality search strategy in evidence synthesis[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2021, 18(10):883-888.
|
| [13] |
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, et al. Summarizing systematic reviews:methodological development,conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach[J]. Int J Evid Based Healthc, 2015, 13(3):132-140.
doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
|
| [14] |
Barker TH, Stone JC, Sears K, et al. The revised JBI critical appraisal tool for the assessment of risk of bias for randomi-zed controlled trials[J]. JBI Evid Synth, 2023, 21(3):494-506.
|
| [15] |
Barker TH, Habibi N, Aromataris E, et al. The revised JBI critical appraisal tool for the assessment of risk of bias for quasi-experimental studies[J]. JBI Evid Synth, 2024, 22(3):378-388.
|
| [16] |
de Smalen AW, Chan ZX, Abreu Lopes C, et al. Developing an evidence assessment framework and appraising the acade-mic literature on migrant health in Malaysia:a scoping review[J]. BMJ Open, 2021, 11(1):e041379.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041379
|
| [17] |
王春青, 胡雁. JBI证据预分级及证据推荐级别系统(2014版)[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2015, 30(11):964-967.
|
|
Wang CQ, Hu Y. JBI evidence pre-classification and evidence rank system(2014 edition)[J]. J Nurses Train, 2015, 30(11):964-967.
|
| [18] |
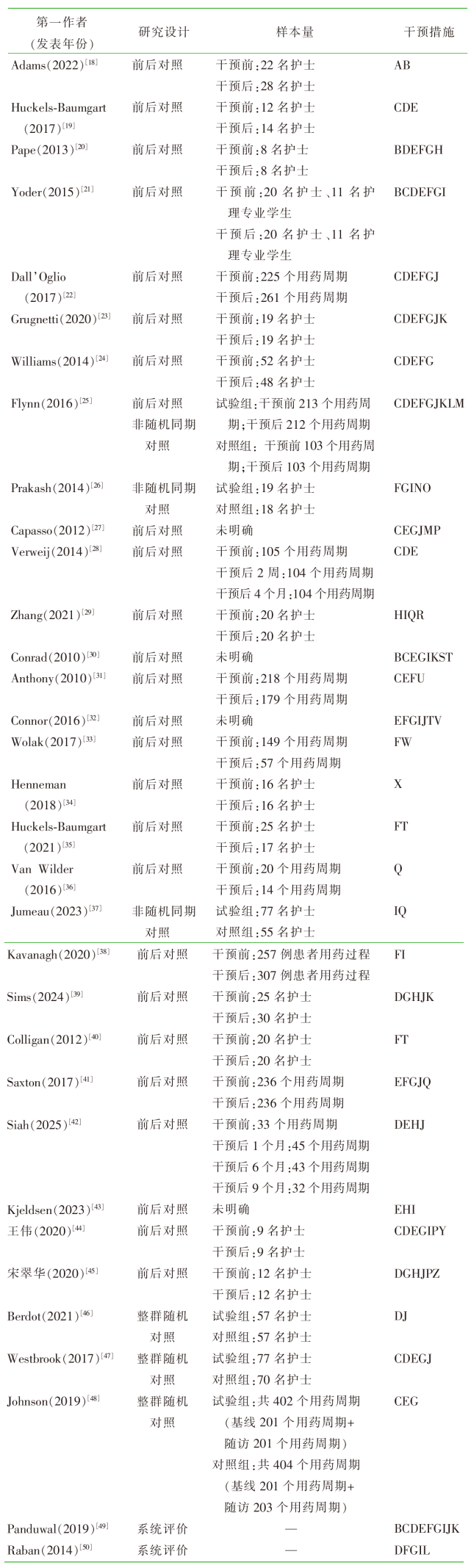
Adams J, Waldo K, Brodie M, et al. Chemo checker:transform-ing care and increasing patient safety by reducing nurse distractions[J]. Clin J Oncol Nurs, 2022, 26(1):100-103.
|
| [19] |
Huckels-Baumgart S, Niederberger M, Manser T, et al. A com-bined intervention to reduce interruptions during medication preparation and double-checking:a pilot-study evaluating the impact of staff training and safety vests[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2017, 25(7):539-548.
doi: 10.1111/jonm.2017.25.issue-7
|
| [20] |
Pape TM. The effect of a five-part intervention to decrease omitted medications[J]. Nurs Forum, 2013, 48(3):211-222.
doi: 10.1111/nuf.12025
pmid: 23889200
|
| [21] |
Yoder M, Schadewald D, Dietrich K. The effect of a safe zone on nurse interruptions,distractions,and medication administra-tion errors[J]. J Infus Nurs, 2015, 38(2):140-151.
doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000095
|
| [22] |
Dall’Oglio I, Fiori M, Di Ciommo V, et al. Effectiveness of an improvement programme to prevent interruptions during medi-cation administration in a paediatric hospital:a preinterven-tion-postintervention study[J]. BMJ Open, 2017, 7(1):e013285.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013285
|
| [23] |
Grugnetti AM, Caruso R, Scognamiglio D, et al. Effects of im-plementing standardized organizational interventions on drug therapy management(DTM):a quasi-experimental study[J]. G Ital Med Lav Ergon, 2020, 42(1):48-54.
pmid: 32614533
|
| [24] |
Williams T, King MW, Thompson JA, et al. Implementing evi-dence-based medication safety interventions on a progressive care unit[J]. Am J Nurs, 2014, 114(11):53-62.
doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000456433.07343.7f
pmid: 25353136
|
| [25] |
Flynn F, Evanish JQ, Fernald JM, et al. Progressive care nurses improving patient safety by limiting interruptions during me-dication administration[J]. Crit Care Nurse, 2016, 36(4):19-35.
doi: 10.4037/ccn2016498
pmid: 27481799
|
| [26] |
Prakash V, Koczmara C, Savage P, et al. Mitigating errors caused by interruptions during medication verification and adminis-tration:interventions in a simulated ambulatory chemotherapy setting[J]. BMJ Qual Saf, 2014, 23(11):884-892.
doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2013-002484
pmid: 24906806
|
| [27] |
Capasso V, Johnson M. Improving the medicine administration process by reducing interruptions[J]. J Healthc Manag, 2012, 57(6):384-390.
pmid: 23297605
|
| [28] |
Verweij L, Smeulers M, Maaskant JM, et al. Quiet please!Drug round tabards:are they effective and accepted? A mixed method study[J]. J Nurs Scholarsh, 2014, 46(5):340-348.
doi: 10.1111/jnu.2014.46.issue-5
|
| [29] |
Zhang WG, Liu JW, Yang SY, et al. A study on the improvement of nursing interruption risk by a closed-loop manage-ment model[J]. Risk Manag Healthc Policy, 2021, 14:2945-2952.
doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S301108
|
| [30] |
Conrad C, Fields W, McNamara T, et al. Medication room mad-ness:calming the chaos[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2010, 25(2):137-144.
doi: 10.1097/NCQ.0b013e3181c3695d
|
| [31] |
Anthony K, Wiencek C, Bauer C, et al. No interruptions please:impact of a No Interruption Zone on medication safety in intensive care units[J]. Crit Care Nurse, 2010, 30(3):21-29.
doi: 10.4037/ccn2010473
pmid: 20067939
|
| [32] |
Connor JA, Ahern JP, Cuccovia B, et al. Implementing a dis-traction-free practice with the red zone medication safety initiative[J]. Dimens Crit Care Nurs, 2016, 35(3):116-124.
doi: 10.1097/DCC.0000000000000179
pmid: 27043397
|
| [33] |
Wolak E, Hill A, Ball P, et al. A novel approach to reducing RN distraction during medication access[J]. Medsurg Nurs, 2017, 26(2):93-98.
pmid: 30304588
|
| [34] |
Henneman EA, Marquard JL, Nicholas C, et al. The stay S.A.F.E. strategy for managing interruptions reduces distraction time in the simulated clinical setting[J]. Crit Care Nurs Q, 2018, 41(2):215-223.
doi: 10.1097/CNQ.0000000000000201
pmid: 29494376
|
| [35] |
Huckels-Baumgart S, Baumgart A, Buschmann U, et al. Sepa-rate medication preparation rooms reduce interruptions and medication errors in the hospital setting:a prospective obser-vational study[J]. J Patient Saf, 2021, 17(3):e161-e168.
|
| [36] |
Van Wilder A, Bell H, Franklin BD. The effect of electronic prescribing and medication administration on nurses’ workflow and activities:an uncontrolled before and after study[J]. Saf Health, 2016, 2(1):13.
doi: 10.1186/s40886-016-0023-8
|
| [37] |
Jumeau M, Francois O, Bonnabry P. Impact of automated dispensing cabinets on dispensing errors,interruptions and pillbox preparation time[J]. Eur J Hosp Pharm, 2023, 30(4):237-241.
doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2021-002849
|
| [38] |
Kavanagh A, Donnelly J. A lean approach to improve medica-tion administration safety by reducing distractions and inter-ruptions[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2020, 35(4):E58-E62.
|
| [39] |
Sims T, Narayanan P, Alex A, et al. Decreasing nonemergent nurse interruptions during peak medication administration time utilizing “the golden hour”[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2024, 39(2):99-101.
doi: 10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000750
|
| [40] |
Colligan L, Guerlain S, Steck SE, et al. Designing for distrac-tions:a human factors approach to decreasing interruptions at a centralised medication station[J]. BMJ Qual Saf, 2012, 21(11):939-947.
doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2011-000289
pmid: 22893697
|
| [41] |
Saxton R, Cahill R. Impact of No-interruption intervention on safety and efficiency[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2017, 32(4):281-284.
doi: 10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000276
pmid: 28658187
|
| [42] |
Siah JW, Cheng CKT, Choy CL, et al. Interruption reduction during oral medication rounds among nurses in hematology-oncology wards:a best practice implementation project[J]. JBI Evid Implement, 2025, 23(3):274-281.
|
| [43] |
Kjeldsen LJ, Schlünsen M, Meijers A, et al. Medication dispen-sing by pharmacy technicians improves efficiency and patient safety at a geriatric ward at a Danish hospital:a pilot study[J]. Pharmacy, 2023, 11(3):82.
doi: 10.3390/pharmacy11030082
|
| [44] |
王伟, 赵小静, 王芳, 等. 护士用药过程中中断事件前馈控制方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020, 26(33):4618-4623.
|
|
Wang W, Zhao XJ, Wang F, et al. Construction and applica-tion of feedforward control plan for interruptions of nurses performing drug use[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2020, 26(33):4618-4623.
|
| [45] |
宋翠华, 张秋玲, 李新平, 等. 应用医疗团队资源管理模式进行呼吸科用药护理中断事件的研究实践[J]. 中国医药科学, 2020, 10(11):167-171.
|
|
Song CH, Zhang QL, Li XP, et al. Practical research on the application of medical team resource management model to the interruption of medication nursing in the department of respiratory medicine[J]. China Med Pharm, 2020, 10(11):167-171.
|
| [46] |
Berdot S, Vilfaillot A, Bezie Y, et al. Effectiveness of a ‘do not interrupt’ vest intervention to reduce medication errors during medication administration:a multicenter cluster rando-mized controlled trial[J]. BMC Nurs, 2021, 20(1):153.
doi: 10.1186/s12912-021-00671-7
pmid: 34429095
|
| [47] |
Westbrook JI, Li L, Hooper TD, et al. Effectiveness of a ‘Do not interrupt’ bundled intervention to reduce interruptions dur-ing medication administration:a cluster randomised controlled feasibility study[J]. BMJ Qual Saf, 2017, 26(9):734-742.
doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2016-006123
pmid: 28232390
|
| [48] |
Johnson M, Langdon R, Levett-Jones T, et al. A cluster rando-mised controlled feasibility study of nurse-initiated behaviou-ral strategies to manage interruptions during medication admi-nistration[J]. Int J Qual Health Care, 2019, 31(8):G67-G73.
|
| [49] |
Panduwal CA, Bilaut EC. The effectiveness of interventions to reduce the nurses’ distractions during medication administra-tion:a systematic review[J]. J Ners, 2019, 14(3):132-140.
doi: 10.20473/jn.v14i3.17048
|
| [50] |
Raban MZ, Westbrook JI. Are interventions to reduce interru-ptions and errors during medication administration effective:a systematic review[J]. BMJ Qual Saf, 2014, 23(5):414-421.
doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2013-002118
|
| [51] |
Hamed MMM, Konstantinidis S. Barriers to incident reporting among nurses:a qualitative systematic review[J]. West J Nurs Res, 2022, 44(5):506-523.
doi: 10.1177/0193945921999449
|
| [52] |
Duruk N, Zencir G, Eşer I. Interruption of the medication pre-paration process and an examination of factors causing interruptions[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2016, 24(3):376-383.
doi: 10.1111/jonm.12331
|
| [53] |
Version O. A human factors approach to medication adminis-tration in nursing homes[D]. Stavanger: University of Stavan-ger, 2020.
|
| [54] |
续璐, 刘慧, 谢怡琼, 等. 医疗机构用药安全的风险因素及其应对策略[J]. 医药导报, 2022, 41(8):1102-1107.
doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2022.08.006
|
|
Xu L, Liu H, Xie YQ, et al. Risk factors and strategies of medication safety in medical institutions[J]. Her Med, 2022, 41(8):1102-1107.
|
| [55] |
刘佳微, 张文光. 重症监护室护理中断事件现况及与护士心理负荷的相关性[J]. 护理学杂志, 2019, 34(19):8-11.
|
|
Liu JW, Zhang WG. Correlation between nursing interruptions in intensive care unit and nurses’ psychological load[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2019, 34(19):8-11.
|
| [56] |
Thomas L, Donohue-Porter P, Stein Fishbein J. Impact of interruptions,distractions,and cognitive load on procedure failures and medication administration errors[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2017, 32(4):309-317.
doi: 10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000256
pmid: 28448299
|
| [57] |
Jin HZ, Liu LY, Luo ZB, et al. The effects of different inter-ruption conditions on mental workload:an experimental study based on multimodal measurements[J]. Ergonomics, 2025, 68(8):1274-1292.
doi: 10.1080/00140139.2024.2400129
|
| [58] |
Johnson M, Sanchez P, Langdon R, et al. The impact of inter-ruptions on medication errors in hospitals:an observational study of nurses[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2017, 25(7):498-507.
doi: 10.1111/jonm.2017.25.issue-7
|