| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3
|
| [2] |
贺晓兰, 马辰莺, 徐晓婷. 宫颈癌放射治疗患者代谢产物表达与急性放射性肠炎相关性的研究[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2020, 40(1):1-10.
|
| [3] |
Loge L, Florescu C, Alves A, et al. Radiation enteritis:diagno-stic and therapeutic issues[J]. J Visc Surg, 2020, 157(6):475-485.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2020.08.012
pmid: 32883650
|
| [4] |
中国医师协会外科医师分会, 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠外科学组. 中国放射性直肠炎诊治专家共识(2018版)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2018, 21(12):1321-1336.
|
| [5] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
pmid: 20652370
|
| [6] |
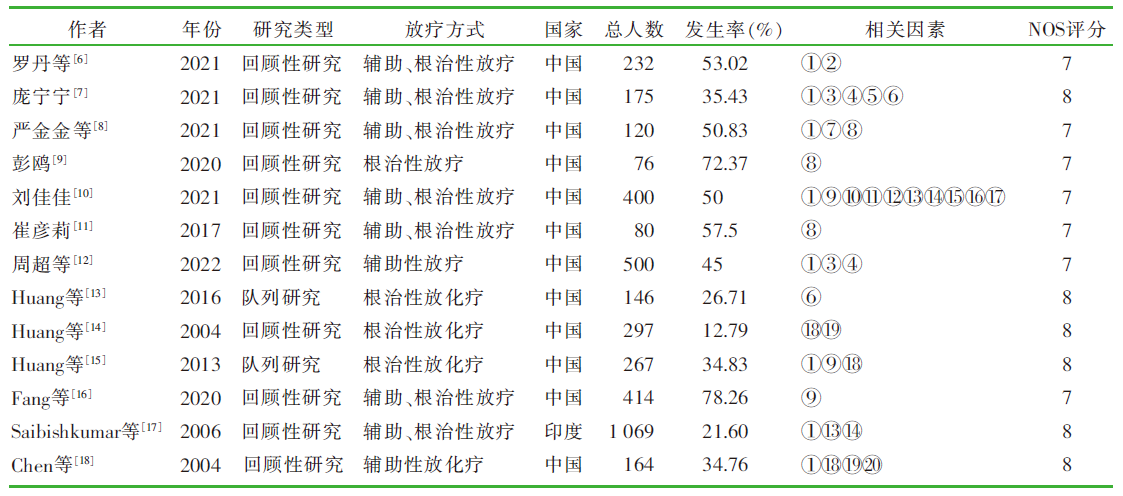
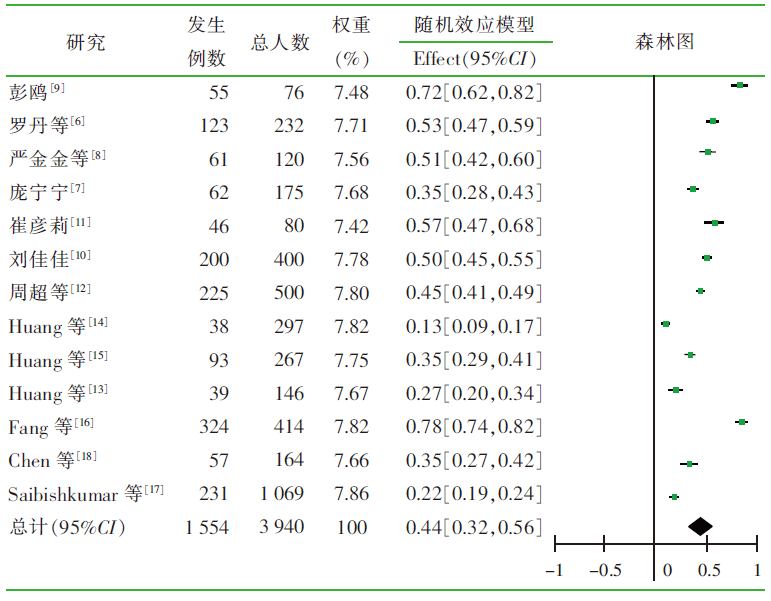
罗丹, 孔为民, 陈姝宁. 宫颈癌放疗后放射性直肠炎发生情况及其相关因素分析[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(2):400-403,408.
|
|
Luo D, Kong WM, Chen SN. Incidence of radiation proctitis after radiotherapy for cervical cancer and analysis of related factors[J]. Med Recapitul, 2021, 27(2):400-403,408.
|
| [7] |
庞宁宁. 宫颈癌放疗患者放射性直肠炎发生危险因素分析及其护理对策[J]. 慢性病学杂志, 2021, 22(8):1293-1295.
|
|
Pang NN. Analysis of risk factors of radiation proctitis in patients with cervical cancer undergoing radiotherapy and its nursing countermeasures[J]. Chronic Pathematology J, 2021, 22(8):1293-1295.
|
| [8] |
严金金, 刘佳. 子宫颈癌患者放射性直肠炎的发生率及其危险因素分析[J]. 中国医学创新, 2021, 18(35):6-9.
|
|
Yan JJ, Liu J. Analysis of the incidence and risk factors of radiation proctitis in patients with cervical cancer[J]. Med Innov China, 2021, 18(35):6-9.
|
| [9] |
彭鸥. 宫颈癌根治性放疗急性反应的发生及相关因素分析及新西兰兔放射性肠炎模型建立[D]. 南充: 川北医学院, 2020.
|
|
Peng O. Acute radiation-induced reactions of cervical cancer and establishment of radiation proctitis model in New Zealand rabbits[D]. Nanchong: North Sichuan Medical College, 2020.
|
| [10] |
刘佳佳. 放射性直肠炎危险因素分析及中西医结合保留灌肠系统评价[D]. 太原: 山西中医药大学, 2021.
|
|
Liu JJ. Analysis of risk factors of radiation proctitis and integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine systematic review of retention enema[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021.
|
| [11] |
崔彦莉. 宫颈癌放疗所致急性放射性直肠炎影响因素[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2017, 40(1):44-47.
|
|
Cui YL. Effect factors of acute radiation proctitis caused by intensity modulated radiotherapy for cervical cancer[J]. J Mol Imaging, 2017, 40(1):44-47.
|
| [12] |
周超, 朱莺, 徐德静, 等. 宫颈鳞癌同期放化疗后放射性肠炎危险因素及综合措施研究[J]. 肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2022, 9(2):241-246.
|
|
Zhou C, Zhu Y, Xu DJ, et al. Study on risk factors and comprehensive measures of radiation enteritis after concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cervical squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Electron J Metab Nutr Cancer, 2022, 9(2):241-246.
|
| [13] |
Huang EY, Lin H, Wang CJ, et al. Impact of treatment time-related factors on prognoses and radiation proctitis after definitive chemoradiotherapy for cervical cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2016, 5(9):2205-2212.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.2016.5.issue-9
|
| [14] |
Huang EY, Wang CJ, Hsu HC, et al. Dosimetric factors predicting severe radiation-induced bowel complications in patients with cervical cancer:combined effect of external parametrial dose and cumulative rectal dose[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2004, 95(1):101-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.06.043
|
| [15] |
Huang EY, Sun LM, Lin H, et al. A prospective cohort study to compare treatment results between 2 fractionation schedules of high-dose-rate intracavitary brachytherapy (HDR-ICBT) in patients with cervical cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2013, 85(1):123-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.03.045
|
| [16] |
Fang JG, Fang JM, AilinWu, et al. Clinical analysis of predisposing factors for radiation enteritis in patients with cervical cancer[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6503).
|
| [17] |
Saibishkumar EP, Patel FD, Sharma SC. Evaluation of late to-xicities of patients with carcinoma of the cervix treated with radical radiotherapy:an audit from India[J]. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol), 2006, 18(1):30-37.
doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2005.06.013
|
| [18] |
Chen SW, Liang JA, Yang SN, et al. Radiation injury to intestine following hysterectomy and adjuvant radiotherapy for cervical cancer[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2004, 95(1):208-214.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.07.003
|
| [19] |
Gupta PK, Lal P, Tiwari A. A case report of carcinoma of uterine cervix throwing heterochronous metastasis to the skin,spleen,and pancreas:the role of multimodality treatment approach[J]. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst, 2019, 31(1):8.
doi: 10.1186/s43046-019-0009-9
pmid: 32372163
|
| [20] |
刘艳梅, 陈卫军, 王赛赛, 等. Ⅱ-Ⅳ期宫颈癌根治性放疗的近期疗效观察[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2016, 24(6):459-463.
|
| [21] |
Yang XJ, Wang JY, Lin LM, et al. Concomitant chemoradiothe-rapy versus pure radiotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer:a retrospective analysis of complications and clinical outcome[J]. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol, 2016, 37(4):499-503.
|
| [22] |
陈雪峰, 吴雪萍, 张飞亚, 等. 全程护理模式在宫颈癌精准放疗中的实施效果[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(S2):250-252.
|
|
Chen XF, Wu XP, Zhang FY, et al. The effect of whole course nursing mode in precise radiotherapy for cervical cancer[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2020, 23(S2):250-252.
|
| [23] |
陈唐庚, 陈玲玲, 陈丽清, 等. 宫颈癌患者调强放疗个体化饮水量及膀胱充盈训练[J]. 护理学杂志, 2018, 33(16):27-29.
|
|
Chen TG, Chen LL, Chen LQ, et al. Individualized water drinking and bladder filling training for cervical cancer patients on intensity modulated radiotherapy[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2018, 33(16):27-29.
|
| [24] |
王磊, 那继文, 董晓红, 等. 中药保留灌肠对急性出血性放射性肠炎的疗效及护理观察[J]. 中国中医急症, 2018, 27(5):842-845,849.
|
| [25] |
邹长鹏, 郑峥, 赵迎春, 等. 中西医结合治疗急性放射性肠炎疗效观察[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(3):80-82.
|
| [26] |
Nosaka K, Shibata K, Utsumi F, et al. Feasibility and benefit of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for elderly patients with uterine cervical cancer[J]. Tumori, 2016, 102(6):600-605.
doi: 10.5301/tj.5000530
pmid: 27443893
|
| [27] |
刘景超, 朱兰. 盆底肌肉锻炼(PFMT)在女性压力性尿失禁中的应用进展[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2018, 27(1):68-71.
|
| [28] |
严培玲, 罗永建, 刘海丰, 等. 老年高血压患者肠道菌群变化及其与血清炎症指标的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(18):3871-3874.
|
| [29] |
Kishida S, Kato-Mori Y, Hagiwara K. Influence of changes in the intestinal microflora on the immune function in mice[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2018, 80(3):440-446.
doi: 10.1292/jvms.17-0485
pmid: 29415902
|
| [30] |
张志革. 针对性护理对宫颈癌放疗患者急性胃肠道反应发生率的影响评价[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2018, 25(S2):222,224.
|
|
Zhang ZG. Effect of targeted nursing on the incidence of acute gastrointestinal reaction in patients with cervical cancer undergoing radiotherapy[J]. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat, 2018, 25(S2):222,224.
|
| [31] |
Shadad AK, Sullivan FJ, Martin JD, et al. Gastrointestinal radi-ation injury:symptoms,risk factors and mechanisms[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(2):185-198.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.185
|
| [32] |
LaCouture TA, Xue JY, Subedi G, et al. Small bowel dose tol-erance for stereotactic body radiation therapy[J]. Semin Radiat Oncol, 2016, 26(2):157-164.
doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2015.11.009
pmid: 27000513
|
| [33] |
黄定凤, 杨洁, 宋爱梅. 氨磷汀保留灌肠在预防前列腺癌放疗患者肠道毒性中的应用[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2021, 36(18):1685-1688.
|
| [34] |
郑利媛, 黄定凤, 王惠芬, 等. 护理流程优化对前列腺癌患者放射性肠炎的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(19):21-25.
|
|
Zheng LY, Huang DF, Wang HF, et al. Effect of nursing process optimization on radiation enteritis in prostate cancer patients[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(19):21-25.
|