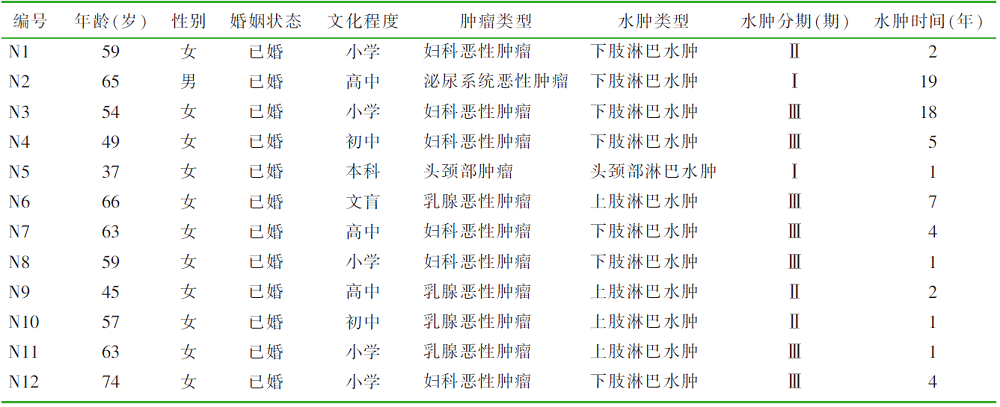
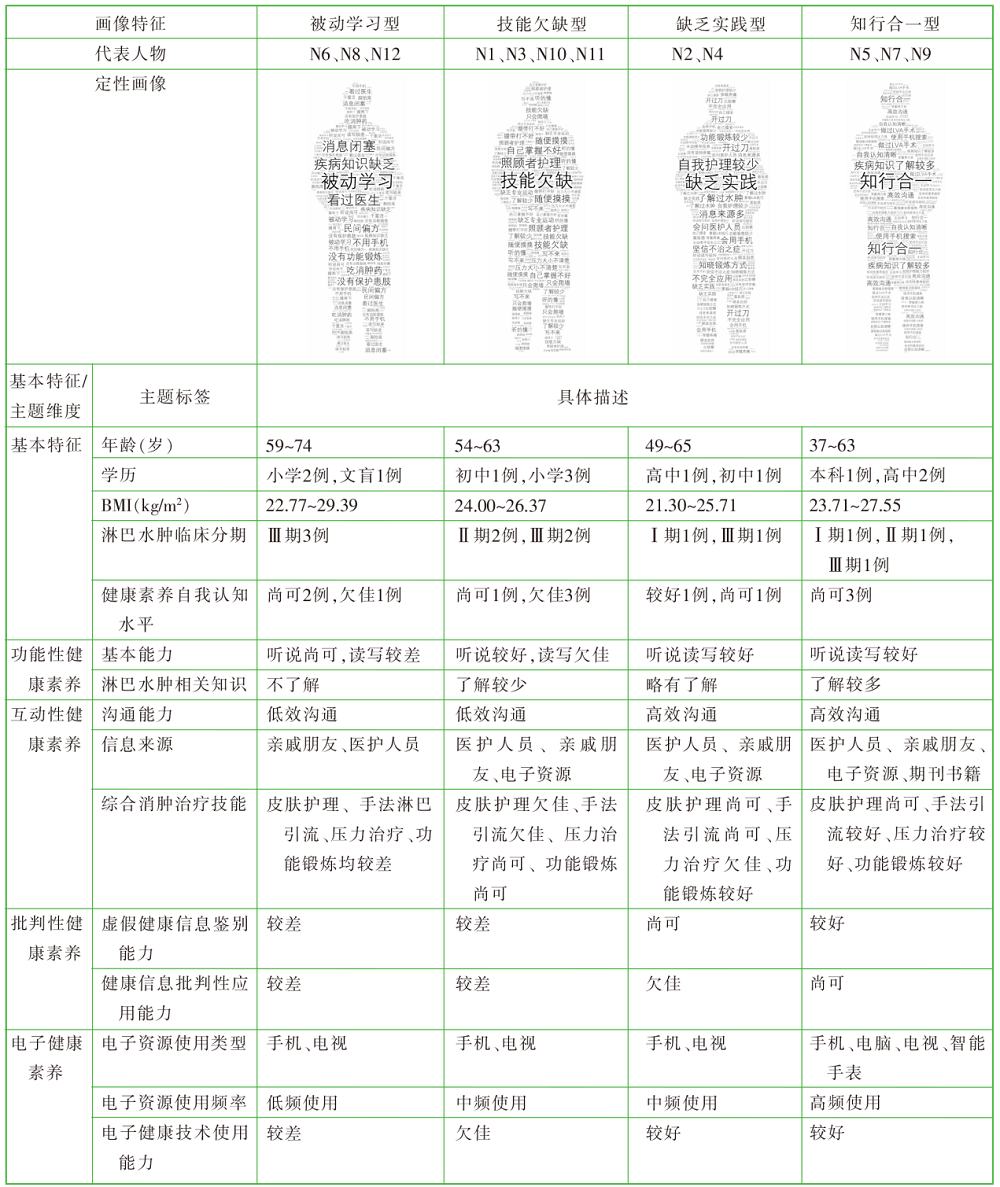
| [1] |
陈天哲, 林樾, 谭谦. 肿瘤相关淋巴水肿病理改变及危险因素的研究进展[J]. 癌症进展, 2023, 21(4):362-365.
|
|
Chen TZ, Lin Y, Tan Q. Research progress on pathological cha-nges and risk factors of tumor-associated lymphedema[J]. Oncol Prog, 2023, 21(4):362-365.
|
| [2] |
DiSipio T, Rye S, Newman B, et al. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013, 14(6):500-515.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70076-7
pmid: 23540561
|
| [3] |
Ryan M, Colleen Stainton M, Slaytor EK, et al. Aetiology and prevalence of lower limb lymphoedema following treatment for gynaecological cancer[J]. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol, 2003, 43(2):148-151.
|
| [4] |
尤渺宁, 康京京, 陆宇晗, 等. 乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿患者综合消肿治疗的居家护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(8):1238-1240.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.08.026
|
|
You MN, Kang JJ, Lu YH, et al. Home nursing care of breast cancer-related lymphedema treated with complete decongestive therapy[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(8):1238-1240.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.08.026
|
| [5] |
Stout NL, Brantus P, Moffatt C. Lymphoedema management:an international intersect between developed and developing coun-tries. Similarities,differences and challenges[J]. Glob Public Health, 2012, 7(2):107-123.
|
| [6] |
Holden CE, Wheelwright S, Harle A, et al. The role of health literacy in cancer care:a mixed studies systematic review[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(11):e0259815.
|
| [7] |
刘海鸥, 孙晶晶, 苏妍嫄, 等. 国内外用户画像研究综述[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2018, 41(11):155-160.
|
|
Liu HO, Sun JJ, Su YY, et al. Literature review of persona at home and abroad[J]. Inf Stud Theory Appl, 2018, 41(11):155-160.
|
| [8] |
Nutbeam D. Health literacy as a public health goal:a chal-lenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century[J]. Health Promot Int, 2000, 15(3):259-267.
|
| [9] |
徐芳, 应洁茹. 国内外用户画像研究综述[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2020(12):7-16.
|
|
Xu F, Ying JR. A review of user profile research at home and abroad[J]. Res Libr Sci, 2020(12):7-16.
|
| [10] |
李婉睿, 文庭孝. 国内外用户画像研究综述[J]. 情报探索, 2024(1):119-126.
|
|
Li WR, Wen TX. A review of user profile research at home and abroad[J]. Inf Res, 2024(1):119-126.
|
| [11] |
Executive Committee of the International Society of Lympho-logy. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema:2020 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology[J]. Lymphology, 2020, 53(1):3-19.
|
| [12] |
郑伟. 宫颈癌术后放疗患者预防下肢淋巴水肿干预方案的构建[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2023.
|
|
Zheng W. Construction of prevention intervention scheme for lower limb lymphedema in patients with postoperative radio-therapy for cervical cancer[D]. Shenyang: China Medical Uni-versity, 2023.
|
| [13] |
Deng J, Murphy BA. Lymphedema self-care in patients with head and neck cancer:a qualitative study[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2016, 24(12):4961-4970.
pmid: 27510315
|
| [14] |
胡进, 叶沙, 刘高明, 等. 头颈部肿瘤综合治疗后并发淋巴水肿患者的护理[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(14):47-49.
|
|
Hu J, Ye S, Liu GM, et al. Nursing care of patients deve-loping lymphedema after comprehensive treatment of head and neck tumor[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(14):47-49.
|
| [15] |
王玲, 尚少梅, 王海燕, 等. 继发性淋巴水肿患者皮肤护理的最佳证据总结[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(9):102-105.
|
|
Wang L, Shang SM, Wang HY, et al. Evidence summary of skin care for patients with secondary lymphedema[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2021, 36(9):102-105.
|
| [16] |
刘高明, 彭政, 胡进, 等. 肿瘤医院淋巴水肿专科护理小组的建立与临床实践[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(24):64-67.
|
|
Liu GM, Peng Z, Hu J, et al. Establishment and clinical practice of lymphedema specialist nursing group in cancer hospital[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(24):64-67.
|
| [17] |
徐敏, 梅冉冉, 罗影红, 等. 乳腺癌术后上肢淋巴水肿患者病耻感的质性研究[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2024, 31(6):115-119.
|
|
Xu M, Mei RR, Luo YH, et al. A qualitative study on stigma in patients with upper limb lymphedema after breast cancer surgery[J]. Mod Nurse, 2024, 31(6):115-119.
|
| [18] |
于洪梅, 谭智慧, 杨雪莲. 基于自我效能的护理对乳腺癌根治术患者病耻感及患肢水肿的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2021, 36(6):805-808.
|
|
Yu HM, Tan ZH, Yang XL. Effect of self-efficacy nursing on stigma and limb edema in patients with radical mastectomy[J]. J N Sichuan Med Coll, 2021, 36(6):805-808.
|
| [19] |
许红蕾, 李英, 梅晓凤, 等. 阶段式综合康复方案在乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿患者中的应用研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2023, 23(12):1848-1853.
|
|
Xu HL, Li Y, Mei XF, et al. Application of stepwise compre-hensive rehabilitation program in the patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2023, 23(12):1848-1853.
|
| [20] |
刘盼. 家庭主要照顾者回授法干预对乳腺癌术后淋巴水肿患者功能锻炼依从性及生活质量的影响[J]. 临床研究, 2022, 30(3):179-182.
|
|
Liu P. The effect of the intervention of the main family caregiver’s feedback method on the compliance of functional exercise and the quality of life in patients with lymphedema after breast cancer surgery[J]. Clin Res, 2022, 30(3):179-182.
|
| [21] |
Karaca-Mandic P, Solid CA, Armer JM, et al. Lymphedema self-care:economic cost savings and opportunities to improve adherence[J]. Cost Eff Resour Alloc, 2023, 21(1):47.
|
| [22] |
陈肖敏, 金艾香, 朱慧, 等. 虚拟认知康复训练在乳腺癌化疗相关认知障碍患者中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(5):664-668.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.05.005
|
|
Chen XM, Jin AX, Zhu H, et al. Application and effect of virtual cognitive rehabilitation training in breast cancer patients with cognitive impairment after chemotherapy[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(5):664-668.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.05.005
|
| [23] |
金艾香, 陈肖敏, 沈利凤, 等. 基于体感交互的循经按摩系统在乳腺癌改良根治术后患者主动康复中的应用[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2020, 35(6):705-709.
|
|
Jin AX, Chen XM, Shen LF, et al. Application of massage system along meridian based on somatosensory interaction in active rehabilitation of patients after modified radical mastectomy[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2020, 35(6):705-709.
|
| [24] |
王安龙, 徐慧, 梁冠冕, 等. 电子游戏在恶性肿瘤患者健康教育中应用的范围综述[J]. 中国护理管理, 2023, 23(1):137-141.
|
|
Wang AL, Xu H, Liang GM, et al. Application of video games in health education for patients with malignant tumors:a scoping review[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2023, 23(1):137-141.
|
| [25] |
彭孔梅, 黄晓英. 对家庭主要照顾者实施回授法干预对老年桡骨远端骨折患者术后营养状况和康复的影响[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(3):229-233,278.
|
|
Peng KM, Huang XY. Effect of teach-back intervention on nutritional status and rehabilitation of elderly patients with distal radius fracture after operation[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(3):229-233,278.
|
| [26] |
佟阳, 金咏梅, 邱霖, 等. 乳腺癌术后上肢淋巴水肿患者社会支持与自我护理能力的关系:链式中介效应分析[J]. 上海护理, 2021, 21(8):20-24.
|
|
Tong Y, Jin YM, Qiu L, et al. Correlation between social support and self-care ability in patients with upper limb lymphedema after breast cancer surgery:a chain mediating effect analysis[J]. Shanghai Nurs, 2021, 21(8):20-24.
|
| [27] |
国家卫生健康委办公厅. 关于开展全民健康素养提升三年行动(2024-2027年)的通知[EB/OL].[2024-07-29]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202406/content_6955867.htm.
|
| [28] |
崔有文, 徐薇, 纪娇, 等. 医护患协同模式下精准健康教育平台建设研究[J]. 江苏卫生事业管理, 2021, 32(7):946-948,952.
|
|
Cui YW, Xu W, Ji J, et al. Research on the construction of precision health education platform under the mode of doctor-patient collaboration[J]. Jiangsu Health Syst Manag, 2021, 32(7):946-948,952.
|