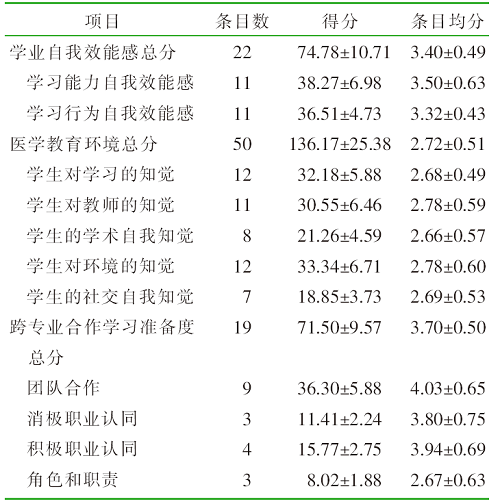
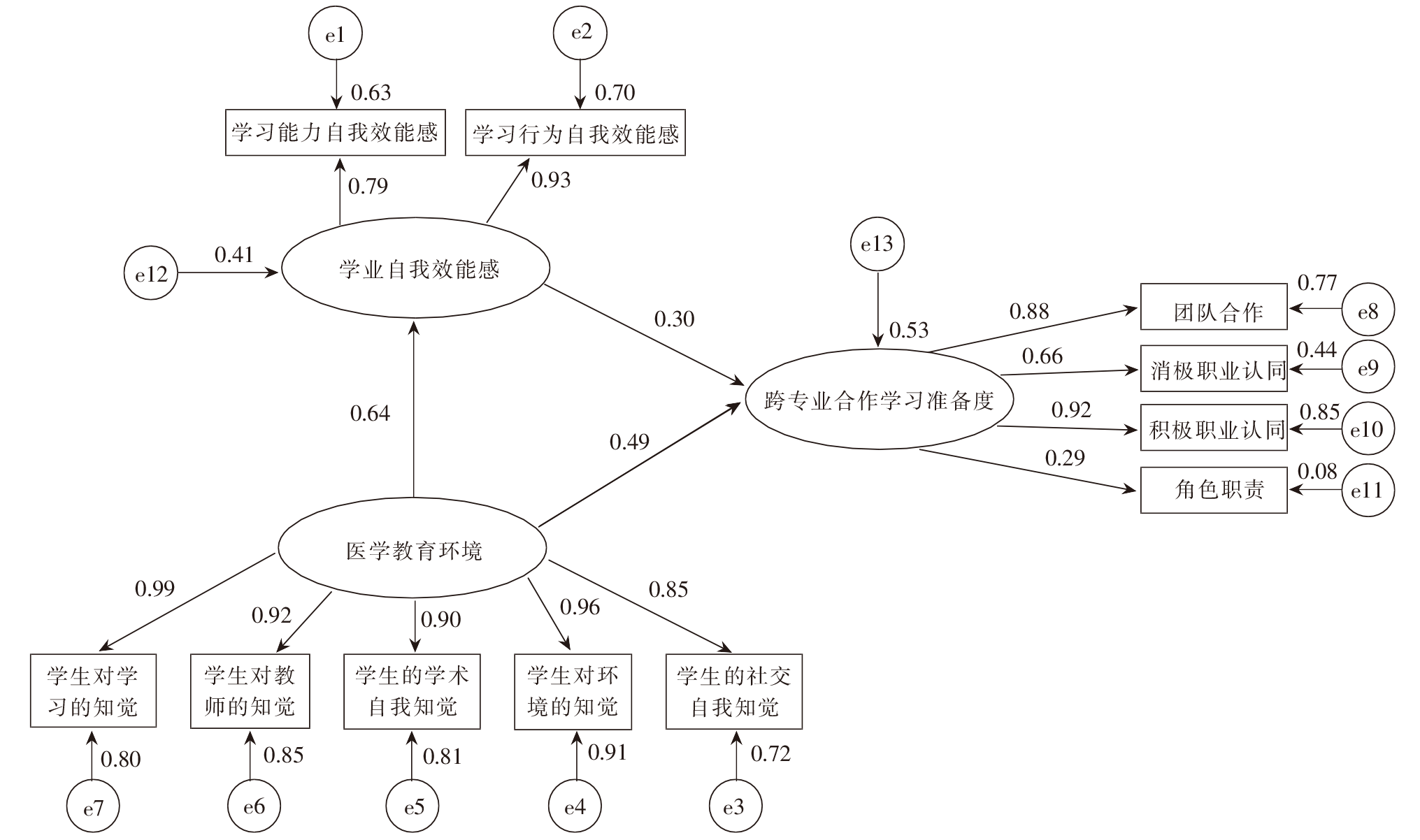
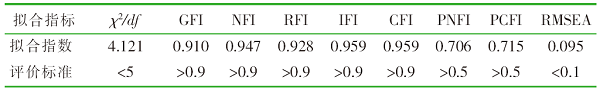
| [1] |
庄一渝, 崔锦, 陈香萍. 跨专业合作能力的研究现状分析及对护理学的启示[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2020, 36(19):1441-1445.
|
|
Zhuang YY, Cui J, Chen XP. Analysis on the research status of interprofessional collaboration compentence and its enlighten-ment to nursing[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2020, 36(19):1441-1445.
|
| [2] |
Brewer ML, Barr H. Interprofessional Education and Practice Guide No. 8:team-based interprofessional practice placements[J]. J Interprof Care, 2016, 30(6):747-753.
pmid: 27797631
|
| [3] |
Lennen N, Miller B. Introducing interprofessional education in nursing curricula[J]. Teach Learn Nurs, 2017, 12(1):59-61.
|
| [4] |
田雨同, 张艳, 赵敬, 等. 本科护理实习生跨专业合作学习准备度及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理教育, 2020, 6(9):794-798.
|
|
Tian YT, Zhang Y, Zhao J, et al. Investigation on the current situation of interprofessional cooperative learning readiness among undergraduate nursing interns[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2020, 6(9):794-798.
|
| [5] |
赵莉, 沈军, 谭敏, 等. 护理本科生学业自我效能感的现状及其对策研究[J]. 中国医药导报, 2012, 9(31):143-145.
|
| [6] |
李敏, 姜昭玲. 自我效能感在临床护士专业认同和职业倦怠之间的中介作用[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志, 2019, 25(19):133-134,封3.
|
| [7] |
吴德芳, 罗阳. 教育环境对护理本科生评判性思维倾向的影响[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2016, 33(9):72-76.
|
| [8] |
周卿照, 龚桂兰. 本科护生跨专业教育态度与临床学习环境的相关性分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(7):19-21,46.
|
|
Zhou QZ, Gong GL. Correlation between attitudes towards inter-professional education and clinical learning environment among nursing undergraduates[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2021, 36(7):19-21,46.
|
| [9] |
勒温. 拓扑心理学原理[M]. 高觉敷,译. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2003. 14-15.
|
| [10] |
梁宇颂. 大学生成就目标、归因方式与学业自我效能感的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2000.
|
| [11] |
单天明, 孙宝志. 医学教育环境测量与高等医学教育改革[J]. 医学教育, 2005, 25(2):91-94.
|
|
Shan TM, Sun BZ. Measuring medical education environment and reforming higher medical education[J]. Chin J Med Educ, 2005, 25(2):91-94.
|
| [12] |
万慧慧. 医学教育环境与住培学员学习倦怠的关系:一般自我效能感的中介效应[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2020.
|
| [13] |
王喜益, 胡韵. 跨专业合作学习准备量表的信效度研究[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2017, 34(2):23-26,47.
|
| [14] |
吴明隆. 结构方程模型:AMOS的操作与应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2010:520.
|
| [15] |
刘明畅, 刘腊梅, 李曈, 等. 护理本科生学业自我效能感与网络课程学习适应性的相关性研究[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2022, 40(8):24-26.
|
| [16] |
田茜. 专科护生学习投入现状及其与医学教育环境感知的相关性[J]. 护理研究, 2017, 31(33):4286-4288.
|
|
Tian Q. Correlation between status quo of learning engage-ment and its correlation with medical education environment perception of college nursing students[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2017, 31(33):4286-4288.
|
| [17] |
韩世范, 张倩, 张培莉, 等. 新时代我国高等护理教育院校的发展战略思考[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(8):1317-1325.
|
|
Han SF, Zhang Q, Zhang PL, et al. Reflections on the deve-lopment strategy of nursing schools in China’s higher educa-tion institutions in the new era[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(8):1317-1325.
|
| [18] |
孙柳, 王艳玲, 肖倩, 等. 北京市三级甲等医院临床护士跨专业合作学习准备度和感知度的调查分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(3):417-421.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.03.018
|
|
Sun L, Wang YL, Xiao Q, et al. Investigation on readiness and perception of interprofessional learning for nurses from tertiary hospitals in Beijing[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(3):417-421.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2019.03.018
|
| [19] |
白井双, 袁媛, 蔡立柏, 等. 护理本科生跨专业教学模式的应用效果[J]. 护理研究, 2024, 38(6):1047-1052.
|
| [20] |
钟汶汐, 毛弦筠, 程静, 等. 应用生成式人工智能培养护理人才跨专业沟通技能的态势分析[J]. 中华护理教育, 2024, 21(3):282-288.
|