| [1] |
SAMHSA. SAMHSA’s concept of trauma and guidance for a trauma-informed approach[EB/OL].(2014-06-01) [2022-10-01]. https://store.samhsa.gov/system/files/sma14-4884.
|
| [2] |
ICD-10. Post traumatic stress disorder[EB/OL].(1994-01-10) [2022-10-20]. https://assisttraumacare.org.uk/diagnoses/icd-10-post-traumatic-stress-disorder/.
|
| [3] |
Merrick MT, Ford DC, Ports KA, et al. Prevalence of adverse childhood experiences from the 2011-2014 behavioral risk factor surveillance system in 23 states[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2018, 172(11):1038-1044.
doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.2537
pmid: 30242348
|
| [4] |
Bellis MA, Hughes K, Ford K, et al. Life course health consequences and associated annual costs of adverse childhood experiences across Europe and North America:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2019, 4(10):e517-e528.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30145-8
|
| [5] |
王雪, 赵庆华, 张国惠, 等. 意外创伤患者应激障碍及社会支持与创伤后成长的相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2019, 34(6):565-568.
|
|
Wang X, Zhao QH, Zhang GH, et al. Study on the correlation between stress disorder,social support and post-traumatic growth in patients with accidental trauma[J]. J Nurses Train, 2019, 34(6):565-568.
|
| [6] |
Kalmakis KA, Chiodo LM, Kent N, et al. Adverse childhood experiences,post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms,and self-reported stress among traditional and nontraditional college students[J]. J Am Coll Health, 2020, 68(4):411-418.
doi: 10.1080/07448481.2019.1577860
pmid: 30908168
|
| [7] |
Beck CT. Secondary traumatic stress in nurses:a systematic review[J]. Arch Psychiatr Nurs, 2011, 25(1):1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2010.05.005
|
| [8] |
Kellogg MB, Knight M, Dowling JS, et al. Secondary traumatic stress in pediatric nurses[J]. J Pediatr Nurs, 2018, 43:97-103.
doi: S0882-5963(18)30110-6
pmid: 30473163
|
| [9] |
Okoli CTC, Seng S, Lykins A, et al. Correlates of post-traumatic growth among nursing professionals:a cross-sectional analysis[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2021, 29(2):307-316.
doi: 10.1111/jonm.v29.2
|
| [10] |
Suarez E, Jackson DS, Slavin LA, et al. Project Kealahou:improving Hawai’i’s system of care for at-risk girls and young women through gender-responsive,trauma-informed care[J]. Hawaii J Med Public Health, 2014, 73(12):387-392.
|
| [11] |
Reeves E. A synthesis of the literature on trauma-informed care[J]. Issues Ment Health Nurs, 2015, 36(9):698-709.
doi: 10.3109/01612840.2015.1025319
|
| [12] |
Jackson ML, Jewell VD. Educational practices for providers of trauma-informed care:a scoping review[J]. J Pediatr Nurs, 2021, 60:130-138.
doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2021.04.029
|
| [13] |
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies:towards a methodological framework[J]. Int J Soc Res Methodol, 2005, 8(1):19-32.
doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616
|
| [14] |
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR):checklist and explanation[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2018, 169(7):467-473.
doi: 10.7326/M18-0850
|
| [15] |
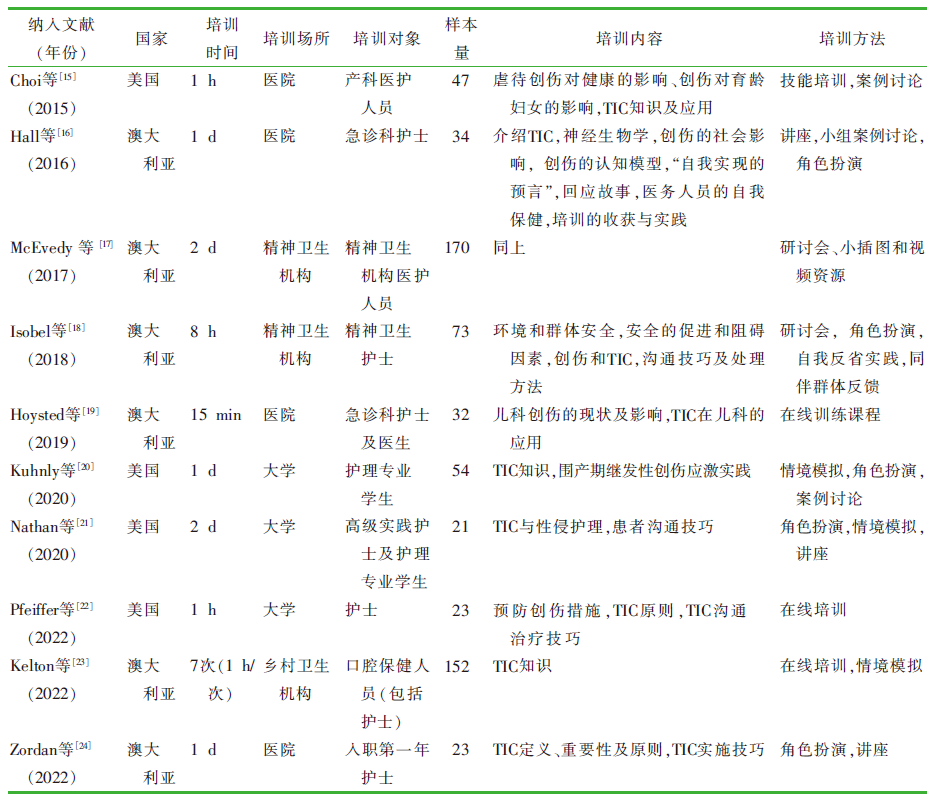
Choi KR, Seng JS. Pilot for nurse-led,interprofessional In-service training on trauma-informed perinatal care[J]. J Contin Educ Nurs, 2015, 46(11):515-521.
doi: 10.3928/00220124-20151020-04
|
| [16] |
Hall A, McKenna B, Dearie V, et al. Educating emergency department nurses about trauma informed care for people pre-senting with mental health crisis:a pilot study[J]. BMC Nurs, 2016, 15:21.
doi: 10.1186/s12912-016-0141-y
|
| [17] |
McEvedy S, Maguire T, Furness T, et al. Sensory modulation and trauma-informed-care knowledge transfer and translation in mental health services in Victoria:evaluation of a state-wide train-the-trainer intervention[J]. Nurse Educ Pract, 2017, 25:36-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2017.04.012
|
| [18] |
Isobel S, Delgado C. Safe and collaborative communication skills:a step towards mental health nurses implementing trauma informed care[J]. Arch Psychiatr Nurs, 2018, 32(2):291-296.
doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2017.11.017
|
| [19] |
Hoysted C, Jobson L, Alisic E. A pilot randomized controlled trial evaluating a web-based training program on pediatric medical traumatic stress and trauma-informed care for emergency department staff[J]. Psychol Serv, 2019, 16(1):38-47.
doi: 10.1037/ser0000247
pmid: 30475043
|
| [20] |
Kuhnly JE, Bourassa D, Dileone C, et al. Evaluation of interprofessional teaching strategy for nursing students on perina-tal trauma-informed care[J]. Nurs Educ Perspect, 2020, 41(3):174-176.
doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000537
pmid: 31232873
|
| [21] |
Nathan S, Ferrara M. An innovative trauma-informed curricu-lum for sexual assault care[J]. J Nurs Educ, 2020, 59(6):336-340.
doi: 10.3928/01484834-20200520-07
pmid: 32497236
|
| [22] |
Pfeiffer KM, Grabbe L. An approach to trauma-informed edu-cation in prelicensure nursing curricula[J]. Nurs Forum, 2022, 57(4):658-664.
doi: 10.1111/nuf.v57.4
|
| [23] |
Kelton S, Marcus K, Liston G, et al. Refugee and asylum seeker trauma informed care training for oral healthcare professionals in NSW,Australia[J]. Front Oral Health, 2022, 3:907758.
doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.907758
|
| [24] |
Zordan R, Lethborg C, Forster J, et al. Development,implementation,and evaluation of a trauma-informed simulation-based training program for graduate nurses:a single arm feasibility and pilot study[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2022, 117:105460.
doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105460
|