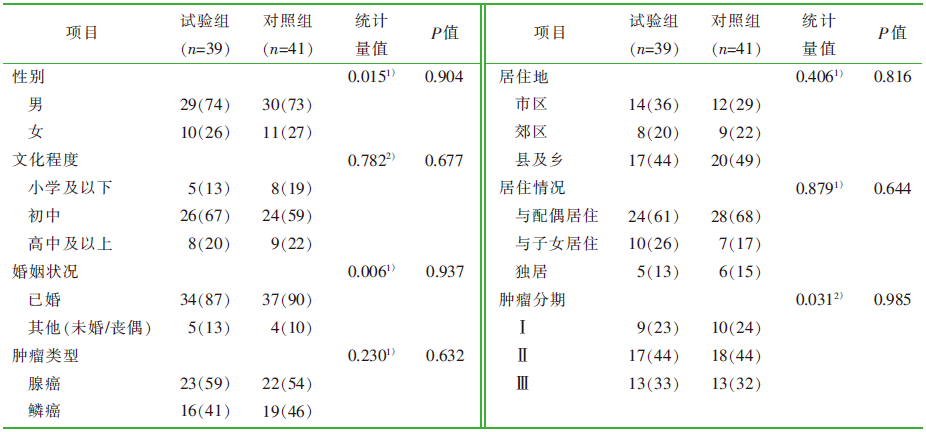
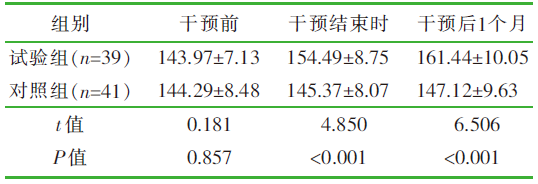
| [1] |
郑荣寿, 孙可欣, 张思维, 等. 2015年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2019(1):19-28.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.01.005
pmid: 30678413
|
|
Zheng RS, Sun KX, Zhang SW, et al. Report of cancer epidemiology in China,2015[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2019(1):19-28.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.01.005
pmid: 30678413
|
| [2] |
Freeman HP, Muth BJ, Kerner JF. Expanding access to cancer screening and clinical follow-up among the medically underserved[J]. Cancer Pract, 1995, 3(1):19-30.
|
| [3] |
Pedersen AE, Hack TF. The British Columbia Patient Navigation Model:a critical analysis[J]. Oncol Nurs Forum, 2011, 38(2):200-206.
doi: 10.1188/11.ONF.200-206
pmid: 21356657
|
| [4] |
Baileys K, McMullen L, Lubejko B, et al. Nurse navigator core competencies:an update to reflect the evolution of the role[J]. Clin J Oncol Nurs, 2018, 22(3):272-281.
doi: 10.1188/18.CJON.272-281
|
| [5] |
Role of the oncology nurse navigator throughout the cancer trajectory[J]. Oncol Nurs Forum, 2018, 45(3):283.
doi: 10.1188/18.ONF.283
pmid: 29683124
|
| [6] |
Tho PC, Ang E. The effectiveness of patient navigation programs for adult cancer patients undergoing treatment:a systematic review[J]. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep, 2016, 14(2):295-321.
|
| [7] |
徐虹霞, 潘红英, 王宏伟, 等. 加速康复外科实施过程中导航护士角色的设立及实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2017, 52(5):530-534.
|
|
Xu HX, Pan HY, Wang HW, et al. The establishment and practice of the role of nurse navigator in multidisciplinary team for enhanced recovery after surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2017, 52(5):530-534.
|
| [8] |
Lubejko BG, Cantril C, Hogg LH, et al. Novice oncology nurse navigator:core elements in establishing training needs and building on competencies[J]. Clin J Oncol Nurs, 2019, 23(4):387-394.
doi: 10.1188/19.CJON.387-394
|
| [9] |
Soto-Perez-de-Celis E, Chavarri-Guerra Y, Ramos-Lopez WA, et al. Patient navigation to improve early access to supportive care for patients with advanced cancer in resource-limited settings:a randomized controlled trial[J]. Oncologist, 2021, 26(2):157-164.
doi: 10.1002/onco.13599
pmid: 33210345
|
| [10] |
Lee T, Ko I, Lee I, et al. Effects of nurse navigators on health outcomes of cancer patients[J]. Cancer Nurs, 2011, 34(5):376-384.
doi: 10.1097/NCC.0b013e3182025007
pmid: 21242774
|
| [11] |
杨廷忠, 于文平, 黄丽. 行为改变的一种策略和方法:行为分阶段转变理论模型介绍[J]. 中国行为医学科学, 2002(3):352-353.
|
| [12] |
Au A, Lam WW, Kwong A, et al. Validation of the Chinese version of the short-form Supportive Care Needs Survey Questionnaire(SCNS-SF34-C)[J]. Psychooncology, 2011, 20(12):1292-1300.
doi: 10.1002/pon.1851
pmid: 22114044
|
| [13] |
程玲灵, 孙玉倩. 癌症患者自我管理测评量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2017, 52(9):1082-1087.
|
|
Cheng LL, Sun YQ. Development and validation of cancer patient self-management assessment scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2017, 52(9):1082-1087.
|
| [14] |
李艳, 黄永霞, 陆晴, 等. 肺癌患者住院期间支持性照顾需求现况调查及影响因素分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(12):2115-2118.
|
|
Li Y, Huang YX, Lu Q, et al. Investigation on the status of supportive care needs of patients with lung cancer during hospitalization and analysis of influencing factors[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2019, 17(12):2115-2118.
|
| [15] |
姚志琪, 高钰琳, 林楠, 等. 基于遗忘规律健康教育对住院肺癌患者的效果观察[J]. 护理学报, 2019, 26(16):72-75.
|
|
Yao ZQ, Gao YL, Lin N, et al. Effect of forgetting curve-based health education on hospitalized patients with lung cancer[J]. J Nurs(China), 2019, 26(16):72-75.
|
| [16] |
季玉婷, 张莉萍. 多元化健康教育对老年肺癌手术患者肺功能锻炼的效果评价[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(22):4889-4892.
|
| [17] |
Harvey C, Palmer J, Hegney D, et al. The evaluation of nurse navigators in chronic and complex care[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2019, 75(8):1792-1804.
doi: 10.1111/jan.14041
pmid: 31037742
|
| [18] |
di Palo KE, Patel K, Assafin M, et al. Implementation of a patient navigator program to reduce 30-day heart failure readmission rate[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2017, 60(2):259-266.
doi: S0033-0620(17)30103-2
pmid: 28743529
|
| [19] |
徐宝兰, 洪金花, 何陆英, 等. 肺癌术后化疗患者多团队协同按需延续护理研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2019, 34(7):80-83,87.
|
|
Xu BL, Hong JH, He LY, et al. Demands-directed,multidisciplinary team based transitional care for lung cancer patients receiving post-operative chemotherapy[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2019, 34(7):80-83,87.
|
| [20] |
胡艺, 吴振华, 杨春莉. 症状管理和延续性护理在改善肺癌患者术后不良反应中的应用[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 21(12):56-59.
|
|
Hu Y, Wu ZH, Yang CL. Application of symptom management and transitional nursing care in improving postoperative adverse reactions of patients with lung cancer[J]. J Clin Med Pract, 2017, 21(12):56-59.
|